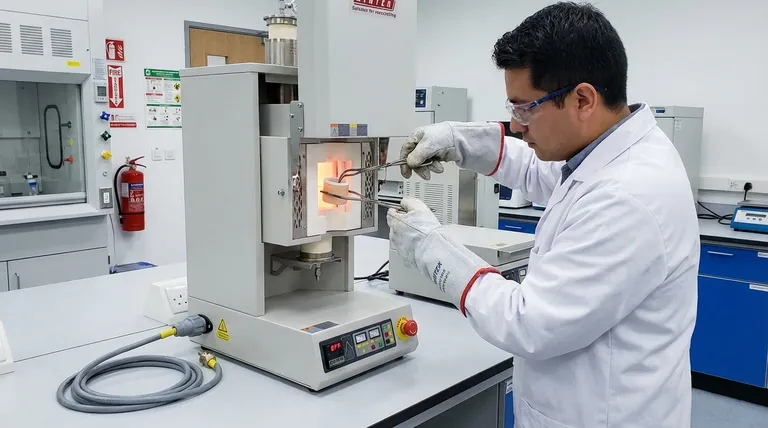
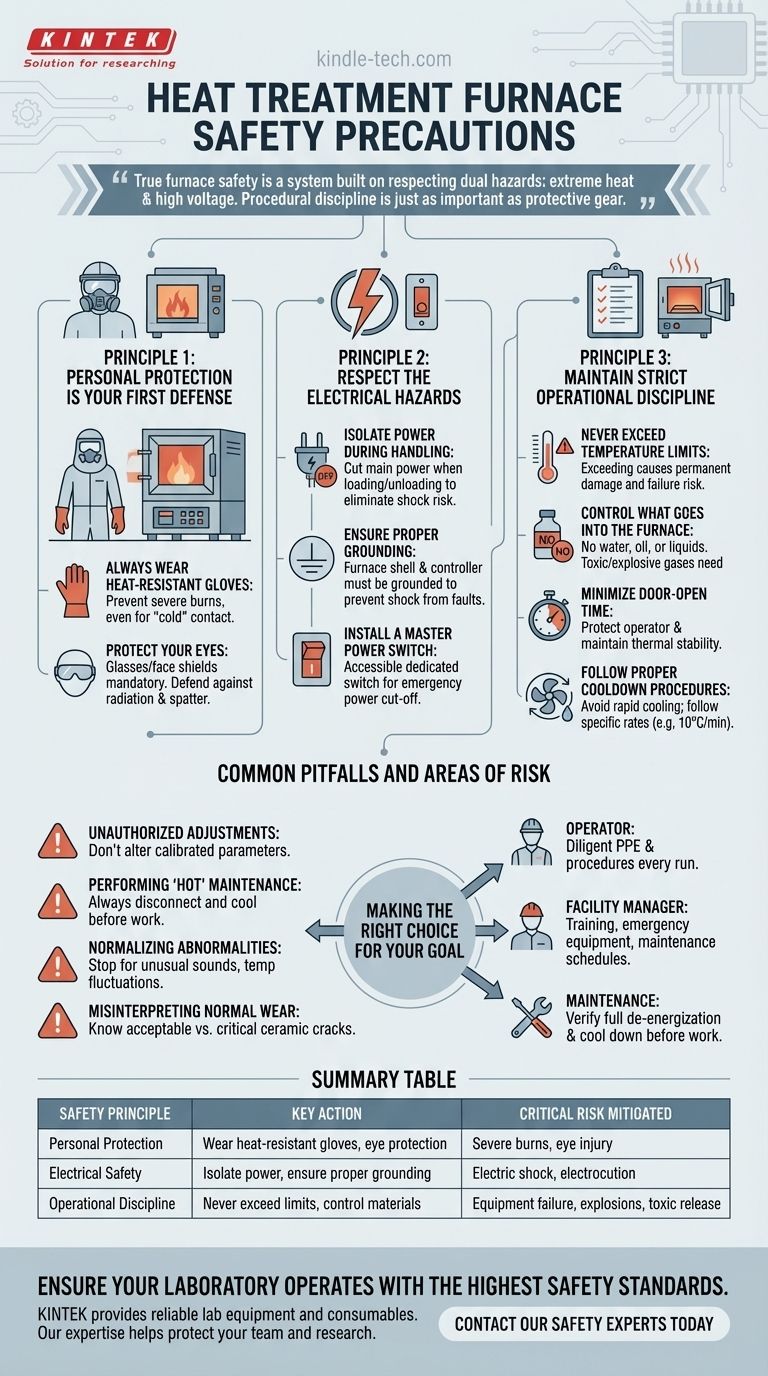
The most critical safety precautions for a heat treatment furnace are a combination of personal protective equipment (PPE), strict adherence to electrical safety protocols, and disciplined operational procedures. Operators must always wear heat-resistant gloves and eye protection, ensure the furnace is properly grounded and de-energized during sample handling, and never exceed the equipment's maximum temperature or introduce volatile materials into the chamber.
True furnace safety is not a simple checklist. It's a system built on respecting the dual hazards of extreme heat and high voltage, where procedural discipline is just as important as the protective gear you wear.

Principle 1: Personal Protection is Your First Defense
Your direct interaction with the furnace presents the most immediate risks. Proper PPE is the essential barrier between you and a serious injury.
### Always Wear Heat-Resistant Gloves
The primary hazard is severe burns. Always wear appropriate thermal gloves when loading or unloading samples, even if you don't expect to touch a hot surface.
### Protect Your Eyes
Protective glasses or face shields are mandatory. They defend against intense heat radiation and the unlikely but possible event of material spatter during heating.
Principle 2: Respect the Electrical Hazards
A heat treatment furnace is a high-power electrical device. Complacency around its electrical systems can be lethal.
### Isolate Power During Handling
Always cut off the main power supply when loading or taking samples. This single action eliminates the risk of electric shock, which is a critical danger when interacting with the furnace's interior components.
### Ensure Proper Grounding
Both the furnace shell and its controller must be reliably grounded. A proper ground provides a safe path for fault currents, preventing the furnace's metal body from becoming energized and causing a severe shock.
### Install a Master Power Switch
For added safety, a dedicated power switch should be installed at the main power line leading to the furnace. This provides a clear, accessible way to cut all power to the unit in an emergency.
Principle 3: Maintain Strict Operational Discipline
The most advanced safety features are useless without consistent, disciplined operator behavior. Following established procedures is paramount.
### Never Exceed Temperature Limits
Every furnace has a maximum designed operating temperature. Exceeding this limit can cause permanent damage to the heating elements and refractory materials, creating a significant failure risk.
### Control What Goes Into the Furnace
Never place samples containing water or oil into a hot furnace, as this can cause a rapid, uncontrolled release of vapor. Do not fill any liquid into the chamber. Furthermore, toxic or explosive gases must only be used with the necessary safety controls and expert supervision.
### Minimize Door-Open Time
Keep the time the furnace door is open to an absolute minimum. This not only protects the operator from prolonged heat exposure but also maintains thermal stability within the chamber, ensuring a more accurate heat treatment process.
### Follow Proper Cooldown Procedures
Avoid rapid cooling unless it is a specific, engineered part of the process. For some furnace types, such as split tube furnaces, the cooling rate should not exceed a set limit (e.g., 10°C/min) to prevent thermal shock and cracking of the ceramic components.
Common Pitfalls and Areas of Risk
Understanding where things can go wrong is key to preventing accidents. Constant vigilance is required, especially during routine operations.
### Unauthorized Adjustments
Never alter set parameters or modify the equipment's structure without authorization. These systems are carefully calibrated, and changes can lead to unsafe conditions or equipment failure.
### Performing "Hot" Maintenance
All maintenance and troubleshooting must be performed only after the equipment is fully disconnected from its power source and has cooled to a safe temperature.
### Normalizing Abnormalities
Operators should continuously monitor the furnace's condition. If any unusual sounds, temperature fluctuations, or other abnormalities are detected, the machine must be stopped immediately for inspection. Ignoring small warning signs can lead to major failures.
### Misinterpreting Normal Wear
Over extended use, small cracks may appear on the surface of refractory ceramics. This can be a normal sign of aging. It is crucial to be trained on the difference between acceptable wear and signs of a critical failure requiring immediate attention.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Implementing a robust safety culture requires tailoring actions to specific roles and responsibilities.
- If you are an operator: Your primary focus is diligent adherence to PPE use and operational procedures during every single run.
- If you are a facility manager: Your responsibility is to ensure proper user training, accessible emergency equipment like fire extinguishers and power cutoffs, and regular maintenance schedules.
- If you are performing maintenance: Your cardinal rule is to verify the equipment is fully de-energized and completely cool before beginning any work.
A disciplined approach to safety is the foundation of reliable and repeatable heat treatment results.
Summary Table:
| Safety Principle | Key Action | Critical Risk Mitigated |
|---|---|---|
| Personal Protection | Wear heat-resistant gloves and eye protection | Severe burns, eye injury from heat/radiation |
| Electrical Safety | Isolate power during handling; ensure proper grounding | Electric shock, electrocution |
| Operational Discipline | Never exceed temperature limits; control materials introduced | Equipment failure, explosions, toxic release |
Ensure your laboratory operates with the highest safety standards. KINTEK specializes in providing reliable lab equipment, including heat treatment furnaces, and the consumables that keep them running safely. Our expertise helps you protect your team and your research. Contact our safety experts today to discuss your laboratory's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- Why does heating increase temperature? Understanding the Molecular Dance of Energy Transfer
- What is quartz tube heating? Achieve Instant, Targeted Heat with Infrared Radiation
- How do you clean a tubular furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Maintenance
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- What is the difference between upflow and horizontal furnace? Find the Perfect Fit for Your Home's Layout



















