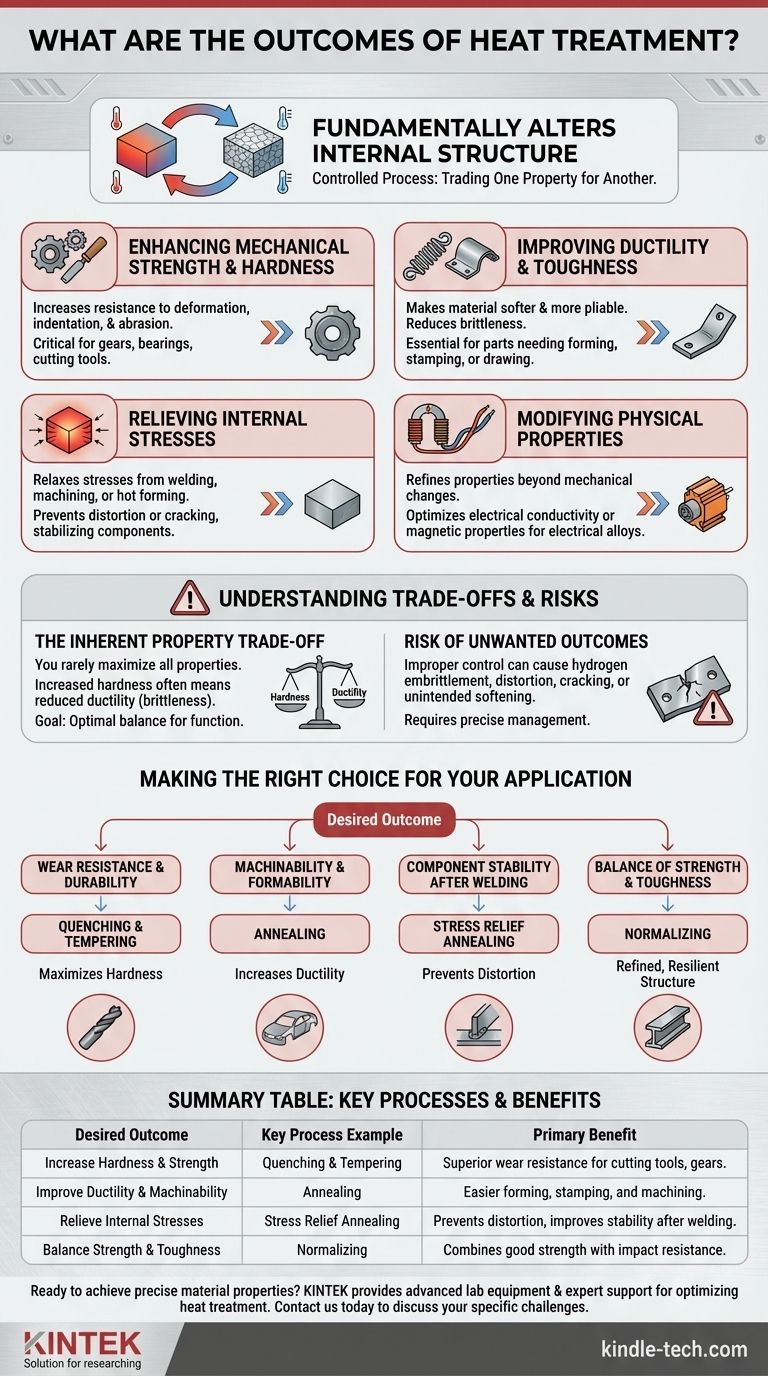
At its core, heat treatment fundamentally alters a material's internal structure to achieve a specific set of enhanced properties. The primary outcomes are predictable changes to mechanical characteristics, such as increasing hardness and strength, improving ductility, relieving internal stresses for better machinability, and enhancing wear resistance.
Heat treatment is best understood as a controlled process of trading one material property for another. By carefully managing heating and cooling cycles, you can precisely tailor a material's performance to meet a specific engineering requirement, whether that's extreme hardness for a cutting tool or ductility for a formed part.

The Primary Goals of Heat Treatment
Heat treatment isn't a single action but a category of processes, each designed to produce a specific, desirable change in a material, most commonly steel.
Enhancing Mechanical Strength and Hardness
One of the most common goals is to make a material stronger and harder. This increases its ability to resist deformation, indentation, and abrasion.
This outcome is critical for components like gears, bearings, and cutting tools that require high wear resistance and structural integrity under load.
Improving Ductility and Toughness
Conversely, heat treatment can make a material softer and more ductile. This reduces brittleness, allowing the material to bend or stretch without fracturing.
This process, often called annealing, is essential for parts that need to be stamped, formed, or drawn into a specific shape. It makes the material easier to work with.
Relieving Internal Stresses
Manufacturing processes like welding, machining, or hot forming introduce internal stresses into a material. These stresses can lead to distortion or cracking over time.
Heat treatment can effectively relax and redistribute these stresses, stabilizing the component and making subsequent machining or use more predictable and reliable.
Modifying Physical Properties
Beyond mechanical changes, heat treatment can also be used to refine a material's physical properties.
This includes optimizing electrical conductivity or enhancing the magnetic properties of certain alloys for use in motors, transformers, and other electrical components.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
While powerful, heat treatment is a precise science where incorrect application can lead to undesirable outcomes. Understanding the trade-offs is key to successful implementation.
The Inherent Property Trade-off
You can rarely maximize all properties at once. For example, processes that dramatically increase a steel's hardness almost always reduce its ductility, making it more brittle.
The goal is not to achieve a "perfect" material but to find the optimal balance of properties for the component's specific function.
Risk of Unwanted Outcomes
Improper control can lead to negative consequences. For instance, using a high-hydrogen atmosphere for certain steels can cause hydrogen embrittlement, a severe loss of ductility.
Other risks include part distortion, surface cracking, or unintended softening if the temperature and cooling rates are not managed with extreme precision.
Process Complexity and Cost
Effective heat treatment is not a simple oven bake. It requires sophisticated, often expensive equipment to precisely control temperature and atmospheric conditions.
Furthermore, it demands significant technical expertise to design the right thermal cycle and diagnose issues, adding to the operational cost and complexity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The desired outcome of heat treatment must align directly with the component's intended function.
- If your primary focus is wear resistance and durability: Your goal is a treatment that maximizes hardness, such as quenching and tempering.
- If your primary focus is machinability or formability: Your goal is a treatment that relieves stress and increases ductility, such as annealing.
- If your primary focus is component stability after welding: Your goal is a post-weld heat treatment (stress relief) to prevent future distortion or failure.
- If your primary focus is a balance of strength and toughness: Your goal is a process like normalizing or austempering to create a refined, resilient internal structure.
By understanding these potential outcomes, you can intentionally select and specify the right process to transform a standard material into a high-performance component.
Summary Table:
| Desired Outcome | Key Process Example | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Increase Hardness & Strength | Quenching & Tempering | Superior wear resistance for cutting tools, gears. |
| Improve Ductility & Machinability | Annealing | Easier forming, stamping, and machining. |
| Relieve Internal Stresses | Stress Relief Annealing | Prevents distortion, improves stability after welding. |
| Balance Strength & Toughness | Normalizing | Combines good strength with impact resistance. |
Ready to achieve the precise material properties your application demands?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the advanced lab equipment and expert support needed for effective heat treatment processes. Whether you're developing cutting tools, forming complex parts, or ensuring the reliability of welded structures, our solutions help you optimize hardness, ductility, and stress relief for superior results.
Contact us today via our Contact Form to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific heat treatment challenges and help you transform standard materials into high-performance components.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is quartz tube heating? Achieve Instant, Targeted Heat with Infrared Radiation
- What is a vertical tube furnace? Leverage Gravity for Superior Uniformity and Process Control
- What is the process of annealing tubes? Achieve Optimal Softness and Ductility for Your Tubing
- What temperature is tube annealing? A Guide to Material-Specific Ranges for Optimal Results
- Why does heating increase temperature? Understanding the Molecular Dance of Energy Transfer



















