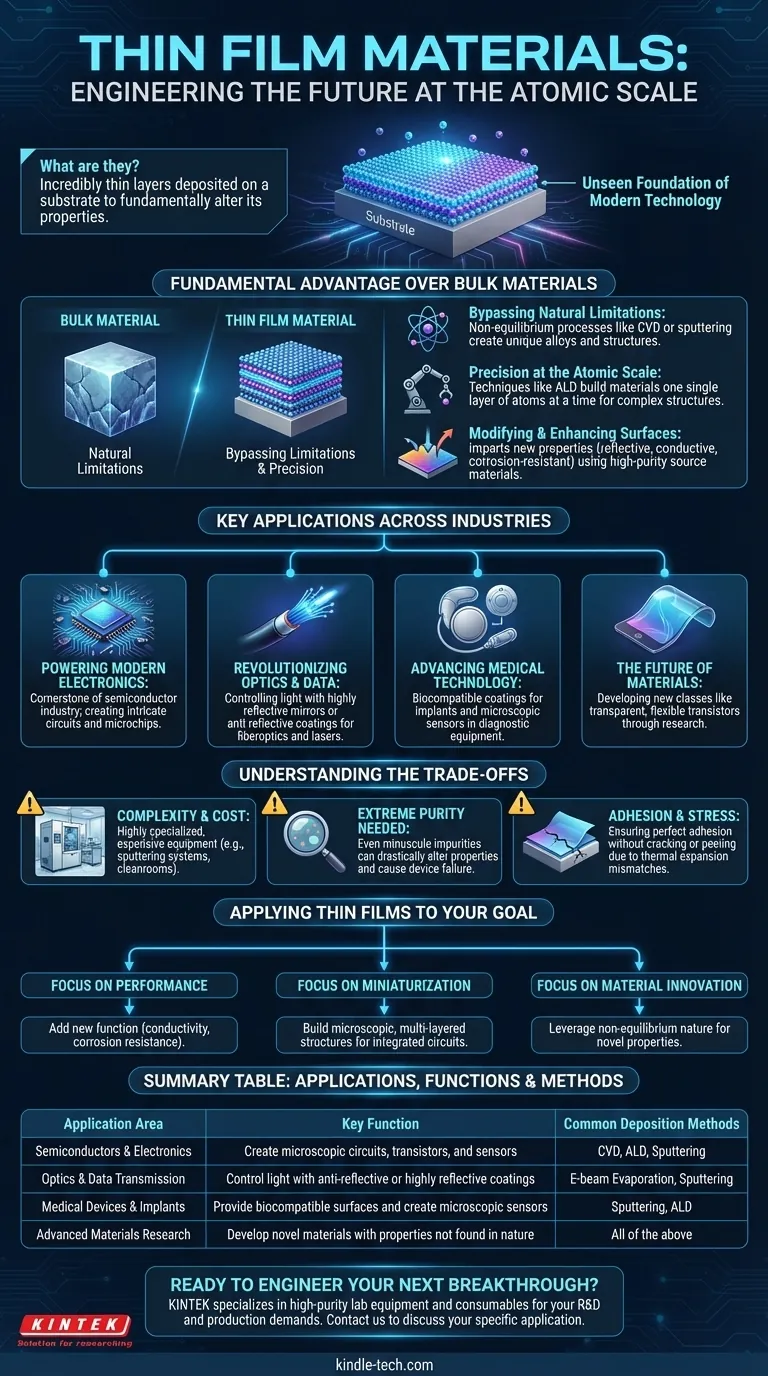
At their core, thin film materials are incredibly thin layers of specific substances deposited onto a surface, or substrate, to fundamentally alter its properties. These materials are the unseen foundation of modern technology, used in everything from semiconductor manufacturing and fiberoptic systems to advanced medical devices and consumer electronics.
The true power of thin films lies in their unique manufacturing process, which allows for the creation of material structures and properties that are often impossible to achieve in a material's normal, or "bulk," state. This enables the precise engineering of surfaces for specific electronic, optical, or physical functions.

The Fundamental Advantage Over Bulk Materials
To understand the widespread use of thin films, you must first understand why they are fundamentally different from standard materials. The key is in how they are made.
Bypassing Natural Limitations
Most methods for creating thin films, such as Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) or sputtering, are "non-equilibrium" processes.
This means the material is deposited atom by atom in a way that is not constrained by the rules of standard metallurgy. It allows engineers to create unique alloys and structures that wouldn't form naturally.
Precision at the Atomic Scale
Techniques like Atomic Layer Deposition (ALD) give manufacturers an extraordinary level of control, allowing them to build a material one single layer of atoms at a time.
This precision is essential for creating the incredibly complex, layered structures required for modern microchips and sensors.
Modifying and Enhancing Surfaces
The primary goal of a thin film is to impart a new property to the surface of a substrate. A film can make a material reflective, electrically conductive, resistant to corrosion, or harder than it was before.
These films are formed using high-purity source materials, such as precursor gases or solid sputtering targets, to ensure the final layer has the exact properties required.
Key Applications Across Industries
The ability to precisely control surface properties has made thin films indispensable in nearly every high-tech field.
Powering Modern Electronics
Thin film deposition is the cornerstone of the semiconductor industry. The intricate circuits inside a computer processor are built by depositing dozens of different thin films of conductive, insulating, and semiconducting materials.
Revolutionizing Optics and Data
In fiberoptic systems and industrial lasers, thin films are used to create highly reflective mirrors or anti-reflective coatings. These coatings precisely control how light behaves, which is critical for data transmission and imaging.
Advancing Medical Technology
Thin films are essential in biomedical devices and medical electronics. They can create biocompatible coatings for implants or form the microscopic electrodes and sensors used in advanced diagnostic equipment.
The Future of Materials
Research is constantly pushing the boundaries of what is possible. New classes of thin films, such as amorphous heavy-metal cation multicomponent oxides, are being developed to create technologies like transparent, flexible transistors.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, working with thin film materials involves significant technical challenges that are important to recognize.
Complexity and Cost of Deposition
The equipment required for thin film deposition, such as electron beam evaporators or magnetron sputtering systems, is highly specialized and expensive. It requires operation in controlled environments, like cleanrooms, adding to the complexity.
The Need for Extreme Purity
The performance of a thin film is directly tied to the purity of its source materials. Even minuscule impurities can drastically alter the film's electrical or optical properties, leading to device failure.
Adhesion and Stress
Ensuring a microscopic film adheres perfectly to its substrate without cracking or peeling is a major engineering challenge. Mismatches in thermal expansion or internal stress can ruin the integrity of the entire component.
Applying Thin Films to Your Goal
Your reason for using a thin film will determine which properties and processes are most important.
- If your primary focus is performance: Use thin films to add a new function—like anti-reflection, conductivity, or corrosion resistance—to an existing substrate.
- If your primary focus is miniaturization: Thin film deposition is the only viable method for building the microscopic, multi-layered structures at the heart of integrated circuits and sensors.
- If your primary focus is material innovation: Leverage the non-equilibrium nature of deposition to create novel material compositions with properties that cannot be found in nature.
Ultimately, thin films empower us to engineer the behavior of matter at its most fundamental level.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Function of Thin Films | Common Deposition Methods |
|---|---|---|
| Semiconductors & Electronics | Create microscopic circuits, transistors, and sensors | CVD, ALD, Sputtering |
| Optics & Data Transmission | Control light with anti-reflective or highly reflective coatings | E-beam Evaporation, Sputtering |
| Medical Devices & Implants | Provide biocompatible surfaces and create microscopic sensors | Sputtering, ALD |
| Advanced Materials Research | Develop novel materials with properties not found in nature | All of the above |
Ready to Engineer Your Next Breakthrough with Thin Films?
Thin film deposition is the key to creating the next generation of high-performance devices. KINTEK specializes in providing the high-purity lab equipment and consumables—from sputtering targets to precision deposition systems—that your R&D or production process demands.
Whether you're developing advanced semiconductors, optical coatings, or biomedical sensors, we have the expertise and products to support your goals.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific application and discover how our solutions can enhance your thin film projects.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- Where is thin film technology used? Powering Modern Electronics, Energy, and Innovation
- What is the thermal conductivity of graphene with temperature? Unlock Its Dynamic Heat Management Potential
- What are the categories of carbon nanotubes? Understand SWCNT vs. MWCNT for Your Application
- What is the purpose of ITO coating? Enabling Transparent Electronics for Modern Devices
- What are the applications of reactive sputtering? Create High-Performance Thin Films for Optics, Tools & Electronics
- What are the applications of carbon nanotubes in biotechnology? Unlock Targeted Drug Delivery & Advanced Biosensing
- What is the difference between CVD and real diamonds? Identical Sparkle, Different Origin Story
- What are the applications of sputtering? Enable Precision Coatings for High-Tech Industries



















