In essence, an induction heater is a tool for precisely and rapidly heating metals without using an open flame. Its core function is to transfer energy to a conductive material through a powerful, high-frequency magnetic field. This makes it exceptionally useful for a wide range of tasks, from industrial processes like forging and heat-treating to common workshop jobs like freeing seized bolts and bending steel.
An induction heater works by creating a magnetic field that induces electrical currents within the metal itself. This internal, flameless heating is the key to its speed, precision, and safety compared to traditional methods like a torch.
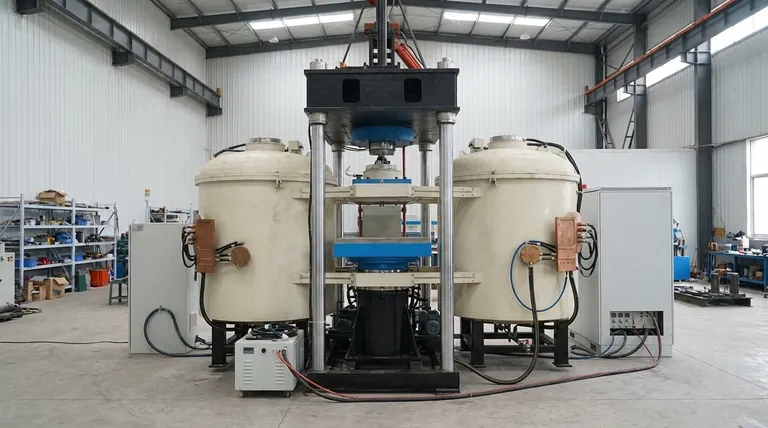

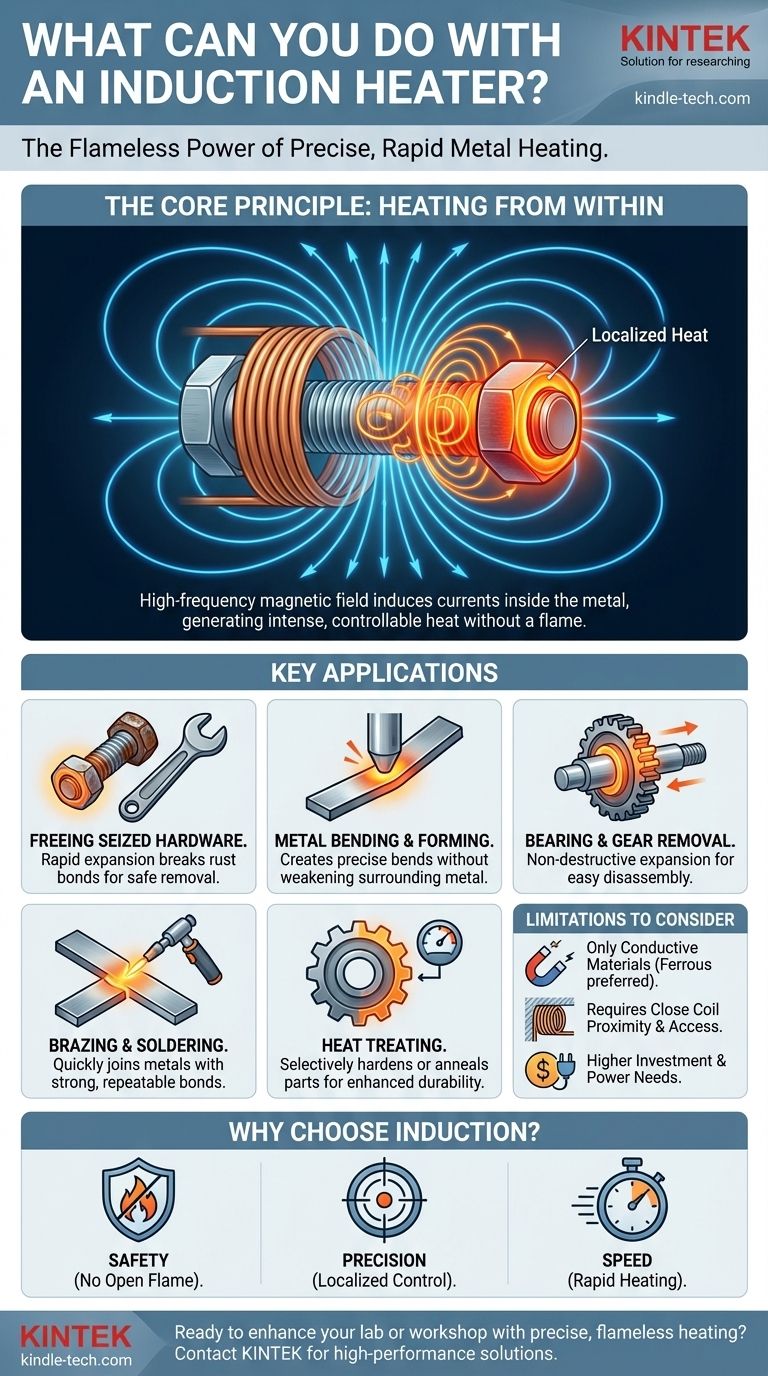
The Core Principle: Heating from Within
To understand what you can do with an induction heater, you first need to grasp how it works. Unlike a torch that applies external heat, an induction heater heats the part from the inside out.
How It Works: The Magnetic Field
An induction heater uses a coil, often made of copper tubing, through which a high-frequency alternating current is passed. This creates a dynamic and powerful magnetic field around the coil. When you place a conductive workpiece (like a steel bolt) into this field, the field induces circulating electrical currents, known as eddy currents, inside the metal.
Why This Matters: Precision and Speed
The resistance of the metal to the flow of these eddy currents generates immediate and intense heat. Because the heating happens only where the magnetic field is strong, you can heat a very specific area—like a single nut on a bolt—without affecting the surrounding components. This process is also incredibly fast, often bringing metal to red-hot temperatures in seconds.
The Critical Component: The Coil
The shape and size of the coil are crucial for efficiency. The coil must be positioned close to the workpiece without touching it. Different coils are used for different jobs, from simple helical coils for bolts and rods to specialized coils designed to fit specific parts. The ease of swapping these coils is a key design feature.
Key Applications in Detail
The unique properties of induction heating make it the ideal solution for several common and specialized tasks.
Freeing Seized Hardware
This is the most common application in automotive and equipment repair. By heating a seized nut, it expands rapidly, cracking rust and corrosion bonds. This allows the nut to be removed with minimal force and, most importantly, without the fire hazard of an open flame near fuel lines or other flammable materials.
Metal Bending and Forming
Induction provides a clean, consistent, and localized heat source perfect for bending and shaping metal rods, plates, and tubes. You can heat a precise line on a piece of steel for a sharp, clean bend without weakening the surrounding metal.
Bearing and Gear Removal
Similar to freeing a seized bolt, heating a press-fit bearing or gear causes it to expand. This expansion is often all that is needed to easily slide it off a shaft, preventing damage to both the shaft and the component being removed.
Brazing and Soldering
Induction heating is an excellent method for joining metals. It quickly brings the parent metals to the correct temperature, allowing the filler material (braze or solder) to flow cleanly into the joint. This creates a strong, reliable bond and is highly repeatable.
Heat Treating Metals
In manufacturing and toolmaking, induction is used for hardening, annealing, or tempering steel parts. For example, you can use it to harden just the cutting edge of a tool or the teeth on a gear, leaving the rest of the part in a softer, less brittle state.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, an induction heater is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is critical to using it effectively.
Material Dependency
The process relies entirely on electromagnetic induction. Therefore, it only works on conductive materials, primarily ferrous metals like iron and steel. It is less effective on non-magnetic metals like aluminum and copper and has no effect on non-conductive materials like plastic, glass, or wood.
Geometry and Accessibility
The efficiency of the heating process depends on the coil's proximity to the workpiece. If you cannot get the coil properly around or near the part you need to heat, the tool will be ineffective. This can be a challenge in tight spaces or with irregularly shaped objects.
Cost and Power Requirements
Professional-grade induction heaters are a significant investment compared to a simple oxy-acetylene torch. They also require a substantial amount of electrical power, with larger units needing dedicated high-amperage circuits.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To decide if an induction heater is the right tool, consider your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is safety in repair: An induction heater is the superior choice for working on vehicles and equipment, as it eliminates the significant fire risk of an open flame.
- If your primary focus is precision and repeatability: For tasks like metal forming, brazing, or heat treating, the localized and controllable heat of induction provides results that are very difficult to match with a torch.
- If your primary focus is speed for seized parts: Nothing removes a stubborn, rusted-on nut or bearing faster or more effectively than an induction heater.
By leveraging its unique ability to heat metal internally and precisely, you can accomplish tasks more safely, quickly, and with a higher degree of control.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefit | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Freeing Seized Hardware | Rapid, flameless expansion | Automotive repair, machinery maintenance |
| Metal Bending & Forming | Precise, localized heat | Workshop fabrication, metalworking |
| Bearing & Gear Removal | Non-destructive expansion | Equipment disassembly, press-fit parts |
| Brazing & Soldering | Clean, repeatable joints | Manufacturing, assembly, repairs |
| Heat Treating | Selective hardening or annealing | Toolmaking, industrial part production |
Ready to enhance your lab or workshop with precise, flameless heating? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including induction heating solutions that deliver speed, safety, and repeatability for your metalworking and repair tasks. Contact us today to find the perfect induction heater for your needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a vacuum hot press furnace improve the density of Ti2AlN ceramics? Achieve 98.5%+ Density & Superior Strength
- What role does a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace play in the fabrication of CuCrFeMnNi alloys? Achieve High Purity
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing furnace over HIP? Optimize Fiber-Foil Composite Production
- How does the mechanical pressure from a vacuum hot-pressing furnace facilitate the densification of B4C/Al composites?
- Why use vacuum in hot-press sintering for boron carbide? Achieve Superior Density and Material Purity

















