At its core, a heat treatment furnace is a specialized industrial chamber engineered to modify the physical and mechanical properties of materials, typically steel. It achieves this by subjecting the material to a precisely controlled thermal cycle of heating and cooling, often within a carefully managed atmosphere to prevent unwanted chemical reactions like oxidation.
The crucial distinction of a modern heat treatment furnace is not just its ability to generate high temperatures, but its capacity to create and maintain an exceptionally controlled and stable environment. This precision in both temperature and atmosphere is what allows for the creation of components with specific, repeatable, and reliable properties.

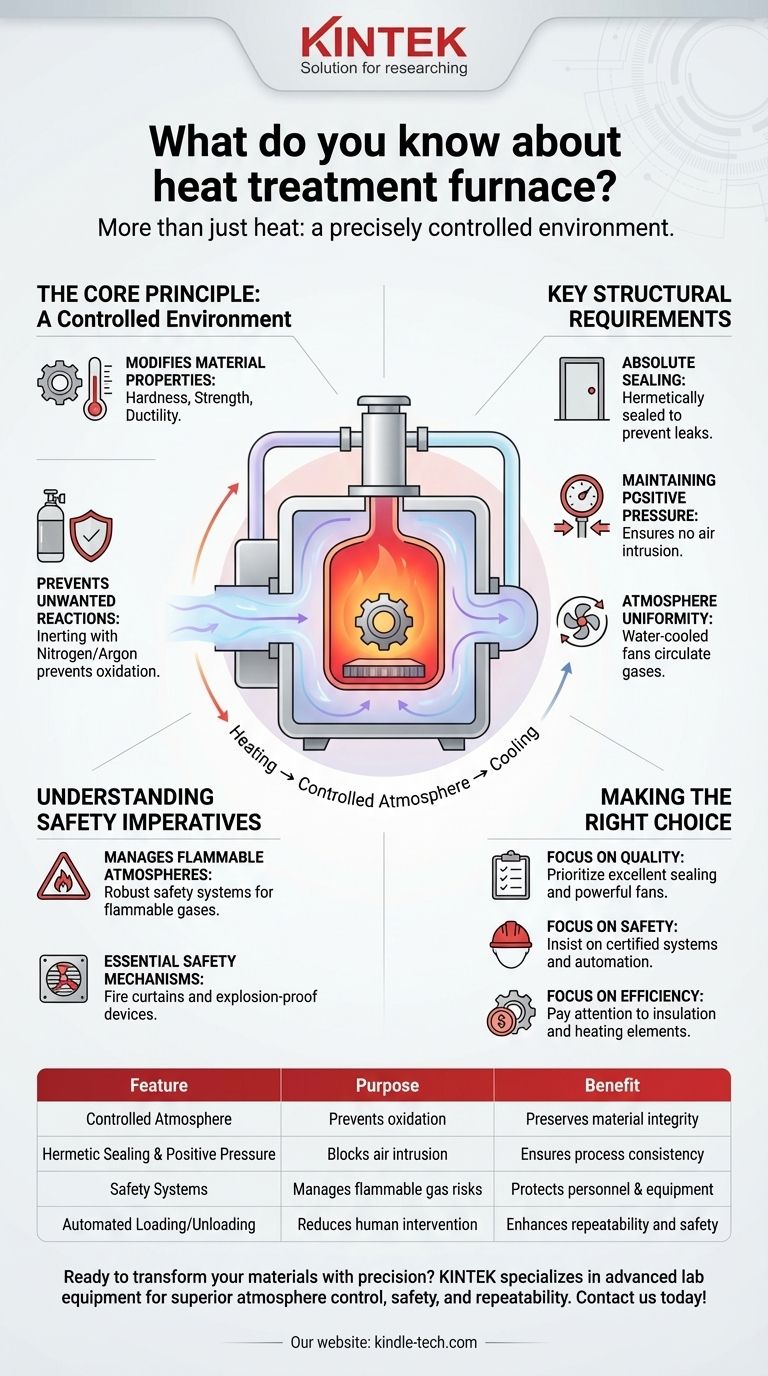
The Core Principle: A Controlled Environment, Not Just Heat
The fundamental purpose of heat treatment is to alter a material's microstructure to achieve desired characteristics like hardness, strength, or ductility. This requires far more than simple heating.
Beyond Simple Heating
A heat treatment furnace is not an ordinary oven. Its primary function is to execute a specific temperature profile over time to impart reproducible, useful properties to components.
Preventing Unwanted Reactions
At high temperatures, materials like steel react readily with oxygen in the air, forming a layer of scale or oxide on the surface. To prevent this, many heat treatment processes are conducted in a controlled atmosphere.
The Role of Inert Gases
A process known as inerting involves purging the furnace with a gas like nitrogen or argon. This displaces oxygen, water vapor, and any flammable gases, creating an inert environment that protects the component's surface integrity.
Key Structural Requirements for Atmosphere Control
To manage the internal environment effectively, these furnaces are built with specific design principles that set them apart from simpler heating equipment.
Absolute Sealing
The furnace body must be hermetically sealed to prevent the controlled atmosphere from leaking out and, more importantly, to stop outside air from leaking in.
Maintaining Positive Pressure
To further ensure no air intrusion, furnaces are operated at a slight positive pressure. This means the internal pressure is just above the external atmospheric pressure, so any potential leak would force gas out, not suck air in.
Ensuring Atmosphere Uniformity
To guarantee every part of the component receives the same treatment, the furnace atmosphere must be uniform. This is achieved with water-cooled, sealed fans that circulate the gases, eliminating hot spots or inconsistent gas composition.
Specialized Furnace Lining
The internal lining is constructed from materials like anti-carburizing or impermeable bricks. This prevents the lining itself from reacting with the controlled atmosphere, which could alter the gas chemistry and compromise the treatment process.
Isolated Heating Elements
Heating is often accomplished using large-section resistor boards or radiation tubes. This design allows the chamber to be heated without the electric heating elements coming into direct contact with the furnace's internal atmosphere.
Understanding the Safety Imperatives
The use of controlled, and sometimes combustible, atmospheres introduces significant safety considerations that must be engineered into the furnace's design.
The Inherent Risk of Flammable Atmospheres
Some heat treatment processes use atmospheres containing flammable gases. The risk of these gases mixing with air creates a potential for explosion, which must be managed through robust safety systems.
Essential Safety Mechanisms
Furnaces are equipped with fire curtains at openings and explosion-proof devices on the furnace body. In the event of an uncontrolled ignition, these devices are designed to safely vent the high-pressure wave, protecting personnel and the equipment from catastrophic failure.
The Need for Automation
Modern furnaces feature a high degree of mechanization and automation. Automated systems for loading, unloading, and process control not only ensure process repeatability but also minimize human exposure to high temperatures and hazardous atmospheres.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding these design principles allows you to focus on what matters most for your specific application.
- If your primary focus is process quality and repeatability: Prioritize features that ensure absolute atmosphere control, such as excellent sealing, positive pressure maintenance, and powerful circulation fans.
- If your primary focus is operational safety: Insist on certified and properly maintained safety systems, including explosion-proof vents, reliable purging cycles, and comprehensive automation.
- If your primary focus is efficiency and cost: Pay close attention to insulation quality, the minimization of door and port openings to reduce heat loss, and the efficiency of the heating elements.
Ultimately, a heat treatment furnace transforms a raw material into a high-performance component through the meticulous control of its internal environment.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Purpose | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Controlled Atmosphere | Prevents oxidation/scaling | Preserves material integrity |
| Hermetic Sealing & Positive Pressure | Blocks air intrusion | Ensures process consistency |
| Safety Systems (explosion-proof vents) | Manages flammable gas risks | Protects personnel and equipment |
| Automated Loading/Unloading | Reduces human intervention | Enhances repeatability and safety |
Ready to transform your materials with precision? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables, including heat treatment furnaces designed for superior atmosphere control, safety, and repeatability. Whether you need to enhance hardness, strength, or durability, our solutions ensure reliable results for your laboratory. Contact us today to discuss your specific heat treatment requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- How does a constant temperature drying oven facilitate the CBD process of a SnO2 ETL? Optimize Your Film Morphology
- How does a high-temperature sintering furnace improve NASICON electrolytes? Optimize Grain Boundary Conductivity
- What is done by ashing in muffle furnace? A Guide to Precise Inorganic Content Analysis
- What is the heat treatment process for steel? A Guide to Controlling Hardness, Toughness, and Performance
- What is the porosity of sintered ceramics? A Guide to Engineering Material Properties
- Why is a high-temperature muffle furnace necessary for NiO nanoparticle calcination? Master Precise Phase Control
- How do high-precision programmable temperature-controlled furnaces contribute to the evaluation of catalytic performance?
- Dry Ashing vs Wet Ashing: Which Method is Best for Your Sample Analysis?



















