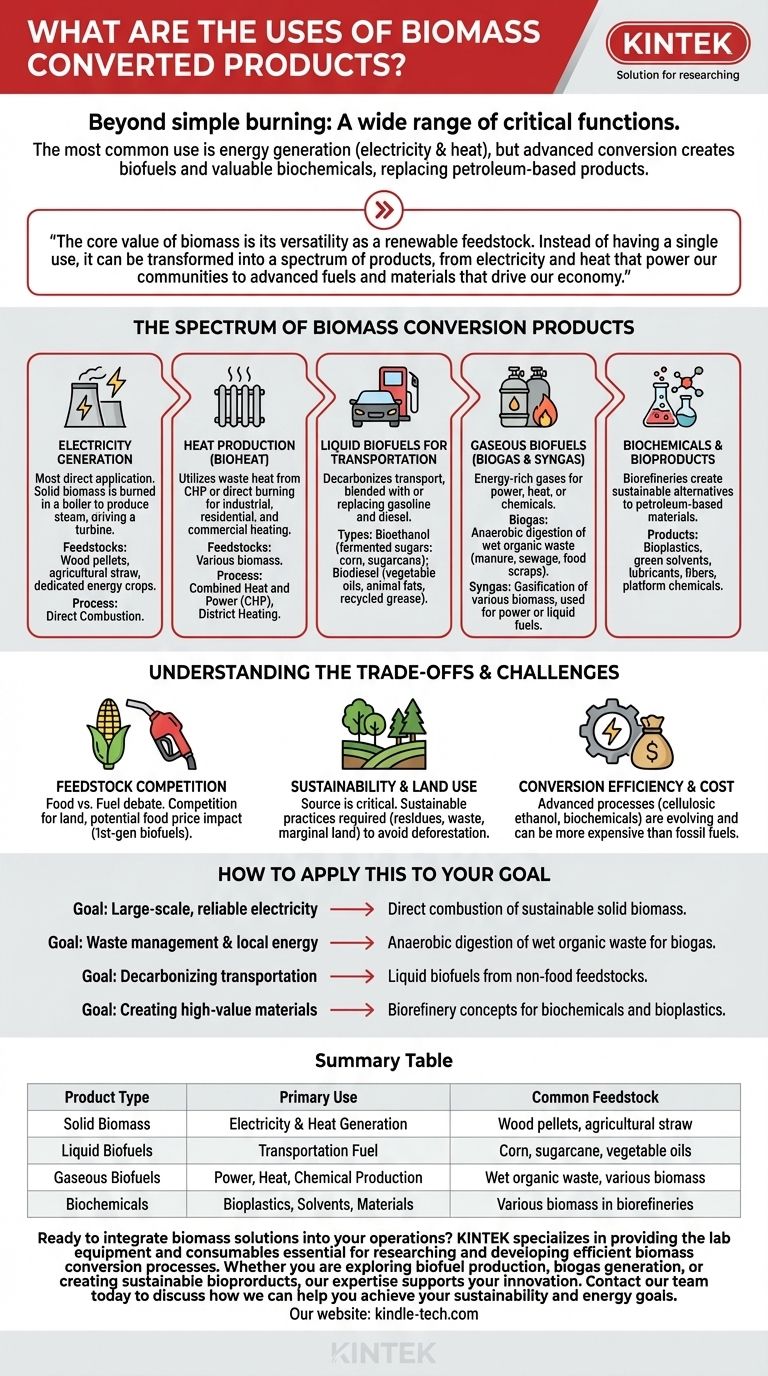
Beyond simple burning, the products derived from biomass conversion serve a wide range of critical functions. The most common use is the generation of energy, including electricity and heat, often by burning the biomass to create steam that drives turbines. However, advanced conversion processes also create liquid biofuels for transportation and valuable biochemicals that can replace petroleum-based products.
The core value of biomass is its versatility as a renewable feedstock. Instead of having a single use, it can be transformed into a spectrum of products, from electricity and heat that power our communities to advanced fuels and materials that drive our economy.

The Spectrum of Biomass Conversion Products
Biomass is not a single-source solution but a flexible resource. The final product depends entirely on the type of biomass used (the feedstock) and the conversion technology applied.
Electricity Generation
This is the most direct and widely used application. Solid biomass, such as wood pellets, agricultural straw, or dedicated energy crops, is burned in a boiler to produce high-pressure steam.
This steam then drives a turbine connected to a generator, producing electricity that is fed into the grid. This process, known as direct combustion, is a mature technology used in dedicated biomass power plants.
Heat Production (Bioheat)
Biomass is an excellent source of thermal energy. In combined heat and power (CHP), or cogeneration plants, the waste heat from electricity generation is captured and utilized.
This captured heat can be used for industrial processes or to provide hot water and heating for residential and commercial buildings through a district heating system, dramatically increasing overall energy efficiency.
Liquid Biofuels for Transportation
One of the most critical uses of biomass is in producing liquid fuels to decarbonize the transportation sector. These fuels are often blended with or directly replace gasoline and diesel.
The two primary types are bioethanol, an alcohol fuel typically made by fermenting sugars from crops like corn or sugarcane, and biodiesel, produced from vegetable oils, animal fats, or recycled cooking grease.
Gaseous Biofuels (Biogas & Syngas)
Biomass can be converted into energy-rich gases that offer flexible applications.
Biogas is primarily methane produced through the anaerobic digestion of wet organic waste, such as manure, sewage sludge, or food scraps. It can be burned to generate electricity and heat or upgraded to renewable natural gas.
Syngas (synthesis gas) is created through a high-temperature process called gasification. This gas can then be used to generate power or as an intermediate step to produce liquid fuels and valuable chemicals.
Biochemicals and Bioproducts
Looking beyond energy, modern biorefineries use biomass to create sustainable, high-value products that traditionally come from petroleum.
These include bioplastics, green solvents, lubricants, fibers, and a wide range of platform chemicals. This application is central to building a circular, bio-based economy.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While biomass offers significant potential, its application is not without challenges. Acknowledging these trade-offs is crucial for sustainable implementation.
Feedstock Competition
The "food vs. fuel" debate is a significant concern, particularly for first-generation biofuels that use food crops like corn or sugarcane. This can create competition for land and potentially impact food prices.
Sustainability and Land Use
The source of the biomass is critical. Sustainable practices require using agricultural residues, forestry waste, municipal solid waste, and dedicated energy crops grown on marginal land to avoid deforestation and protect biodiversity.
Conversion Efficiency and Cost
The cost-effectiveness and efficiency of biomass conversion technologies vary widely. While direct combustion is well-established, more advanced processes like cellulosic ethanol or biochemical production are still evolving and can be more expensive than their fossil-fuel counterparts.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
The best use for a biomass product depends entirely on the available resources and the specific problem you aim to solve.
- If your primary focus is large-scale, reliable electricity: Direct combustion of solid biomass from sustainable forestry or agricultural residues is the most mature and dependable pathway.
- If your primary focus is waste management and local energy: Anaerobic digestion of wet organic waste to create biogas for heat and power is an ideal circular solution.
- If your primary focus is decarbonizing transportation: Developing liquid biofuels from non-food feedstocks is the key strategy, though it requires more advanced conversion technologies.
- If your primary focus is creating high-value, sustainable materials: Pursuing biorefinery concepts to produce biochemicals and bioplastics represents the future of a sustainable industrial economy.
Ultimately, leveraging biomass effectively is about matching the right conversion technology and feedstock to a specific energy or material need.
Summary Table:
| Product Type | Primary Use | Common Feedstock |
|---|---|---|
| Solid Biomass | Electricity & Heat Generation | Wood pellets, agricultural straw |
| Liquid Biofuels (Bioethanol, Biodiesel) | Transportation Fuel | Corn, sugarcane, vegetable oils |
| Gaseous Biofuels (Biogas, Syngas) | Power, Heat, Chemical Production | Wet organic waste, various biomass |
| Biochemicals | Bioplastics, Solvents, Materials | Various biomass in biorefineries |
Ready to integrate biomass solutions into your operations? KINTEK specializes in providing the lab equipment and consumables essential for researching and developing efficient biomass conversion processes. Whether you are exploring biofuel production, biogas generation, or creating sustainable bioproducts, our expertise supports your innovation. Contact our team today to discuss how we can help you achieve your sustainability and energy goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Is it safe to store samples at -70°C? A Proven Standard for Long-Term Sample Integrity
- Why argon is the usual gas for the sputtering processes? Optimize Your Thin Film Deposition
- Does biofuels damage the environment? The Truth About Their Carbon Neutral Promise
- What is the process of gold sputtering? A Guide to High-Precision Thin Film Deposition
- What is the RF frequency for sputtering? Unlocking the Standard for Insulating Materials
- Why is a precision laboratory heater essential for the acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of waste paper? Optimize Glucose Yield
- On what principle does magnetron sputtering work? Achieve High-Quality Thin Films with Precision
- What are laser sintering methods? Unlock Complex 3D Printing with Powder Bed Fusion



















