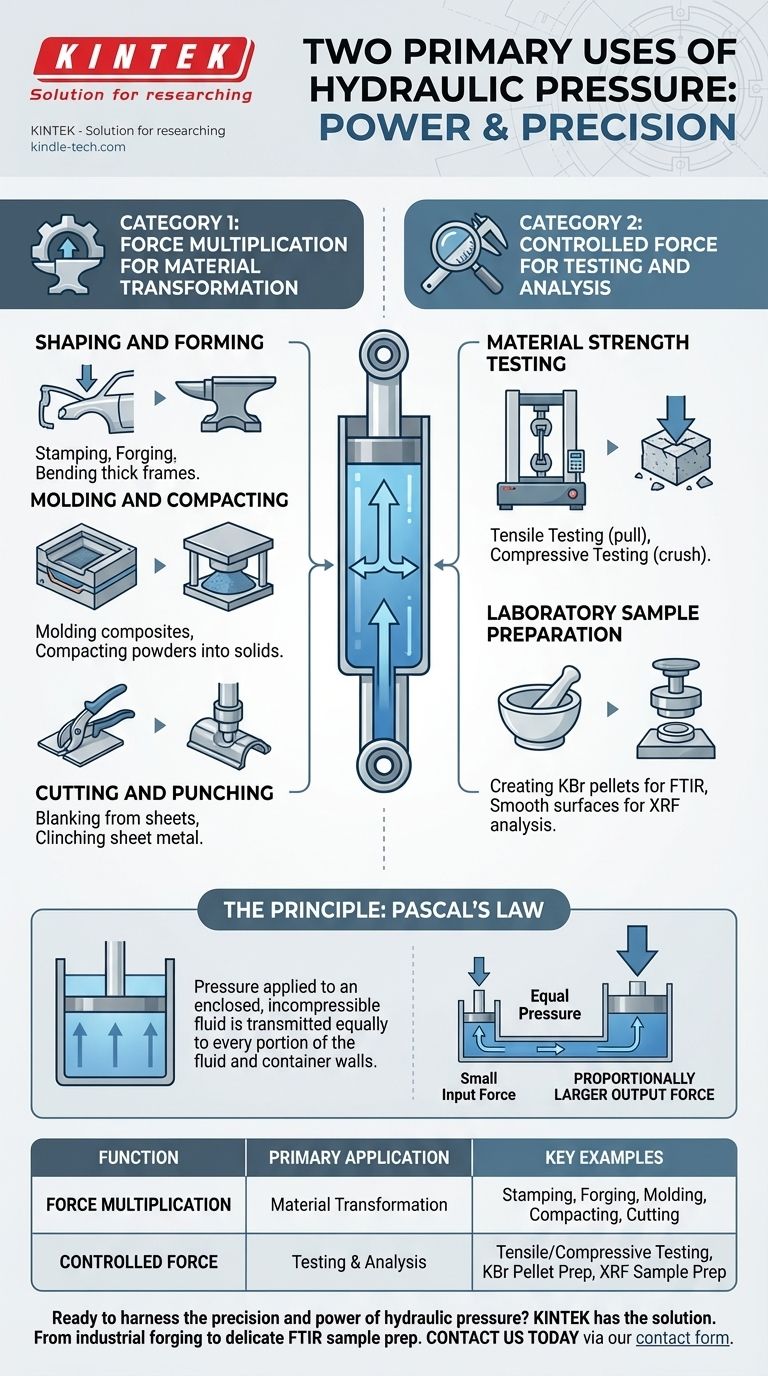
At its core, hydraulic pressure serves two primary functions. These are the multiplication of force to transform materials and the precise application of force to test or analyze materials. While applications range from massive industrial forging to delicate laboratory sample preparation, they all fall into one of these two fundamental categories.
While often associated with immense crushing power, the true value of hydraulic pressure lies in its versatility. It can be used for both brute-force material transformation (shaping, cutting, forming) and for highly controlled, precise force application (testing, analysis, and sample preparation).

Category 1: Force Multiplication for Material Transformation
The most common use of hydraulic pressure is to take a small input force and multiply it into an immense output force. This principle is the backbone of heavy industry, enabling processes that would otherwise be impossible.
Shaping and Forming
Hydraulic presses excel at applying the sustained, powerful pressure needed to permanently change the shape of a material without breaking it.
This is seen in automotive and aerospace industries for stamping body panels, forging engine components from metal billets, and bending thick structural frames.
Molding and Compacting
This application uses pressure to force raw material into a mold or compact loose material into a solid form.
Examples include molding composites like carbon fiber or thermoplastics for high-performance parts, and compacting powders into dense solids for manufacturing or, in a lab setting, for creating homogenous samples.
Cutting and Punching
Beyond shaping, hydraulic force can be used to shear or punch through materials with incredible precision.
This includes blanking operations, where shapes are cut from large sheets of metal, and clinching, a process that joins sheet metal by locally deforming it under high pressure.
Category 2: Controlled Force for Testing and Analysis
The second major use of hydraulic pressure is not about brute strength, but about precision and control. Because the force can be applied smoothly and measured accurately, it is an essential tool in research and quality control.
Material Strength Testing
Before a material can be used in a critical application, its limits must be understood. Hydraulic systems are used to perform these tests.
This includes tensile testing, where a sample is pulled apart to measure its breaking point, and compressive testing, where a sample is crushed to determine its durability under load.
Laboratory Sample Preparation
In scientific analysis, the quality of the sample is critical. Hydraulic pressure is used to create ideal samples for various analytical techniques.
For example, a lab press creates thin, uniform KBr pellets containing a sample for FTIR spectroscopy. This requires a specific, controlled pressure to create a transparent pellet without damaging the chemical compounds. Similarly, it is used to create smooth, flat sample surfaces for XRF analysis.
The Principle That Makes It Possible: Pascal's Law
Both of these categories—brute force and precise control—are enabled by a single, elegant principle of fluid dynamics discovered in the 17th century.
What is Pascal's Law?
Pascal's Law states that pressure applied to an enclosed, incompressible fluid is transmitted equally and undiminished to every portion of the fluid and the walls of the containing vessel.
How It Enables Force Multiplication
Imagine a sealed container with two pistons of different sizes. If you apply a small force to the small piston, the pressure created is transmitted throughout the fluid.
Because that same pressure is now acting on the much larger surface area of the second piston, the resulting output force is proportionally larger. This is how a 100-pound force can be transformed into a 10,000-pound force, enabling the vast range of hydraulic applications.
How These Principles Apply in Practice
Understanding these two core functions helps clarify the purpose behind any hydraulic system you encounter.
- If your primary focus is manufacturing and fabrication: You are leveraging the principle of force multiplication to efficiently shape, cut, and form materials on a large scale.
- If your primary focus is research and quality control: You are using the principle of controlled force application to test material properties and prepare highly standardized samples for accurate analysis.
Ultimately, hydraulic pressure provides a reliable and scalable method for applying force, whether the goal is to shape the body of a car or to prepare a microscopic sample for analysis.
Summary Table:
| Function | Primary Application | Key Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Force Multiplication | Material Transformation | Stamping, Forging, Molding, Compacting, Cutting |
| Controlled Force | Testing & Analysis | Tensile/Compressive Testing, KBr Pellet Prep, XRF Sample Prep |
Ready to harness the precision and power of hydraulic pressure for your specific needs?
Whether you are in manufacturing and need robust equipment for shaping materials, or in a research lab requiring precise control for sample preparation and testing, KINTEK has the solution. Our expertise in lab equipment and consumables ensures you get the right hydraulic press for your application—from industrial forging to delicate FTIR sample prep.
Contact us today to discuss how our hydraulic solutions can enhance your efficiency and accuracy. Get in touch via our contact form and let our experts guide you to the perfect equipment.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Press for XRF & KBR Pellet Press
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press Machine for Glove Box
- Laboratory Manual Hydraulic Pellet Press for Lab Use
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press for Button Battery
People Also Ask
- What is the use of KBr? Master Sample Prep for Accurate IR Spectroscopy
- How does a laboratory hydraulic press improve XRF accuracy for catalyst samples? Enhance Precision & Signal Stability
- What role does a laboratory hydraulic press play in the preparation of solid electrolyte pellets? Ensure Data Accuracy
- Why use KBr for IR? Achieve Clear, Unobstructed Spectra for Solid Samples
- Why are KBr pellets used in FTIR? Achieve Clear, Accurate Solid Sample Analysis



















