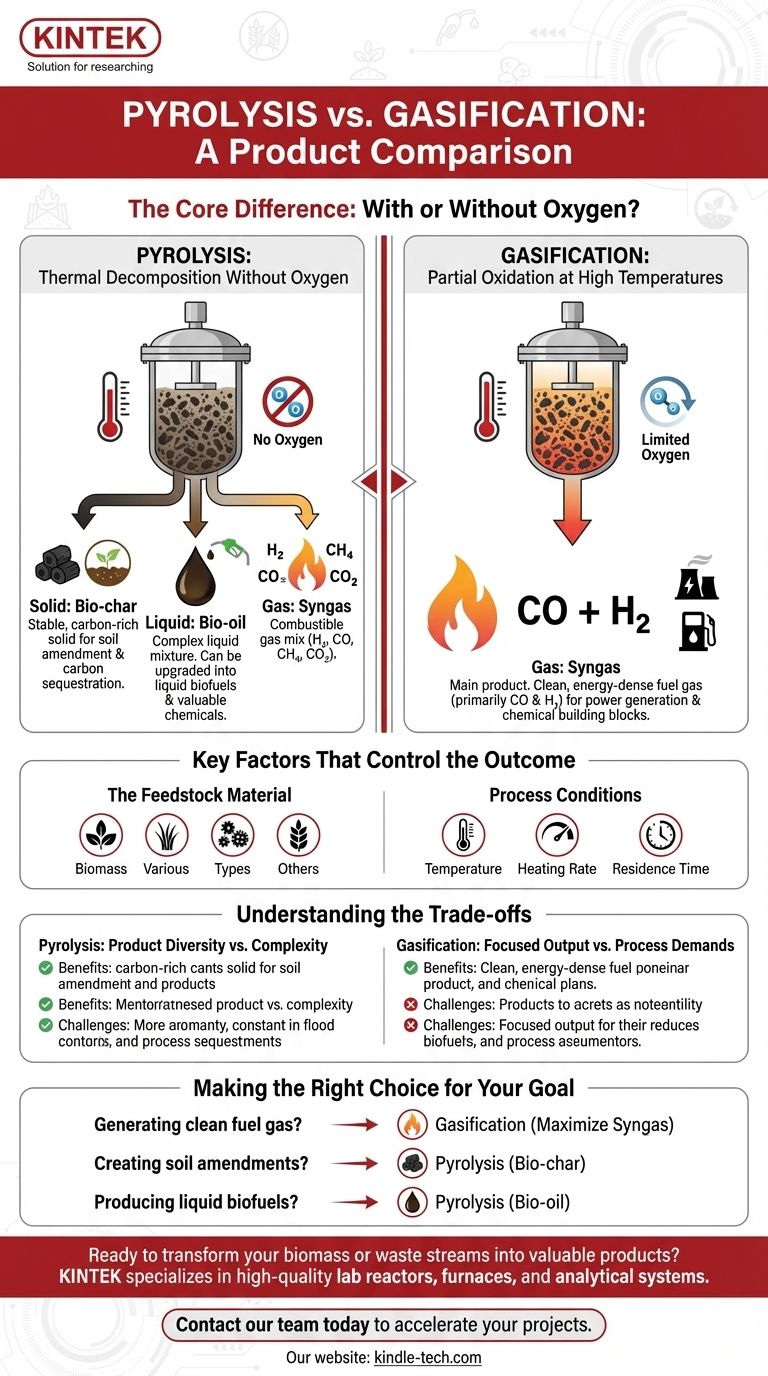
In short, pyrolysis and gasification produce different primary outputs due to their core process. Pyrolysis breaks down biomass without oxygen, yielding a balanced mix of solid bio-char, liquid bio-oil, and gaseous syngas. Gasification, conversely, uses a limited amount of oxygen at high temperatures to convert biomass almost entirely into a combustible gas called syngas, composed mainly of carbon monoxide and hydrogen.
The fundamental difference lies in the presence of oxygen. Pyrolysis is thermal decomposition in an oxygen-free environment, creating solids, liquids, and gases. Gasification is a high-temperature reaction with a controlled amount of oxygen, designed specifically to maximize fuel gas production.

The Core Difference: With or Without Oxygen?
Understanding the role of oxygen is the key to differentiating these two powerful thermochemical processes. They begin with the same feedstocks but follow divergent paths to create distinct sets of products.
Pyrolysis: Thermal Decomposition Without Oxygen
Pyrolysis is essentially the process of "cooking" organic material, like biomass or waste, in a completely oxygen-free environment.
This absence of oxygen is critical. It prevents combustion and instead causes the complex molecules within the feedstock to break down into a variety of smaller, simpler compounds across all three states of matter: solid, liquid, and gas.
Gasification: Partial Oxidation at High Temperatures
Gasification intentionally introduces a controlled, limited amount of an oxidant (like oxygen, air, or steam) into a high-temperature environment, typically above 700°C.
This small amount of oxygen is not enough for full combustion. Instead, it triggers chemical reactions that convert the solid feedstock primarily into a gaseous mixture, maximizing the yield of syngas.
A Detailed Look at the Products
The specific outputs of each process are tailored for different applications, from energy generation to soil improvement.
Pyrolysis Outputs: A Mix of States
The balanced output of pyrolysis makes it a versatile process for creating multiple co-products.
-
Solid: Bio-char This stable, carbon-rich solid is similar to charcoal. It is a valuable soil amendment that improves water retention and can be used for carbon sequestration.
-
Liquid: Bio-oil Also known as pyrolysis oil, wood vinegar, or bio-crude, this is a complex liquid mixture of water and organic compounds. It can be upgraded into liquid biofuels or refined to extract valuable chemicals.
-
Gas: Syngas The gaseous fraction, often called synthesis gas or syngas, is a mixture of combustible gases. Its primary components are hydrogen (H₂), carbon monoxide (CO), methane (CH₄), and carbon dioxide (CO₂).
Gasification Output: Primarily Syngas
The goal of gasification is to convert as much of the initial feedstock's energy as possible into a single, useful product.
- Gas: Syngas This is the main product. The syngas from gasification is composed almost entirely of carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrogen (H₂). This clean, energy-dense gas can be burned to generate electricity or used as a chemical building block to produce fuels like ethanol and methanol.
Key Factors That Control the Outcome
The exact yield and composition of the products from either process are not fixed. They are heavily influenced by the raw materials and the precise operating conditions.
The Feedstock Material
The type of biomass used is a major factor. Common feedstocks include wood waste, agricultural residues like corn husks and nut shells, dedicated energy crops, and even municipal solid waste. Each material's unique chemical makeup will alter the final product ratios.
Process Conditions (The "Recipe")
Controlling the reaction environment is critical for achieving the desired output.
-
Temperature Higher temperatures generally favor gas production. Gasification operates at significantly higher temperatures than most pyrolysis processes to maximize the conversion to syngas.
-
Heating Rate & Residence Time How quickly the feedstock is heated and how long it remains at the target temperature directly impact which chemical reactions dominate, thus influencing the final split between solid, liquid, and gas products.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between pyrolysis and gasification involves evaluating which set of benefits and complexities aligns with your ultimate goal.
Pyrolysis: Product Diversity vs. Complexity
The primary advantage of pyrolysis is its ability to create three distinct product streams (solid, liquid, and gas) from a single process.
However, this diversity is also its main challenge. It requires downstream infrastructure to separate, collect, and refine each of the three product types, adding operational complexity.
Gasification: Focused Output vs. Process Demands
Gasification offers the benefit of converting a solid feedstock into one primary, relatively clean, and easy-to-handle gaseous fuel.
The trade-off is that it requires higher temperatures and precise control over the process oxidant, making the equipment more demanding and energy-intensive to operate compared to pyrolysis.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your intended application should dictate which process is the superior choice.
- If your primary focus is generating a clean fuel gas for power or chemical synthesis: Gasification is the optimal path, as it is designed to maximize the production of syngas.
- If your primary focus is creating soil amendments or sequestering carbon: Pyrolysis is the clear choice because its main solid product, bio-char, is perfectly suited for this purpose.
- If your primary focus is producing liquid biofuels or a variety of chemical precursors: Pyrolysis is the only process that yields a significant liquid fraction in the form of bio-oil.
By understanding the fundamental chemistry and resulting products, you can effectively select the right technology to transform waste into value.
Summary Table:
| Process | Core Condition | Primary Products | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pyrolysis | No Oxygen | Bio-char (solid), Bio-oil (liquid), Syngas (gas) | Soil amendment, liquid biofuels, chemical precursors |
| Gasification | Limited Oxygen | Syngas (primarily CO + H₂) | Power generation, synthetic fuel production |
Ready to transform your biomass or waste streams into valuable products? The right lab equipment is critical for R&D and process optimization. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab reactors, furnaces, and analytical systems tailored for pyrolysis and gasification research. Our experts can help you select the perfect setup to achieve your specific yield and composition targets. Contact our team today to discuss your application and discover how KINTEK's solutions can accelerate your bio-energy or bio-material projects.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Stainless High Pressure Autoclave Reactor Laboratory Pressure Reactor
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- High Performance Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Research and Development
People Also Ask
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output



















