At its core, sintering is a thermal process that bonds individual powder particles into a solid, coherent mass using heat below the material's melting point. The primary mechanism is atomic diffusion, where atoms migrate across the boundaries of the particles, causing them to fuse together, increase in density, and gain strength. This process effectively removes the empty spaces, or pores, that exist between the loose particles.
Sintering is not about melting a material into a liquid; it is about using thermal energy to encourage atoms to move and rearrange themselves, effectively "knitting" a collection of loose particles into a strong, dense object. The central challenge is achieving high density while controlling the material's final microstructure.

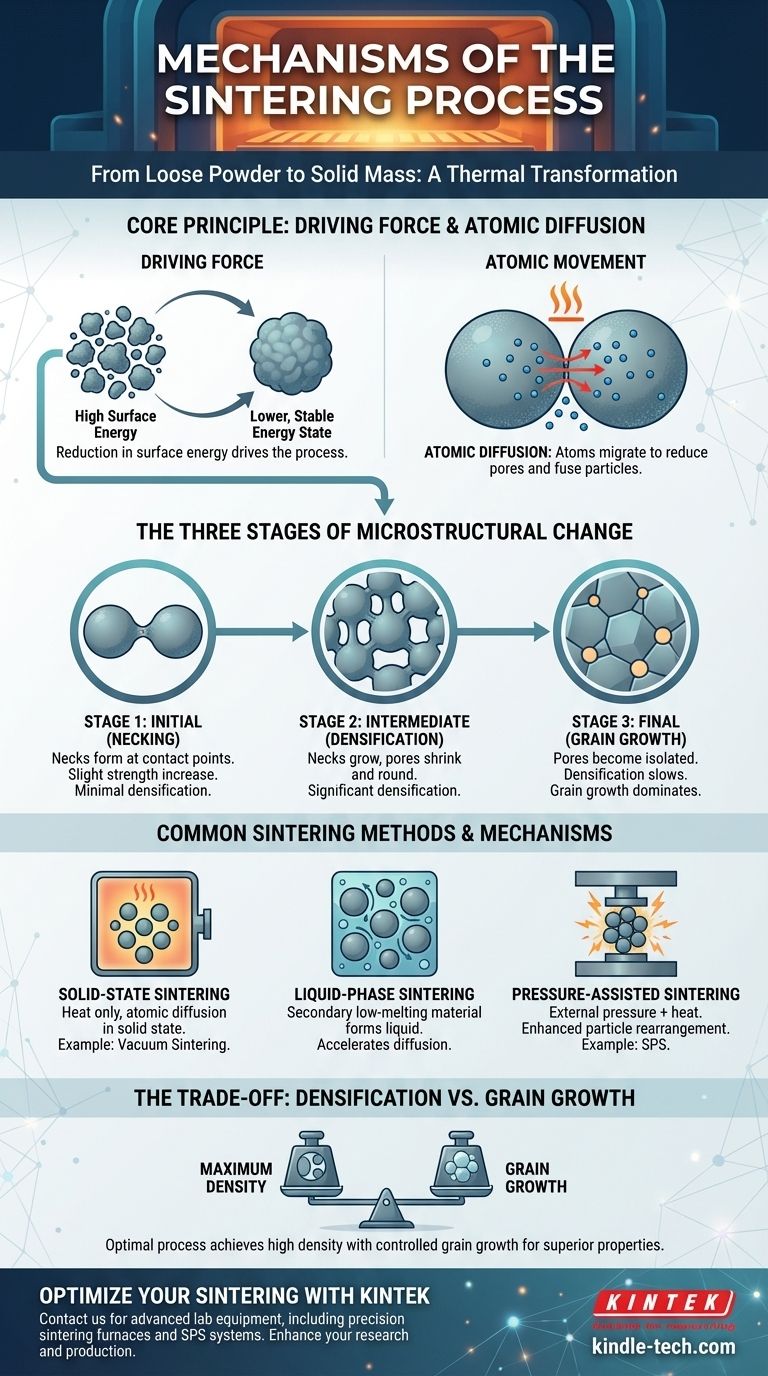
The Core Principle: Driving Force and Atomic Diffusion
The Driving Force of Sintering
The entire process is driven by a reduction in surface energy. A loose powder has an enormous amount of surface area, which is energetically unfavorable.
By bonding together and reducing the total surface area of the pores, the material achieves a lower, more stable energy state. Heat acts as the catalyst, providing the energy needed for atoms to overcome their activation barriers and move.
The Mechanism of Atomic Movement
Atomic diffusion is the fundamental mechanism responsible for material transport during sintering. At elevated temperatures, atoms become mobile and move from areas of high stress (at the particle contact points) to areas of low stress (on the particle surfaces and pore walls).
This movement of material fills the voids between particles, causing the component to shrink and increase in density.
The Three Stages of Microstructural Change
Sintering is a continuous process, but it is typically analyzed in three distinct stages based on the evolution of the material's internal structure.
Stage 1: Initial Stage (Necking)
As the temperature rises, the first points of contact between adjacent particles begin to grow, forming connections called "necks."
During this stage, the particles largely maintain their individual identity, but the formation of these necks marks the beginning of bonding and a slight increase in the material's strength. The overall density of the part increases only slightly.
Stage 2: Intermediate Stage
As the necks grow larger, they begin to merge, forming a network of interconnected solid material and a network of interconnected, cylindrical pore channels.
This is the stage where densification accelerates significantly. The pores shrink and become smoother and more rounded, and the component shrinks noticeably.
Stage 3: Final Stage
In the final stage, the pore channels collapse and become isolated, spherical pores. These remaining pores are much more difficult to remove, and densification slows down considerably.
During this stage, grain growth often becomes the dominant process, where larger grains grow at the expense of smaller ones. Controlling this stage is critical for achieving the desired final properties.
Common Sintering Methods and Mechanisms
Different methods are used to apply heat and pressure, which alters how the sintering mechanisms proceed.
Solid-State Sintering
This is the most fundamental form of sintering, relying purely on heat to drive atomic diffusion in a solid material.
Vacuum sintering is a common example. The material is heated in a vacuum, which prevents oxidation and removes trapped gases from the pores, facilitating a purer and more effective bonding process.
Liquid-Phase Sintering
In this method, a small amount of a secondary material with a lower melting point is mixed with the primary powder.
When heated, this secondary material melts, creating a liquid phase that surrounds the solid particles. This liquid accelerates diffusion, pulling the solid particles together through capillary action and leading to rapid densification at lower temperatures.
Pressure-Assisted Sintering
This approach uses external pressure in addition to heat to compact the powder. The pressure enhances particle rearrangement and aids the diffusion process, resulting in higher densities and finer grain structures in less time.
A prominent example is Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS). In SPS, a pulsed electrical current and pressure are applied simultaneously. The current rapidly heats the material and can generate plasma between particles, cleaning their surfaces and dramatically accelerating the sintering process.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Densification vs. Grain Growth
The primary goal of sintering is densification (pore removal), but it is always in competition with grain growth.
Both processes are driven by heat. Excessive time at high temperatures can cause grains to grow too large, which can negatively impact the material's mechanical properties, such as its strength and toughness.
The ideal sintering process achieves maximum density with minimal grain growth, a balance that requires precise control over temperature, time, and (if applicable) pressure.
How to Select the Right Sintering Approach
Your choice of sintering method depends directly on the material and the desired outcome for the final component.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective, large-scale production of simple parts: Conventional solid-state or vacuum sintering is often the most practical choice.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum density and superior mechanical properties: Pressure-assisted methods like Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) or Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) are necessary.
- If your primary focus is sintering difficult-to-bond materials or composites: Liquid-phase sintering can provide an effective pathway by creating a bonding matrix at lower temperatures.
Ultimately, mastering sintering is about precisely controlling the movement of atoms to engineer a final material with desired density and strength.
Summary Table:
| Sintering Mechanism | Key Process | Primary Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Atomic Diffusion | Atoms migrate from particle contact points to pore walls. | Particle bonding and pore removal. |
| Neck Formation | Initial bonding at particle contacts grows into necks. | Increased strength and slight densification. |
| Densification | Pores shrink and become isolated; material shrinks. | Significant increase in density and coherence. |
| Grain Growth | Larger grains consume smaller ones at high temperatures. | Microstructural evolution; must be controlled for optimal properties. |
Ready to optimize your sintering process for superior material performance? At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced lab equipment, including precision sintering furnaces and Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) systems, to help you achieve maximum density and controlled microstructures. Whether you're working with ceramics, metals, or composites, our solutions are designed to meet your specific research and production needs. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can enhance your laboratory's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Mesh belt controlled atmosphere furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the considerations for vacuum system design? Achieve Optimal Performance for Your Lab
- What is the significance of thermal gradient simulation and thermal cycling furnaces? Ensure Reactor Component Safety
- What are the steps in vacuum brazing? Achieve Superior, Clean Metallurgical Bonds
- What is the difference between liquid phase sintering and solid phase sintering? Achieve Optimal Material Density
- What's the difference between brazing and braze welding? Mastering Joint Strength & Application
- How much will a new furnace cost? Get the Full Price Breakdown for Your Home
- What do you need to consider to have a good brazing process? A Guide to Strong, Reliable Joints
- What is the temperature of the heat of the arc in arc welding? Mastering Extreme Heat for Perfect Welds



















