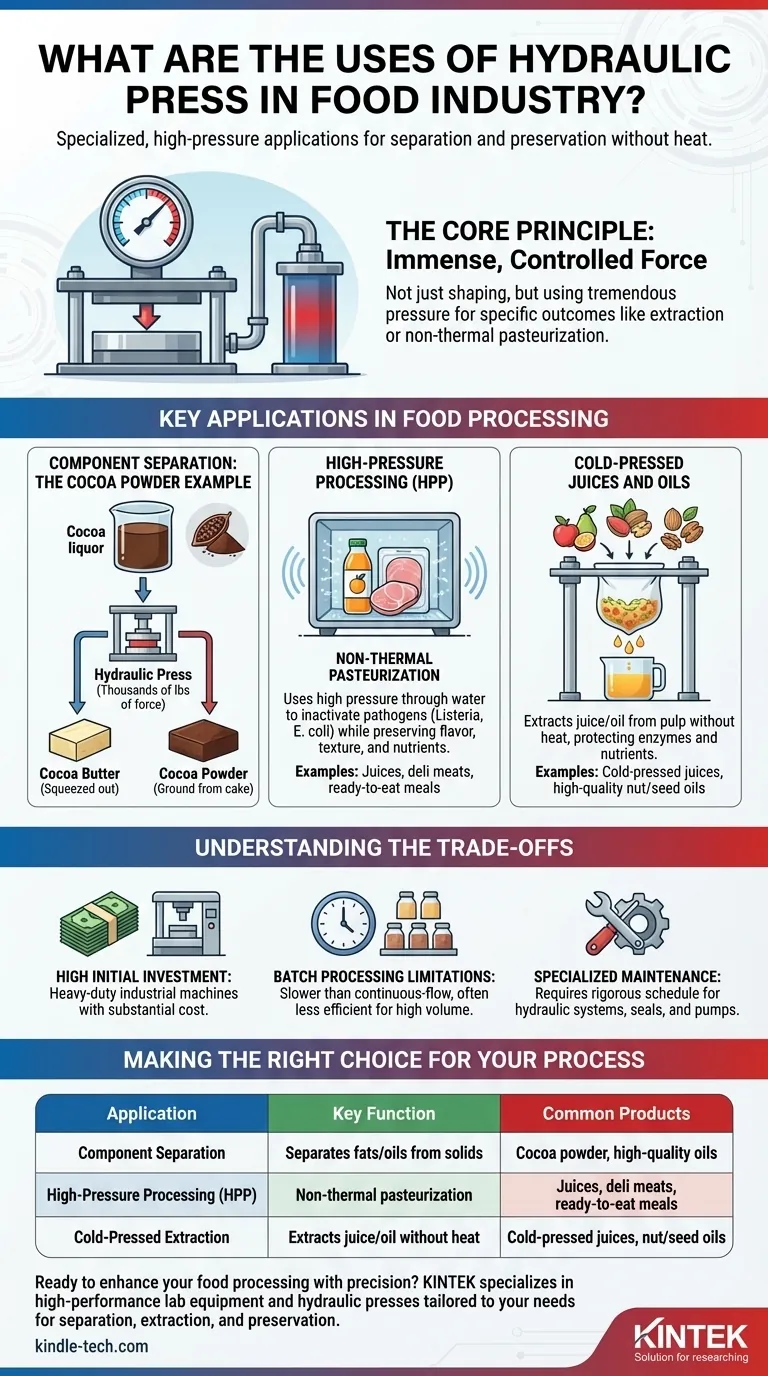
In the food industry, a hydraulic press is primarily used for specialized, high-pressure applications that require immense force to separate components or preserve products without heat. Its most well-known use is in the production of cocoa powder, where it presses cocoa liquor to separate the fat (cocoa butter) from the solid components.
The core function of a hydraulic press in a food context is not just about shaping or crushing, but about using tremendous, controlled pressure to achieve specific outcomes—like extraction or non-thermal pasteurization—that are difficult to accomplish with other methods.

The Core Principle: Applying Immense, Controlled Force
The value of a hydraulic press comes from its ability to generate exceptional force from a simple mechanical principle. This makes it ideal for tasks that require more than just simple mechanical squeezing.
From Industrial Crushing to Food Processing
The same technology used to bend steel beams or compact scrap metal is harnessed in the food industry for highly specialized tasks.
The key is the precise control over massive amounts of pressure, which can be used to fundamentally alter the state of a food product.
The Mechanism of Separation
When applied to a food product like cocoa liquor or ground seeds, the immense pressure forces the liquid component (fat or oil) to separate and drain away, leaving the solid component behind. This is a purely mechanical process that avoids the use of heat or chemical solvents.
Key Applications in Food Processing
While not as widespread as in manufacturing, the hydraulic press serves critical functions in producing high-value or specialty food items.
Component Separation: The Cocoa Powder Example
This is the classic application. After cocoa beans are fermented, dried, roasted, and ground into a thick paste called cocoa liquor, a hydraulic press is used.
The press exerts thousands of pounds of force on the liquor, squeezing out the rich fat known as cocoa butter. What remains is a solid "cake," which is then ground into cocoa powder.
High-Pressure Processing (HPP)
Though often seen as a distinct technology, HPP relies on the same principles as a hydraulic press. It uses high pressure transmitted through water to inactivate pathogens like Listeria and E. coli.
This process acts as a non-thermal pasteurization, preserving the food's flavor, texture, and nutritional content, which would otherwise be damaged by heat. It is commonly used for juices, deli meats, and ready-to-eat meals.
Cold-Pressed Juices and Oils
The term "cold-pressed" often involves a hydraulic press. First, fruits and vegetables are ground into a pulp.
This pulp is then placed in filter bags and subjected to a hydraulic press, which slowly extracts the juice without generating heat from fast-spinning blades. This method is believed to protect enzymes and nutrients. A similar process is used for extracting high-quality oils from nuts and seeds.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing to use a hydraulic press is a strategic decision that involves significant considerations, particularly regarding cost and operational workflow.
High Initial Investment
Hydraulic presses are heavy-duty industrial machines. The cost of purchasing, installing, and integrating one into a food production line is substantial compared to other processing equipment.
Batch Processing Limitations
Many hydraulic press applications, such as for cold-pressed juice, are batch processes. This can be slower and less efficient for high-volume production compared to continuous-flow systems.
Specialized Maintenance
The high-pressure systems involve hydraulic fluids, seals, and powerful pumps that require a specific and rigorous maintenance schedule to ensure safety and operational reliability.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
The decision to use a hydraulic press should be directly tied to the desired quality and nature of your final product.
- If your primary focus is premium quality and nutritional preservation: A hydraulic press for HPP or cold-pressing is an excellent choice for creating high-value products.
- If your primary focus is efficient separation of liquids from solids: For products like cocoa or high-quality oils, the hydraulic press is an industry-standard tool.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, low-cost production: A hydraulic press may create a bottleneck, and other technologies like centrifugal extractors might be more suitable.
Ultimately, a hydraulic press is a powerful tool for when immense, controlled force is the only way to achieve your desired food processing outcome.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Function | Common Products |
|---|---|---|
| Component Separation | Separates fats/oils from solids | Cocoa powder, high-quality oils |
| High-Pressure Processing (HPP) | Non-thermal pasteurization | Juices, deli meats, ready-to-eat meals |
| Cold-Pressed Extraction | Extracts juice/oil without heat | Cold-pressed juices, nut/seed oils |
Ready to enhance your food processing with precision hydraulic solutions? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, providing reliable hydraulic presses tailored to your laboratory's needs. Whether you're focused on separation, extraction, or preservation, our expertise ensures you achieve superior results. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your food industry applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Warm Isostatic Press WIP Workstation 300Mpa for High Pressure Applications
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Anti-Cracking Press Mold for Lab Use
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
People Also Ask
- Is hot isostatic pressing a heat treatment? A Guide to Its Unique Thermomechanical Process
- What are some of the attractive properties of hot isostatic pressed products? Achieve Perfect Density and Superior Performance
- What is HIP in material processing? Achieve Near-Perfect Density for Critical Components
- What is the historical background of the Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) process? From Nuclear Roots to Industry Standard
- What pressure is hot isostatic press? Achieve Full Density & Superior Material Performance



















