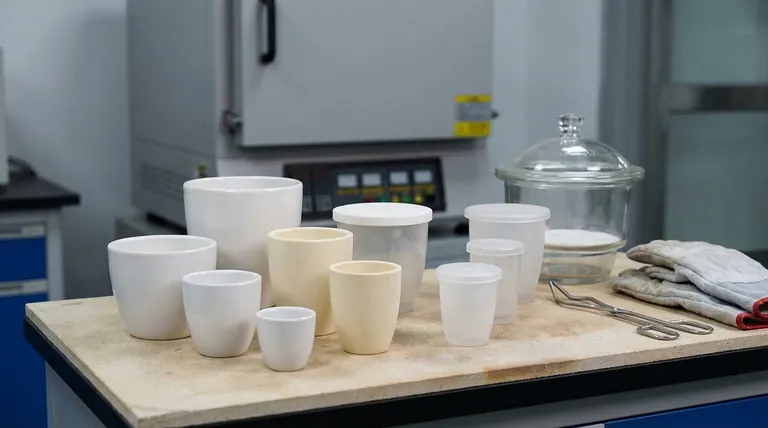
The most common crucibles used in a muffle furnace are made from ceramic materials, primarily porcelain and alumina (aluminum oxide). These materials are chosen for their ability to withstand the extremely high, uniform temperatures that muffle furnaces generate without melting, deforming, or reacting with most samples.
The selection of a crucible is not a one-size-fits-all decision. The ideal choice depends entirely on two factors: the chemical composition of your sample and the maximum temperature of your procedure, as choosing incorrectly can lead to sample contamination or crucible failure.

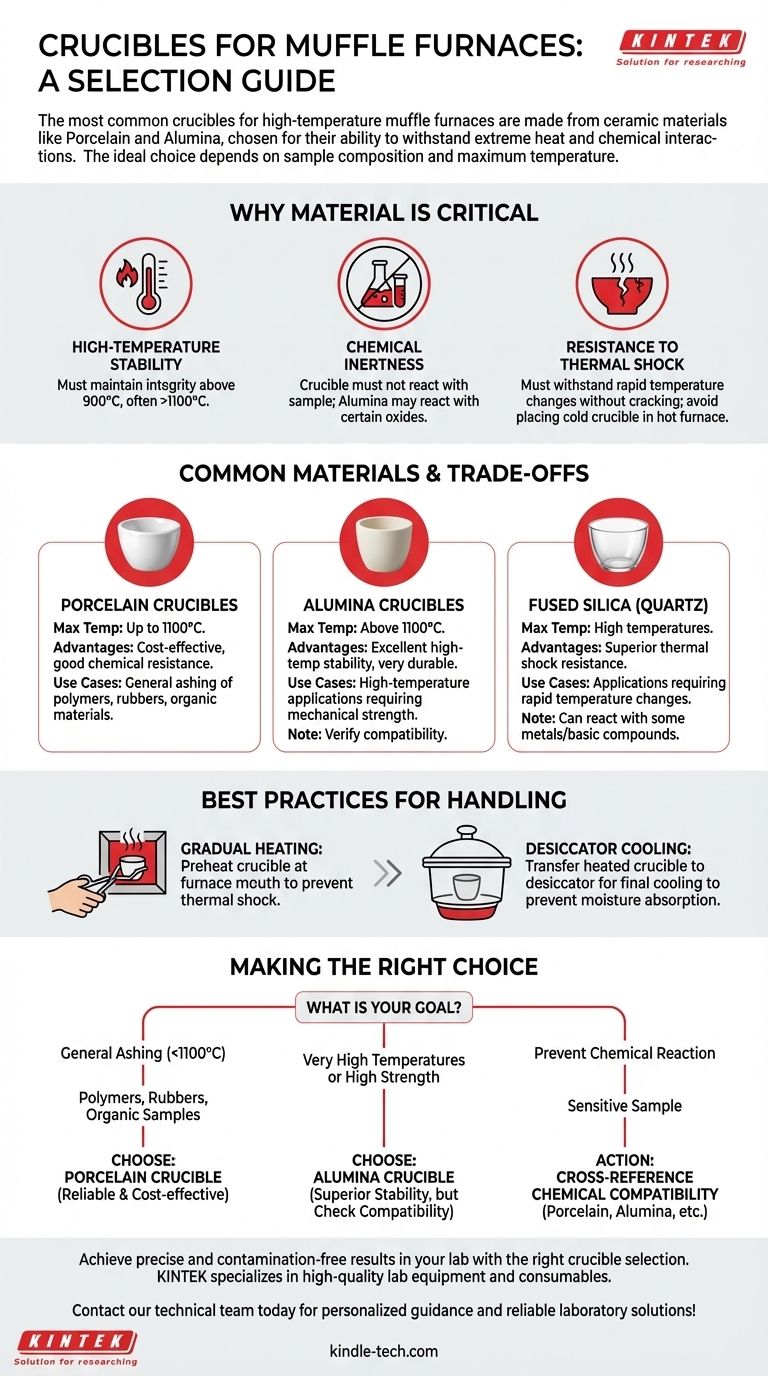
Why Crucible Material is the Critical Factor
A muffle furnace provides a highly controlled, high-temperature environment. The crucible is the vessel that contains your sample within this environment, making its material properties fundamental to the success of your work.
High-Temperature Stability
A muffle furnace's primary function is heating, often to temperatures of 900°C or higher for applications like ashing polymers and rubbers. The crucible must maintain its structural integrity well above the target temperature of your process.
Chemical Inertness
The crucible should be a neutral container that does not interact with your sample. This is the most common point of failure. As noted, alumina crucibles can react with certain materials, such as transition metal oxides or rare earth oxides, at high temperatures, which can contaminate your sample and ruin your results.
Resistance to Thermal Shock
Ceramic materials can crack or shatter if their temperature changes too rapidly—a phenomenon known as thermal shock. A quality crucible must be able to withstand the transition from room temperature to the furnace's intense heat and back again, with proper handling.
Understanding the Trade-offs of Common Materials
While many materials can be heated, only a few are suitable for containing samples inside a muffle furnace. Each comes with its own set of advantages and limitations.
Porcelain Crucibles
Porcelain is a cost-effective and widely used material for general-purpose laboratory work. It is excellent for determining the ash content of most organic materials and offers good resistance to many chemical reagents. Its primary limitation is a lower maximum operating temperature compared to more advanced ceramics.
Alumina Crucibles
For work requiring temperatures above 1100°C, alumina is a superior choice. It has excellent high-temperature stability and is very hard and durable. However, its potential to react with specific oxides means you must verify its compatibility with your sample material before use.
Fused Silica (Quartz) Crucibles
Fused silica is another high-temperature option known for its exceptional thermal shock resistance. You can heat it rapidly without the same level of risk as other ceramics. Its main drawback is that it can react with certain metals or basic compounds at elevated temperatures.
Best Practices for Crucible Handling
Proper handling is just as important as proper selection. Following these steps prevents crucible damage and ensures accurate results.
Gradual Temperature Changes
To prevent thermal shock, never place a room-temperature crucible directly into a hot furnace. Hold it at the mouth of the furnace for a few moments with crucible tongs to preheat it before placing it inside. Do the same when removing it to allow for gradual cooling.
Safe Post-Use Cooling
Once your process is complete, the heated crucible should be transferred to a desiccator for final cooling. This prevents the crucible and its contents from absorbing atmospheric moisture, which is critical for applications like gravimetric analysis where precise weight is required.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application dictates the correct crucible. Consider your primary objective to make a clear decision.
- If your primary focus is general ashing of polymers, rubbers, or organic samples below 1100°C: A standard porcelain crucible is the most reliable and cost-effective choice.
- If you are working at very high temperatures or require high mechanical strength: An alumina crucible is superior, provided you have confirmed it will not react with your sample.
- If you must prevent chemical reaction with a sensitive sample: Always cross-reference the chemical compatibility of your sample against porcelain, alumina, and other potential crucible materials before beginning your experiment.
Ultimately, selecting the correct crucible is a foundational step for achieving accurate and repeatable results in any high-temperature process.
Summary Table:
| Crucible Material | Max Temperature | Key Advantages | Primary Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Porcelain | Up to 1100°C | Cost-effective, good chemical resistance | General ashing of polymers, rubbers, organic materials |
| Alumina (Aluminum Oxide) | Above 1100°C | Excellent high-temp stability, durable | High-temperature applications requiring mechanical strength |
| Fused Silica (Quartz) | High temperatures | Superior thermal shock resistance | Applications requiring rapid temperature changes |
Achieve precise and contamination-free results in your lab with the right crucible selection. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including a full range of muffle furnace crucibles designed for durability and chemical inertness. Our experts can help you select the perfect crucible material for your specific application, ensuring optimal performance and accurate outcomes. Contact our technical team today for personalized guidance and to explore our reliable laboratory solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible for Laboratory Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- How do I choose a tube furnace? A Guide to Matching Your Process Needs
- Why is a horizontal alumina tube furnace ideal for mixed gas corrosion at 650 °C? Ensure Pure Experimental Integrity
- How do you clean a tube furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Cleaning
- What are the common applications for a tube furnace? Essential for Heat Treatment, Synthesis, and Purification
- What is the ceramic tube high temperature? From 1100°C to 1800°C, Choose the Right Material



















