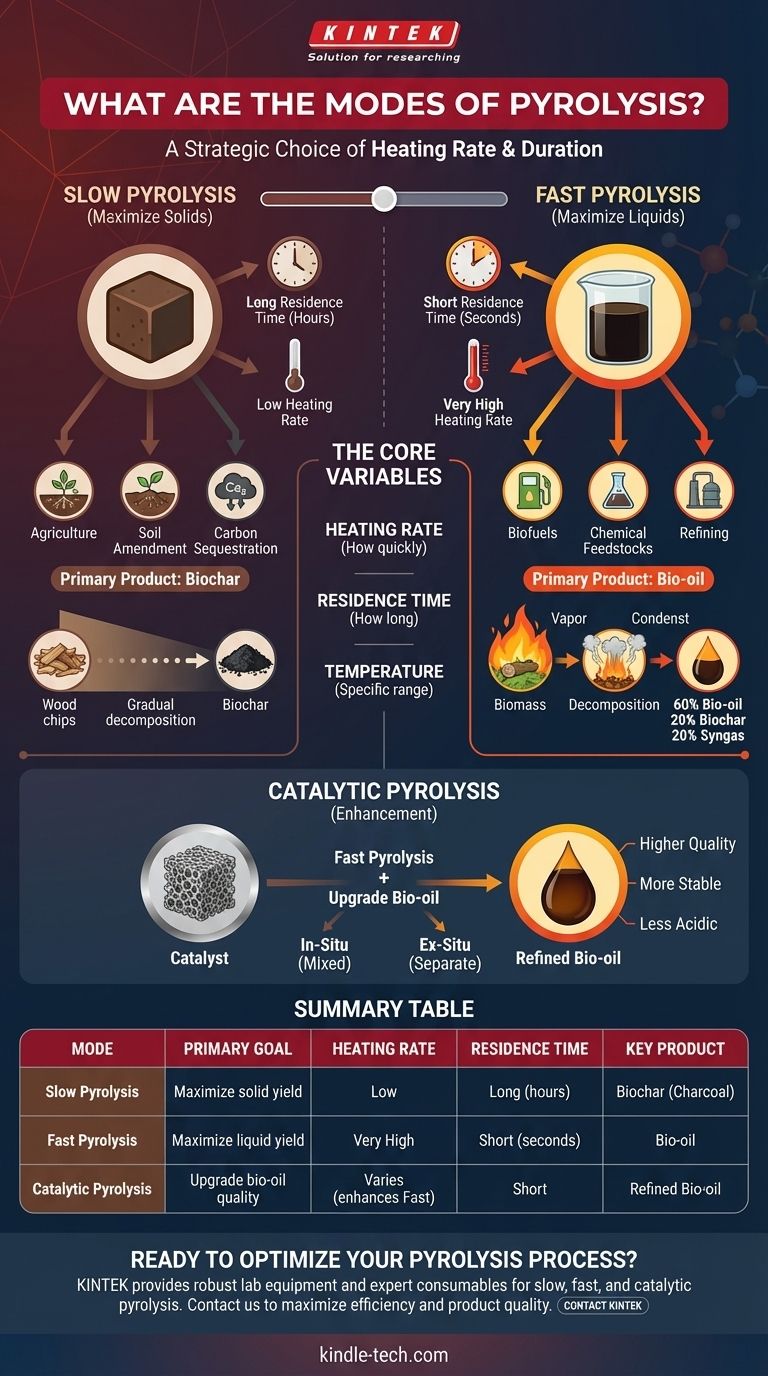
The primary modes of pyrolysis are defined by their heating rate and duration: slow pyrolysis and fast pyrolysis. These methods are fundamentally different approaches to the thermal decomposition of material in the absence of oxygen, each designed to maximize a specific type of product—either a solid, a liquid, or a gas. A third variation, catalytic pyrolysis, introduces a catalyst to further refine the output.
The mode of pyrolysis you choose is not a technical detail but a strategic decision. The core difference is a trade-off between time and temperature, which directly determines whether your primary output will be solid biochar (from slow pyrolysis) or liquid bio-oil (from fast pyrolysis).

The Core Variables: Heat, Time, and Temperature
To understand the different modes, you must first understand the three process conditions that define them. The specific combination of these variables dictates the final product distribution.
Heating Rate
This is how quickly the feedstock is brought to the target pyrolysis temperature. This is arguably the most critical factor distinguishing fast from slow pyrolysis.
Residence Time
This refers to the amount of time the material spends at the reaction temperature. It can range from a few seconds to several hours.
Temperature
While all pyrolysis occurs at elevated temperatures, the specific range influences the chemical reactions that take place, favoring the formation of certain products over others.
Slow Pyrolysis: Maximizing Solids (Biochar)
Slow pyrolysis is the traditional method, characterized by its long duration and focus on producing a solid carbon-rich product.
How It Works
This process involves a low heating rate and a long residence time, often lasting several hours. The temperatures are typically in the lower range of the pyrolysis spectrum.
Primary Product: Biochar
The primary output of slow pyrolysis is biochar (also known as charcoal or coke). This stable, porous solid is the main goal, with bio-oil and syngas being less significant byproducts.
Common Applications
The classic example of slow pyrolysis is the production of charcoal from wood. Its primary uses today are in agriculture for soil amendment and for carbon sequestration.
Fast Pyrolysis: Maximizing Liquids (Bio-oil)
Fast pyrolysis is a more modern, intensive process designed specifically to convert biomass or plastic waste into a liquid fuel precursor.
How It Works
This mode uses an extremely high heating rate and a very short residence time—the entire process is often completed in seconds. This rapid heating cracks the large organic molecules into smaller, condensable vapors before they can further decompose into char and gas.
Primary Products: Bio-oil
Fast pyrolysis is optimized to produce bio-oil, a dark, viscous liquid. A typical yield distribution is roughly 60% bio-oil, 20% biochar, and 20% syngas.
Common Applications
This is the most common method for creating liquid fuels from solid biomass or converting waste plastics into a liquid chemical feedstock that can be refined further.
A Third Dimension: Catalytic Pyrolysis
Catalytic pyrolysis is not a standalone mode but rather an enhancement, typically applied to fast pyrolysis to improve the quality of the end products.
The Role of the Catalyst
A catalyst is introduced into the process to steer the chemical reactions toward producing more desirable molecules. This is primarily done to "upgrade" the bio-oil, making it more stable, less acidic, and with a higher energy content.
In-Situ vs. Ex-Situ Methods
This can be done in one of two ways. In-situ catalytic pyrolysis involves mixing the catalyst directly with the feedstock. Ex-situ pyrolysis keeps the catalyst in a separate reactor bed, treating the pyrolysis vapors after they are generated.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a pyrolysis mode involves balancing process complexity against product value and intended application.
Product Yield vs. Equipment Complexity
Slow pyrolysis is a relatively simple, robust process, often achievable with basic equipment like batch furnaces or kilns. Fast pyrolysis requires much more sophisticated and energy-intensive reactors to achieve the rapid heating and short residence times needed for high bio-oil yields.
Energy Balance
A key advantage of pyrolysis is its potential for energy self-sufficiency. The non-condensable syngas produced during the process is almost always captured and combusted on-site to provide the heat needed to run the reactor, significantly improving the system's overall energy efficiency.
Feedstock Quality
The composition of the initial feedstock (e.g., wood, agricultural waste, plastic) has a profound impact on the final product distribution and quality, regardless of the mode used.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your selection of a pyrolysis mode should be driven entirely by your target end product.
- If your primary focus is soil amendment or carbon sequestration: Slow pyrolysis is the definitive choice to maximize the yield of stable, solid biochar.
- If your primary focus is producing liquid biofuels or chemical feedstocks: Fast pyrolysis is the necessary method to maximize the conversion of solid waste into valuable bio-oil.
- If your primary focus is improving bio-oil quality and reducing downstream refining: Catalytic pyrolysis is the logical enhancement to produce a higher-grade liquid fuel.
Ultimately, mastering pyrolysis is about precisely controlling heat and time to transform a given feedstock into your desired high-value product.
Summary Table:
| Mode | Primary Goal | Heating Rate | Residence Time | Key Product |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Slow Pyrolysis | Maximize solid yield | Low | Long (hours) | Biochar (Charcoal) |
| Fast Pyrolysis | Maximize liquid yield | Very High | Short (seconds) | Bio-oil |
| Catalytic Pyrolysis | Upgrade bio-oil quality | Varies (enhances Fast) | Short | Refined Bio-oil |
Ready to Optimize Your Pyrolysis Process?
Choosing the right pyrolysis mode is critical for achieving your target product yield, whether it's high-quality biochar for soil amendment or premium bio-oil for fuel production. KINTEK specializes in providing robust lab equipment and expert consumables tailored to your specific pyrolysis needs—from slow pyrolysis furnaces for biochar research to advanced fast pyrolysis reactors for bio-oil optimization.
Let our experts help you select the perfect setup to maximize efficiency and product quality in your laboratory. Contact KINTEL today to discuss your project and discover the ideal pyrolysis solution for your research.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Stainless High Pressure Autoclave Reactor Laboratory Pressure Reactor
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas



















