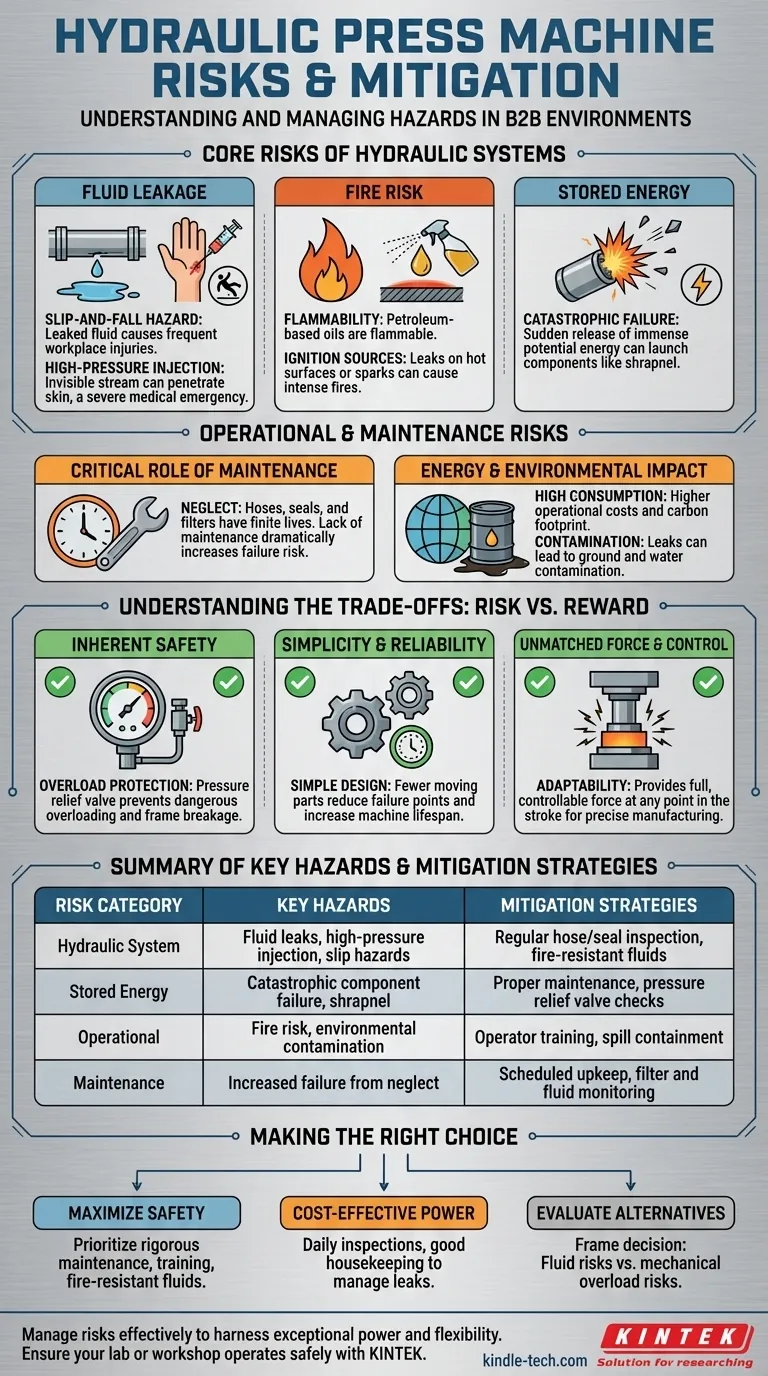
The primary risks of a hydraulic press stem directly from its core components: the high-pressure hydraulic fluid and the immense force it generates. The most significant hazards include fluid leaks, which create slip and fire risks, and the potential for catastrophic failure due to the stored energy within the pressurized system.
While hydraulic presses present manageable risks related to their fluid-based power systems, these are often offset by inherent safety features like overload protection and a simple, reliable design. Understanding this trade-off is essential for safe and effective operation.
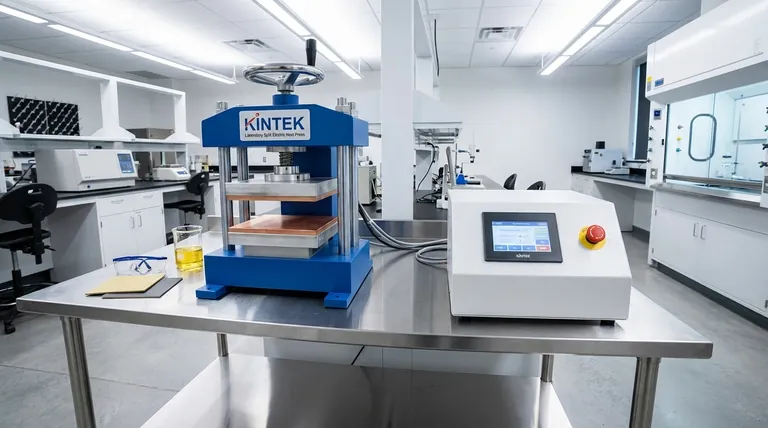

The Core Risks of Hydraulic Systems
The power of a hydraulic press comes from containing a fluid under immense pressure. This fundamental principle is also the source of its primary hazards.
Hydraulic Fluid Leakage
A leak is the most common failure mode in a hydraulic system. Even a small leak can introduce significant risk.
Leaked fluid on the floor creates a serious slip-and-fall hazard, one of the most frequent causes of workplace injuries.
Furthermore, if a leak occurs from a pinhole in a high-pressure line, the escaping fluid can form a nearly invisible, high-velocity stream capable of penetrating skin. This type of high-pressure injection injury is a severe medical emergency.
Flammability and Fire Risk
Many standard hydraulic oils are petroleum-based and therefore flammable.
A fluid leak that sprays onto a hot surface or near an ignition source—like a welding arc or grinding spark—can ignite, leading to a torch-like fire that is difficult to extinguish.
The Danger of Stored Energy
A hydraulic system is an energy storage device. The compressed fluid holds a massive amount of potential energy.
If a component like a hose, fitting, or cylinder fails catastrophically, this stored energy can be released suddenly and violently, potentially launching failed components like shrapnel.
Operational and Maintenance Risks
Beyond the immediate system-level dangers, the day-to-day operation and upkeep of a hydraulic press introduce another layer of risk.
The Critical Role of Maintenance
Hydraulic systems require more diligent maintenance than their mechanical counterparts. Hoses, seals, and filters have a finite lifespan.
Neglecting regular maintenance dramatically increases the likelihood of leaks and component failure. A poorly maintained machine is an unsafe machine.
High Energy Consumption and Environmental Impact
While not a direct physical danger to the operator, hydraulic presses are known for high energy consumption, which translates to higher operational costs and a larger carbon footprint.
Additionally, fluid leaks or spills can lead to ground and water contamination, creating an environmental risk that must be properly managed and mitigated.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Risk vs. Reward
The risks of a hydraulic press do not exist in a vacuum. They must be weighed against its significant advantages, particularly when compared to mechanical presses.
Inherent Safety: Built-in Overload Protection
Perhaps the single greatest advantage of a hydraulic press is its natural overload protection. The pressure in the system can only reach the limit set by the pressure relief valve.
This makes it impossible to dangerously overload and break the press frame, a known and catastrophic risk with mechanical presses. This feature provides a fundamental layer of safety against excessive force.
Simplicity and Reliability
Hydraulic presses have a simple design with far fewer moving parts than complex mechanical presses.
This simplicity reduces the number of potential failure points, contributing to a longer machine lifespan and, when properly maintained, high reliability.
Unmatched Force and Control
The reason these machines are used is their ability to generate immense tonnage in a relatively small footprint. They provide full force at any point in the stroke.
This adaptability and controllable power are often essential for manufacturing processes, making the management of hydraulic-related risks a worthwhile endeavor.
Making the Right Choice for Your Operation
Evaluating the risks of a hydraulic press requires understanding your specific goals and operational context.
- If your primary focus is maximizing safety in an industrial setting: Prioritize rigorous maintenance schedules, operator training on high-pressure hazards, and consider using fire-resistant hydraulic fluids.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective power for a small workshop or lab: Recognize that the scale of risk is lower, but fundamental safety—like daily machine inspection and good housekeeping to manage leaks—remains critical.
- If your primary focus is evaluating the technology against alternatives: Frame the decision as a choice between managing the fluid-related risks of a hydraulic press versus the mechanical overload risks of a mechanical press.
Ultimately, the risks associated with a hydraulic press are well-understood and can be effectively managed to harness its exceptional power and flexibility.
Summary Table:
| Risk Category | Key Hazards | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Hydraulic System | Fluid leaks, high-pressure injection, slip hazards | Regular hose/seal inspection, use of fire-resistant fluids |
| Stored Energy | Catastrophic component failure, shrapnel | Proper maintenance, pressure relief valve checks |
| Operational | Fire risk, environmental contamination | Operator training, spill containment measures |
| Maintenance | Increased failure from neglect | Scheduled upkeep, filter and fluid monitoring |
Ensure your lab or workshop operates safely and efficiently with the right equipment. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing reliable lab equipment and consumables tailored to your needs. Whether you're evaluating hydraulic presses or seeking safer alternatives, our experts can help you choose the best solution for your application. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's safety and productivity goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press Machine for Glove Box
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Press for XRF & KBR Pellet Press
- 24T 30T 60T Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Vacuum Box Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- What is the pressed powder pellet method? A Guide to Accurate FTIR Sample Preparation
- What role does a laboratory hydraulic press play in the preparation of solid electrolyte pellets? Ensure Data Accuracy
- What is the pellet technique in IR? Master Solid Sample Preparation for Clear Spectroscopy
- What is the use of KBr? Master Sample Prep for Accurate IR Spectroscopy
- Why are KBr pellets used in FTIR? Achieve Clear, Accurate Solid Sample Analysis



















