In essence, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a highly controlled process that builds a solid thin film on a surface from a chemical reaction in the gas phase. It involves transporting reactant gases (precursors) to a substrate, where they react and deposit a new material, followed by the removal of the gaseous byproducts.
The entire CVD process can be understood as a molecular assembly line. It meticulously manages the journey of gas molecules as they are delivered to a surface, chemically transformed into a solid film, and have their waste products efficiently exhausted.

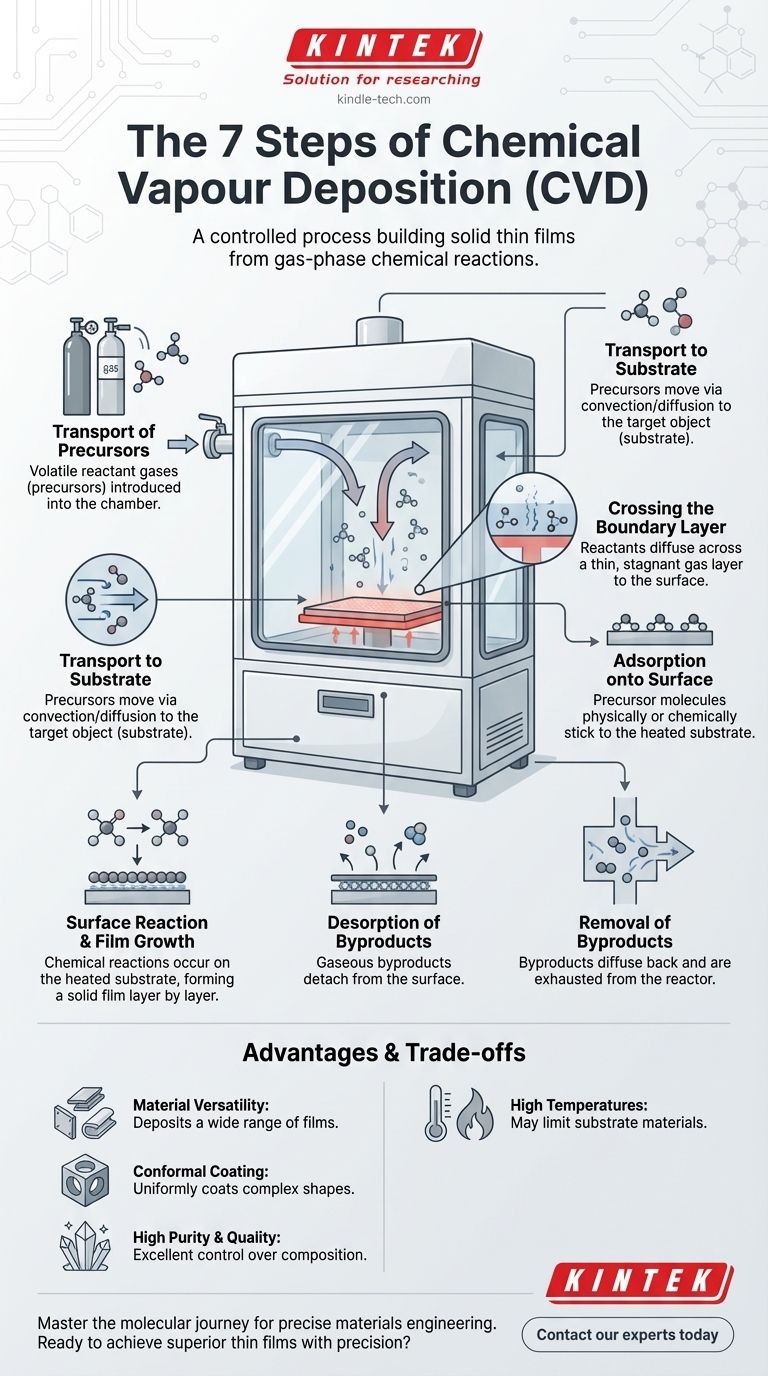
The CVD Journey: From Gas to Solid Film
To truly understand CVD, we must break down the process into its fundamental sequence of events. Each step is a critical control point that determines the quality and properties of the final film.
Step 1: Transport of Precursors into the Reactor
The process begins by introducing precise amounts of one or more volatile reactant gases, known as precursors, into the reaction chamber. These gases are the chemical building blocks for the final film.
Step 2: Transport to the Substrate
Once inside the chamber, the precursor molecules travel through the main gas stream via convection and diffusion toward the target object, called the substrate. This substrate is the surface where the film will be grown.
Step 3: Crossing the Boundary Layer
Directly above the substrate surface exists a thin, relatively stagnant layer of gas known as the boundary layer. Reactant molecules must diffuse across this layer to reach the surface, a step that can often be the slowest and most critical part of the entire process.
Step 4: Adsorption onto the Surface
When a precursor molecule successfully reaches the substrate, it physically or chemically sticks to the surface. This process is called adsorption.
Step 5: Surface Reaction and Film Growth
With the precursor adsorbed onto the heated substrate, chemical reactions occur. These reactions break down the precursors and form a stable, solid material, creating the thin film layer by layer through nucleation and growth.
Step 6: Desorption of Byproducts
The chemical reactions that form the film also create unwanted gaseous byproducts. These byproduct molecules must detach, or desorb, from the surface to make room for new reactants to arrive.
Step 7: Removal of Byproducts from the Reactor
Finally, the desorbed byproducts diffuse back across the boundary layer and are carried away by the main gas flow, exiting the chamber through an exhaust system.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Advantages
CVD is a powerful technique, but its use is governed by a distinct set of characteristics and limitations. Understanding these is key to deciding if it's the right process for a specific application.
Advantage: Material Versatility
CVD is not limited to one type of material. It can be used to deposit a vast range of films, including metals, multi-component alloys, and complex ceramic or compound layers.
Advantage: Conformal Coating
One of the most significant strengths of CVD is its ability to produce highly conformal coatings. This means it can uniformly coat complex, three-dimensional shapes, a property often described as having good "wrap-around."
Advantage: High Purity and Quality
The process allows for excellent control over the chemical composition, resulting in films that are exceptionally pure, dense, and well-crystallized.
Trade-off: High Temperatures and Substrate Limitations
Traditional CVD processes often require very high temperatures to provide the necessary energy for the chemical reactions. This can limit the types of substrate materials that can be used without being damaged.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
A detailed understanding of these steps allows you to control and troubleshoot the process effectively. Your primary goal will determine which steps demand the most attention.
- If your primary focus is film quality and uniformity: Concentrate on the transport through the boundary layer (Step 3) and the surface reaction kinetics (Step 5), as these control the growth rate and structure.
- If your primary focus is creating a specific material: Your main concern will be the selection of precursors (Step 1) and the precise control of temperature and pressure to drive the desired surface reaction (Step 5).
- If your primary focus is troubleshooting defects: Investigate byproduct removal (Steps 6 & 7), as trapped byproducts can cause impurities, and unwanted reactions in the gas phase (Step 2) can create particles that fall onto the film.
Ultimately, mastering the CVD process means controlling each stage of this molecular journey to engineer materials with precision.
Summary Table:
| Step | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Transport of Precursors | Introduce reactant gases into the chamber |
| 2 | Transport to Substrate | Move gases toward the target surface |
| 3 | Cross Boundary Layer | Diffuse through stagnant gas layer to surface |
| 4 | Adsorption | Precursor molecules stick to substrate |
| 5 | Surface Reaction | Chemical transformation creates solid film |
| 6 | Desorption | Gaseous byproducts detach from surface |
| 7 | Byproduct Removal | Exhaust waste gases from reactor |
Ready to achieve superior thin films with precision? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for Chemical Vapor Deposition processes. Our solutions help you control every step—from precursor delivery to byproduct removal—ensuring high-purity, conformal coatings for your most demanding applications.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our CVD systems can enhance your laboratory's capabilities and accelerate your materials research.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between CVD and PECVD? Choose the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method
- What is plasma enhanced chemical vapour deposition process? Unlock Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Films
- What is plasma in CVD process? Lowering Deposition Temperatures for Heat-Sensitive Materials
- What is PECVD used for? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Performance Thin Films
- What is plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Films



















