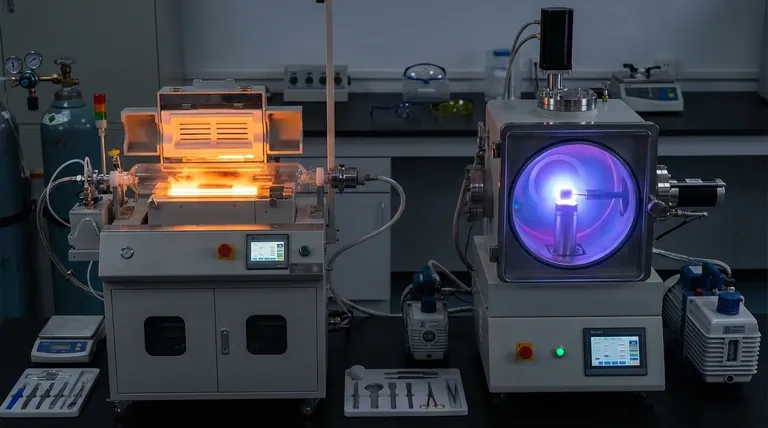
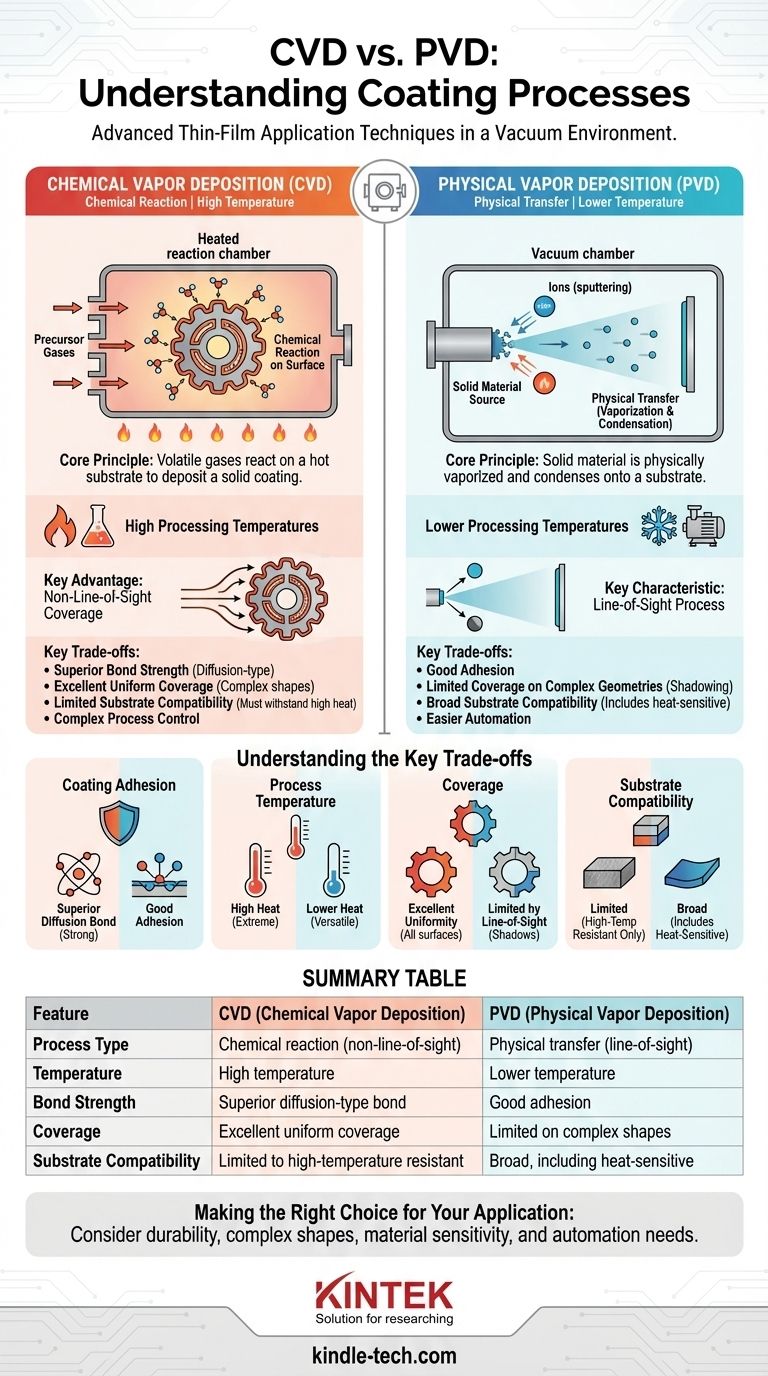
At their core, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) and Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) are advanced processes used to apply a very thin, high-performance coating onto a substrate. Both techniques operate in a vacuum environment to deposit material layer by layer, but they achieve this goal through fundamentally different mechanisms. PVD physically transfers a solid material into a vapor state to coat a part, while CVD uses chemical reactions between precursor gases to create and deposit the coating material.
The critical distinction between these methods lies in their trade-offs. CVD offers a stronger bond and superior coverage on complex shapes due to its high-temperature, chemical-reaction-based nature. PVD operates at lower temperatures, making it more versatile for a wider range of materials, but its physical, line-of-sight process can limit coverage on intricate geometries.
How Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) Works
The Core Principle: Physical Transfer
PVD is a "line-of-sight" process where a solid coating material is vaporized through physical means, travels through a vacuum chamber, and condenses onto the substrate as a thin film. Think of it as an atomic-level form of spray painting.
Key PVD Methods
The vaporization of the source material is typically achieved through methods like sputtering, where the material is bombarded with ions, or through evaporation using high heat. Other methods include ion plating and ion implantation.
The Operating Environment
PVD processes are conducted under a high vacuum and at relatively low temperatures. This makes PVD suitable for a broad array of substrates, including materials that cannot withstand high heat.
How Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) Works
The Core Principle: Chemical Reaction
In CVD, the substrate is placed in a reaction chamber and exposed to one or more volatile precursor gases. These gases decompose or react on the hot surface of the substrate, leaving behind the desired solid coating material.
The Gas-Phase Advantage
Because the process relies on gases, CVD is not a line-of-sight process. The precursor gases can flow into and around complex shapes, resulting in a highly uniform and consistent coating, even on intricate internal surfaces.
The Operating Environment
CVD requires very high processing temperatures to initiate the necessary chemical reactions on the substrate's surface. This high heat is a defining characteristic and a primary limitation of the process.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
Coating Adhesion and Bonding
The high temperatures of the CVD process promote the formation of a diffusion-type bond between the coating and the substrate. This bond is exceptionally strong and generally more durable than the bond created by PVD.
Process Temperature and Substrate Compatibility
This is the most significant differentiator. CVD's high heat limits its use to substrates that can withstand extreme temperatures without deforming or altering their properties. PVD's lower temperature operation provides far greater flexibility and is compatible with heat-sensitive materials.
Coverage on Complex Shapes
CVD excels at coating complex geometries uniformly due to its gas-based, non-line-of-sight nature. PVD, being a line-of-sight process, can struggle to coat shadowed areas or intricate internal features without complex part rotation.
Automation and Process Control
PVD coatings can often be more easily automated compared to the complexities of managing the precursor gases and high temperatures involved in many CVD processes, making it a favorable choice for certain high-volume production environments.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Ultimately, the choice between PVD and CVD depends entirely on the specific requirements of your component and operational needs.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability and coating complex internal surfaces: CVD is the superior choice, provided your substrate material can tolerate the high processing temperatures.
- If your primary focus is coating temperature-sensitive materials or leveraging process automation: PVD is the clear solution due to its lower-temperature operation and versatility.
- If your primary focus is a balance of performance and material compatibility on a simple shape: Both processes may be viable, and the decision will depend on the specific coating material and cost considerations.
Understanding these fundamental differences is the key to selecting the ideal process for your engineering goals.
Summary Table:
| Feature | PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) | CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) |
|---|---|---|
| Process Type | Physical transfer (line-of-sight) | Chemical reaction (non-line-of-sight) |
| Temperature | Lower temperature | High temperature |
| Bond Strength | Good adhesion | Superior diffusion-type bond |
| Coverage | Limited on complex shapes | Excellent uniform coverage |
| Substrate Compatibility | Broad, including heat-sensitive | Limited to high-temperature resistant |
Still unsure which coating process is right for your lab's needs? KINTEK specializes in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables for both CVD and PVD applications. Our experts can help you select the ideal solution for your specific substrate materials and performance requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our coating technologies can enhance your research and development outcomes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
People Also Ask
- Are all lab grown diamonds CVD? Understanding the Two Main Methods
- How high of temperature do carbon nanotubes in air have the ability to sustain? Understanding the Oxidation Limit
- How does chirality affect carbon nanotubes? It Determines If They Are Metal or Semiconductor
- What are the challenges of carbon nanotubes? Overcoming Production and Integration Hurdles
- What are the methods of producing CNT? Scalable CVD vs. High-Purity Lab Techniques



















