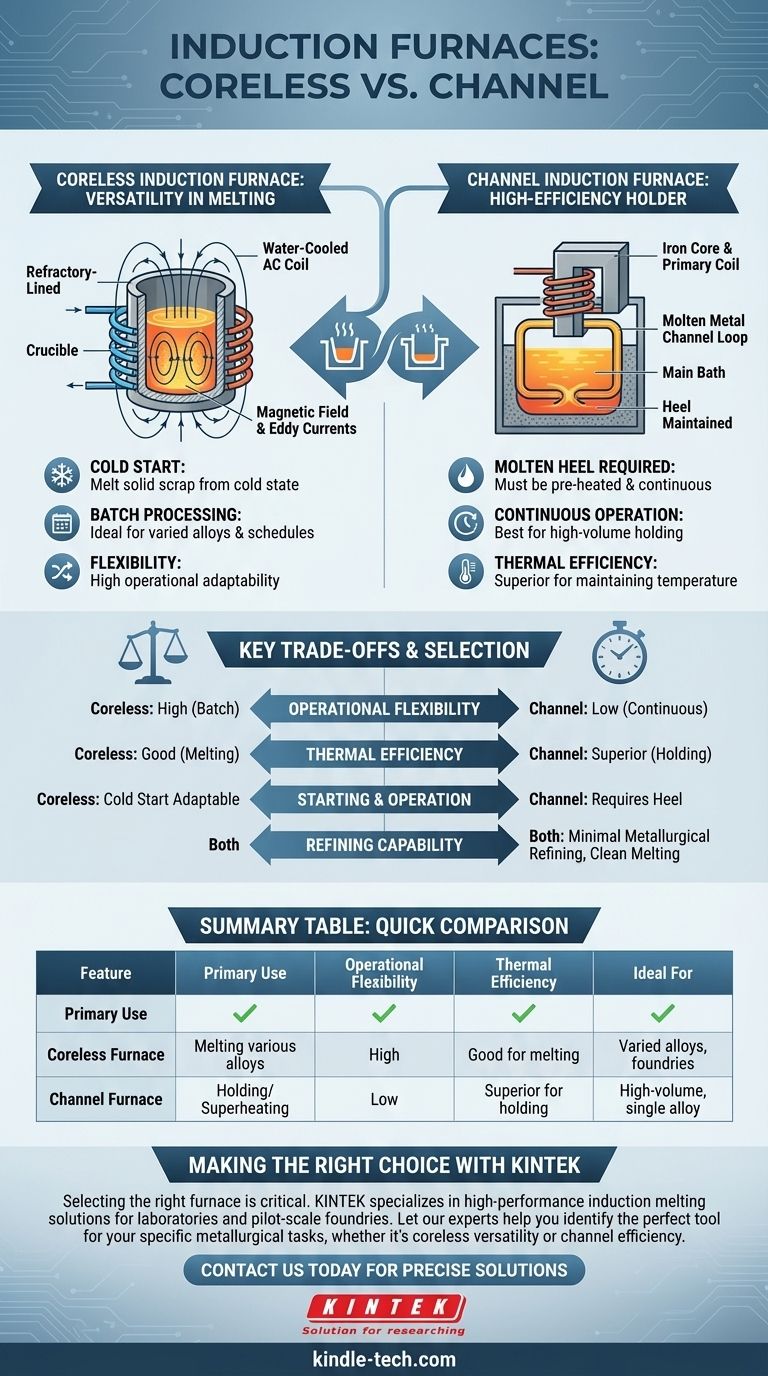
Fundamentally, there are two primary types of induction furnaces: the coreless induction furnace and the channel induction furnace. The coreless design heats metal placed in a crucible that is surrounded by a water-cooled alternating current coil. In contrast, the channel design uses a loop of already molten metal that acts as a secondary winding for an iron core, heating the metal as it circulates through the "channel."
The choice between a coreless and a channel furnace is not about which is better overall, but which is the right tool for a specific metallurgical task. Coreless furnaces provide operational flexibility for varied alloys, while channel furnaces offer superior efficiency for holding and continuous melting.

The Coreless Induction Furnace: Versatility in Melting
A coreless furnace is the more common and versatile of the two designs, often what people picture when thinking of an induction furnace.
Design and Operation
The furnace is essentially a refractory-lined crucible surrounded by a powerful, water-cooled copper coil. When alternating current flows through the coil, it creates a strong magnetic field.
This magnetic field induces powerful eddy currents within the metal charge inside the crucible, generating intense heat and melting the material from the inside out. This process also creates a natural stirring action, ensuring a uniform temperature and homogenous alloy.
Key Applications
Because it can be started with a cold, solid charge and completely emptied after each melt, the coreless furnace is extremely flexible. It is ideal for foundries that produce a wide variety of alloys.
Common uses include melting steel, iron, precious metals, copper, and aluminum for casting and alloy manufacturing.
The Channel Induction Furnace: The High-Efficiency Holder
The channel furnace operates on a different principle, functioning more like an electrical transformer.
Design and Operation
This furnace features an iron core with a primary coil, similar to a standard transformer. The "secondary coil" is a closed loop or channel of molten metal that encircles the primary assembly.
Current induced in this molten metal loop generates heat, which is then transferred to the main bath of the furnace. A key characteristic is that a "heel" of molten metal must be maintained at all times for the furnace to operate, as it cannot efficiently melt a solid charge from a cold state.
Key Applications
Due to its design, the channel furnace is exceptionally energy-efficient for holding large volumes of molten metal at a constant temperature or for superheating.
It is typically used in high-volume, continuous operations involving low-melting-point alloys or as a holding unit for metals like cast iron.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
Choosing the correct furnace requires understanding the fundamental differences in their operational capabilities.
Flexibility vs. Efficiency
The coreless furnace offers maximum flexibility. It can be started and stopped easily, making it perfect for batch operations or foundries that switch between different alloys frequently.
The channel furnace provides superior thermal efficiency for holding applications. Because it maintains a molten heel, it avoids the energy loss associated with repeatedly melting a full charge from a solid state.
Starting and Operation
Coreless furnaces can be started cold with a charge of solid scrap metal. This makes them highly adaptable to fluctuating production schedules.
Channel furnaces must be pre-heated and require a continuous supply of molten metal to start. They are designed for continuous or semi-continuous operation and are not suited for intermittent work.
Refining Capability
It is important to note that neither furnace type offers significant metallurgical refining. While the electromagnetic stirring promotes homogeneity, they do little to remove impurities. Their primary advantage is clean melting with minimal metal loss.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your specific production requirements will dictate the ideal furnace type.
- If your primary focus is operational flexibility and melting various alloys: The coreless induction furnace is the superior choice due to its ability to start from a cold charge and handle batch processing.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, continuous operation with a single alloy: The channel induction furnace provides higher thermal efficiency for holding and superheating large quantities of molten metal.
- If your primary focus is precise temperature control and clean melts: Both furnace types excel, offering uniform heating and minimal material losses compared to combustion-based methods.
Understanding these fundamental design differences empowers you to select the precise induction technology that aligns with your production goals.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Coreless Induction Furnace | Channel Induction Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Melting various alloys, batch processing | Holding/superheating metal, continuous operation |
| Operational Flexibility | High - can start from a cold, solid charge | Low - requires a molten metal "heel" to operate |
| Thermal Efficiency | Good for melting | Superior for holding large volumes |
| Ideal For | Foundries with varied alloys and schedules | High-volume operations with a single alloy |
| Refining Capability | Minimal metallurgical refining | Minimal metallurgical refining |
Selecting the right furnace is critical to your operation's efficiency and success.
KINTEK specializes in providing high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including induction melting solutions for laboratories and pilot-scale foundries. Whether you require the versatility of a coreless furnace or the holding efficiency of a channel furnace, our experts can help you identify the perfect tool for your specific metallurgical tasks.
Contact us today to discuss your application and let KINTEK provide the reliable equipment you need to achieve precise temperature control and clean melts. Get in touch via our contact form!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the power supply of induction furnace? The Heart of Your Metal Melting System
- What are the disadvantages of inductive heating? High Cost and Material Limitations Explained
- What is a furnace used in melting non-ferrous metals? Choose Between Induction & Fuel-Fired
- How can I improve my induction furnace efficiency? A Systematic Guide to Lower Costs & Higher Output
- What is the function of asbestos boards in the induction furnace lining? Essential Insulation & Moisture Control
- How does a high frequency induction heater work? Achieve Fast, Precise, and Efficient Heating
- Which furnace is most commonly used for melting non ferrous metals? Induction Furnaces for Purity & Efficiency
- What is the difference between resistance brazing and induction brazing? Choose the Right Method for Your Parts



















