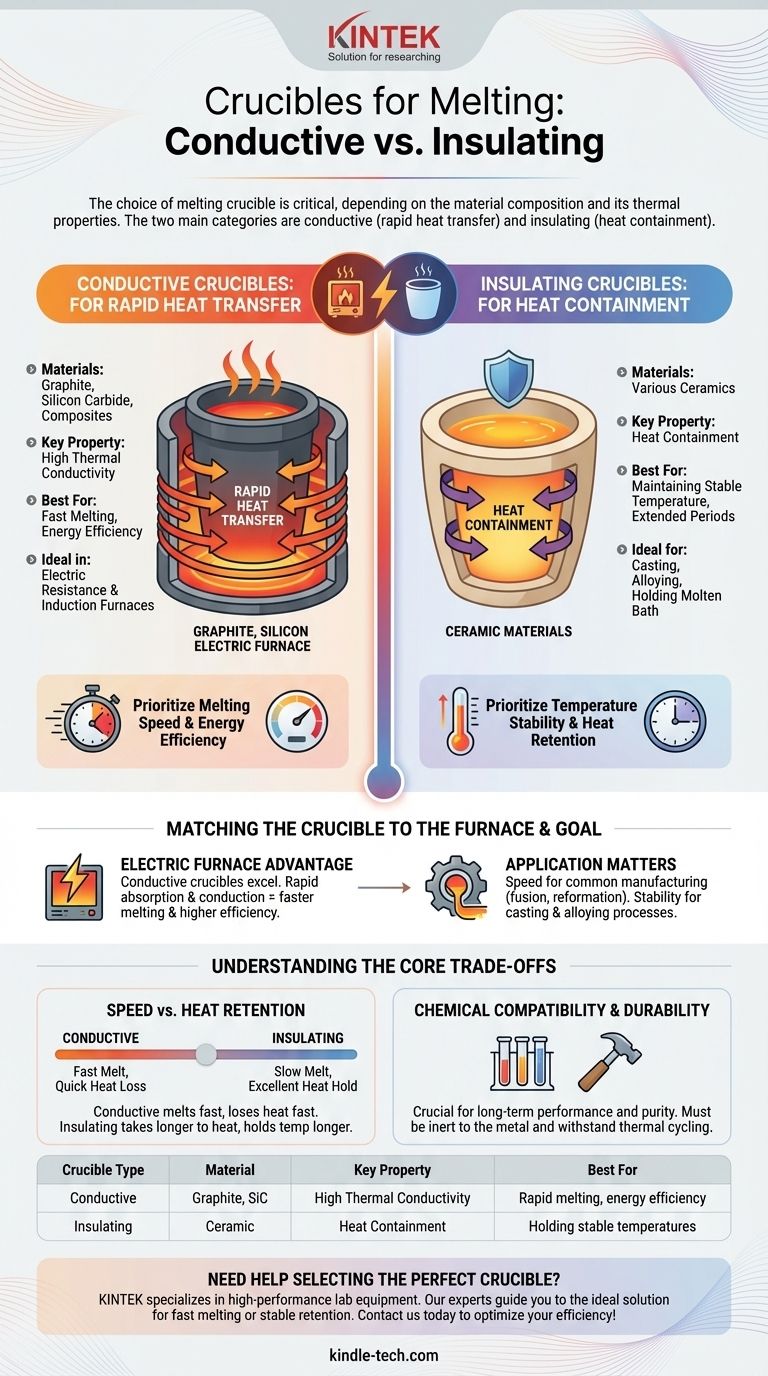
Crucibles used for melting are primarily chosen based on their material composition, which dictates their thermal properties. The most common materials fall into two main categories: conductive materials like graphite and silicon carbide, and insulating materials such as ceramics. This selection is critical and depends directly on the melting application and the type of furnace being used.
The fundamental choice in selecting a melting crucible is between conductive materials like graphite, which rapidly transfer heat for fast melting, and insulating ceramic materials, which are designed to contain heat and maintain temperature.

The Two Primary Classes of Melting Crucibles
The function of a crucible is not just to hold molten material but to interact with the heating source in a predictable way. This leads to a clear division based on thermal properties.
Conductive Crucibles: For Rapid Heat Transfer
Conductive crucibles are typically made from graphite, silicon carbide, or a composite mixture of the two.
Their defining characteristic is high thermal conductivity. This allows them to absorb heat from the furnace and transfer it efficiently and quickly to the metal inside.
Because of this rapid heat transfer, they are often selected for applications where melting speed and energy efficiency are priorities.
Insulating Crucibles: For Heat Containment
Insulating crucibles are constructed from ceramic materials.
Unlike their conductive counterparts, their primary purpose is to contain heat rather than transfer it. They act more like an insulated container, preventing heat from escaping.
These are best suited for processes where maintaining a stable temperature for the molten metal over a longer period is more important than the initial melting speed.
Matching the Crucible to the Furnace
The synergy between the furnace technology and the crucible material is the most important factor in achieving an efficient melting process. Melting is used across manufacturing to liquefy metals for joining, alloying, or reforming them into new shapes.
The Advantage in Electric Furnaces
Electric resistance and induction furnaces work by directly heating the crucible, which then transfers that heat to its contents.
In this environment, a conductive crucible with high graphite content is superior. The crucible's ability to quickly absorb and conduct energy results in significantly faster melting times and greater overall energy efficiency.
Application and Material Properties
The goal of the melt also influences the choice. While melting can be used to alter physical properties, such as demagnetizing steel by heating it past its Curie temperature, its main industrial use is for fusion and reformation.
For these common manufacturing tasks, the speed offered by conductive crucibles is often a major production advantage.
Understanding the Core Trade-offs
Choosing a crucible material is not about finding a universally "best" option, but about balancing competing priorities for a specific task.
Speed vs. Heat Retention
A conductive crucible will melt its contents very quickly but will also begin to lose that heat rapidly once the energy source is removed.
An insulating crucible takes longer to bring the metal to its melting point but excels at holding the molten bath at a stable temperature for extended periods, which is crucial for some casting or alloying processes.
Chemical Compatibility and Durability
While thermal properties are primary, the crucible material must also be chemically inert to the metal being melted and durable enough to withstand the extreme thermal cycling of the process. This is a secondary, but still critical, consideration.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific objective dictates the optimal crucible material.
- If your primary focus is rapid melting cycles and energy efficiency: Choose a high-graphite or silicon carbide conductive crucible, especially when using an electric resistance or induction furnace.
- If your primary focus is holding molten metal at a stable temperature for casting or alloying: An insulating ceramic crucible is the superior choice for its ability to contain heat.
Selecting the correct crucible material is the critical first step toward achieving a controlled, safe, and efficient melting process.
Summary Table:
| Crucible Type | Material | Key Property | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conductive | Graphite, Silicon Carbide | High Thermal Conductivity | Rapid melting, energy efficiency in electric/induction furnaces |
| Insulating | Ceramic | Heat Containment | Holding stable temperatures for casting or alloying |
Need help selecting the perfect crucible for your lab's melting process?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including a full range of conductive and insulating crucibles designed for precision and durability. Whether you require fast melting cycles or stable heat retention, our experts can guide you to the ideal solution for your specific application and furnace type.
Contact us today to optimize your melting efficiency and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible for Laboratory Muffle Furnace
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- High Purity Pure Graphite Crucible for Evaporation
- Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible Semicircle Boat with Lid for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
People Also Ask
- What is a crucible material for a furnace? A Guide to Choosing the Right High-Temperature Container
- How does the use of corrosion-resistant ceramic crucibles ensure the chemical purity of materials? | KINTEK
- What is the function of an alumina crucible in NaSICON synthesis? Ensure Purity in High-Temperature Reactions
- Why use an alumina crucible in a stainless steel autoclave? Ensure Purity in Liquid Lead and LBE Exposure Experiments
- What is the temperature range of alumina crucibles? Key Factors for Safe High-Temp Use



















