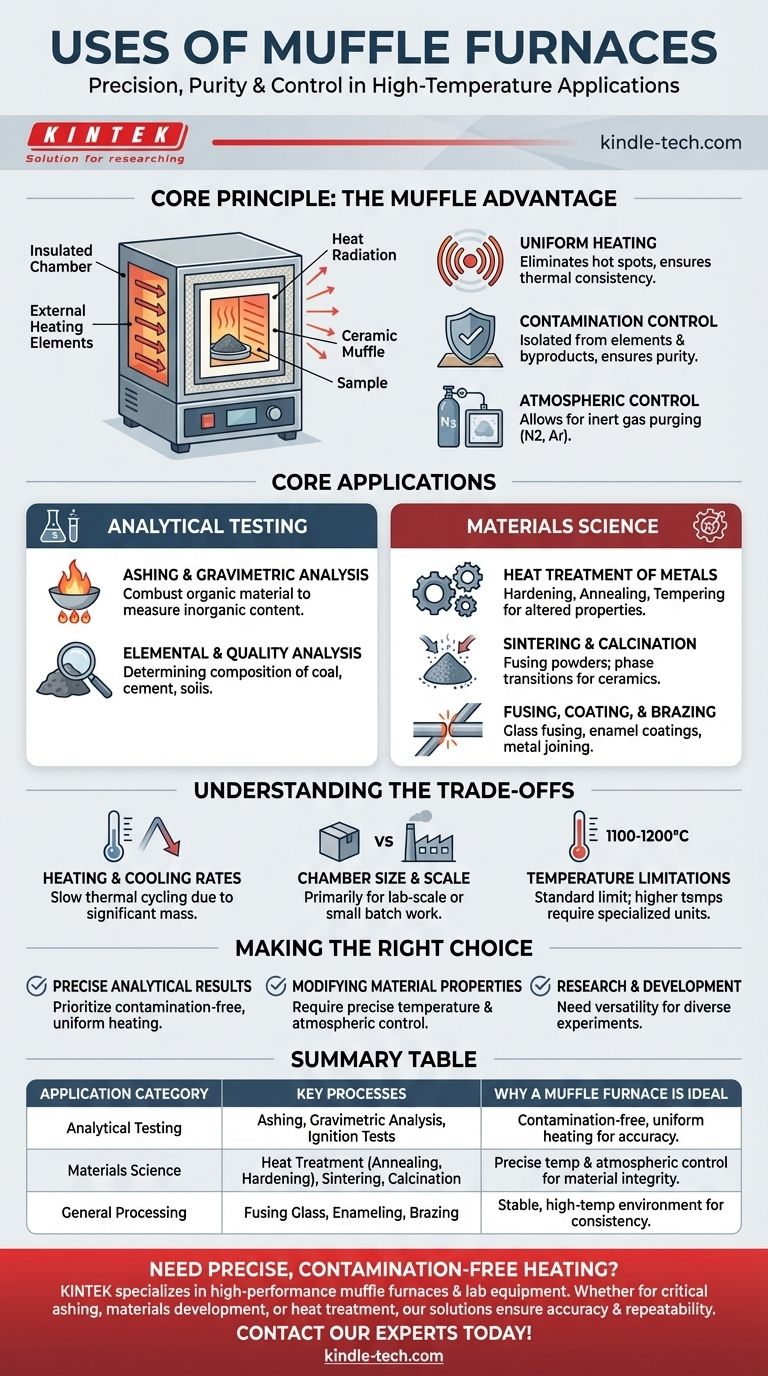
At their core, muffle furnaces are high-temperature ovens used for a vast range of laboratory and industrial processes. They excel in applications requiring precise thermal uniformity and a controlled environment, including analytical testing like ashing, materials science processes like heat-treating metals, and the synthesis of ceramics and glass. Their key feature is an insulated outer chamber that heats a separate inner chamber (the "muffle"), ensuring the sample is not contaminated by the fuel or heating elements.
A muffle furnace is chosen not just for its ability to reach high temperatures, but for its capacity to provide a highly uniform and clean heating environment. This makes it indispensable for processes where precision and sample integrity are paramount.

The Principle: Why a Muffle Furnace?
The name "muffle furnace" comes from its core design feature: the muffle. This is a refractory ceramic chamber that contains the sample, which is then heated externally by heating elements. This simple separation is the key to its utility.
Uniform Heating
The design ensures that heat radiates evenly from all sides of the inner chamber. This eliminates hot spots and provides exceptional thermal uniformity across the entire sample, which is critical for consistent and repeatable results.
Contamination Control
Because the sample is inside the muffle, it is isolated from the heating elements. This prevents any potential contamination from the elements themselves or, in fuel-fired furnaces, from the byproducts of combustion. This purity is essential for sensitive analytical work.
Atmospheric Control
While many processes are performed in air, muffle furnaces can often be sealed and purged with inert gases like nitrogen or argon. This allows for controlled atmosphere heating, which is necessary for preventing oxidation or inducing specific chemical reactions.
Core Applications in Analytical Testing
A primary use for muffle furnaces is in analytical chemistry, where samples must be processed to determine their composition.
Ashing and Gravimetric Analysis
Ashing is the process of burning off all organic material in a sample to measure the remaining inorganic content (the ash). Muffle furnaces provide the high temperatures and oxygen-rich environment needed to ensure complete combustion without contaminating the residue. This is a form of gravimetric analysis, which relies on precise mass measurements before and after a process.
Elemental and Quality Analysis
Industries use muffle furnaces for critical quality control tests. This includes determining the quality of coal, analyzing the composition of cement, and performing ignition tests on soils and aggregates for engineering purposes.
Core Applications in Materials Science
Muffle furnaces are fundamental tools for developing and processing advanced materials.
Heat Treatment of Metals
The precise temperature control of a muffle furnace is ideal for altering the physical properties of metals. Common processes include:
- Hardening: Heating and then rapidly cooling steel to increase its hardness.
- Annealing: Heating and slowly cooling to soften a metal and relieve internal stresses.
- Tempering: Gently reheating a hardened part to reduce brittleness.
Sintering and Calcination
Sintering involves heating powdered materials below their melting point to fuse them into a solid or porous mass, a key step in creating ceramics. Calcination is a thermal treatment process to bring about a phase transition or remove a volatile fraction.
Fusing, Coating, and Brazing
Muffle furnaces provide the stable, high temperatures needed for fusing glass, creating durable enamel coatings on metal, and joining metal parts through soldering and brazing.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly versatile, muffle furnaces are not the solution for every high-temperature need.
Heating and Cooling Rates
The significant thermal mass required for temperature stability means that muffle furnaces generally heat and cool slowly. They are not well-suited for applications requiring rapid thermal cycling.
Chamber Size and Scale
Most muffle furnaces are designed for lab-scale or small batch work. While large industrial versions exist, the term typically refers to smaller, box-style units not intended for high-volume manufacturing.
Temperature Limitations
Standard laboratory muffle furnaces typically operate up to 1100°C or 1200°C. While higher-temperature models exist (up to 1800°C), they are more specialized and costly. They cannot reach the extreme temperatures of induction or arc furnaces.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the right heating equipment depends entirely on your end goal.
- If your primary focus is precise analytical results (e.g., ashing): The contamination-free, uniform heating of a muffle furnace is non-negotiable for accuracy.
- If your primary focus is modifying material properties (e.g., heat treating steel): The furnace's precise temperature and atmospheric control are essential for achieving consistent, repeatable results.
- If your primary focus is research and development (e.g., sintering new ceramics): The versatility of a muffle furnace makes it an ideal tool for a wide range of high-temperature experiments.
Ultimately, a muffle furnace is the definitive tool when your process demands precise, uniform, and clean high-temperature conditions.
Summary Table:
| Application Category | Key Processes | Why a Muffle Furnace is Ideal |
|---|---|---|
| Analytical Testing | Ashing, Gravimetric Analysis, Ignition Tests | Contamination-free, uniform heating for accurate results |
| Materials Science | Heat Treatment (Annealing, Hardening), Sintering, Calcination | Precise temperature & atmospheric control for material integrity |
| General Processing | Fusing Glass, Enameling, Brazing | Stable, high-temperature environment for consistent outcomes |
Need precise, contamination-free heating for your lab? KINTEK specializes in high-performance muffle furnaces and lab equipment. Whether you're performing critical ashing tests, developing new materials, or need reliable heat treatment, our solutions ensure the accuracy and repeatability your work demands. Contact our experts today to find the perfect furnace for your application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is dry ashing? A Reliable Method for Analyzing Inorganic Composition
- What are the safety precautions for using a muffle furnace? Essential Tips for Safe Operation
- Is a muffle furnace used for ash determination? Discover Its Critical Role in Accurate Analysis
- What is the temperature of a muffle furnace for ash determination? Key Insights for Accurate Results
- What is the optimal temperature for ashing in a muffle furnace? Achieve Precise and Efficient Results



















