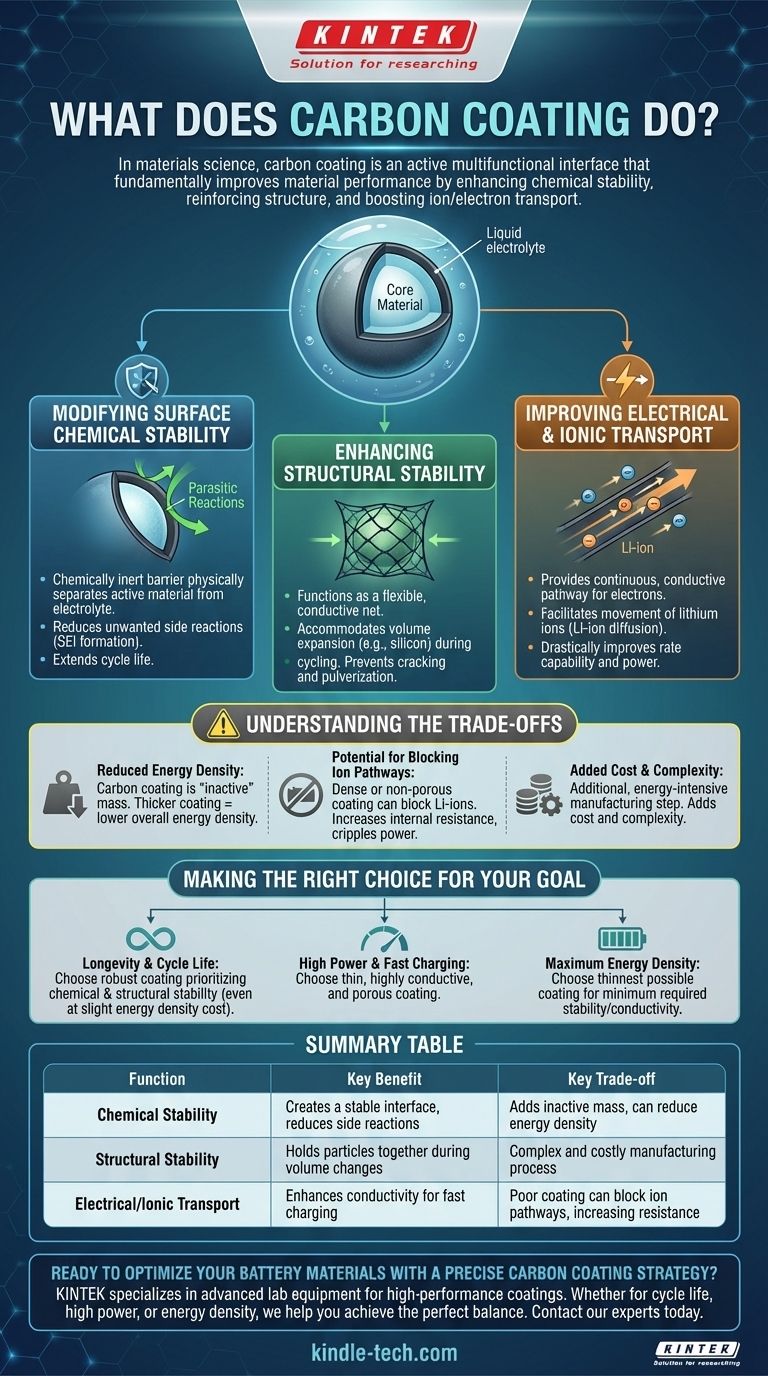
In materials science, a carbon coating is not merely a passive layer but an active component designed to solve several fundamental problems at once. It fundamentally improves a material's performance by enhancing its chemical stability, reinforcing its physical structure, and boosting its ability to transport ions and electrons.
A carbon coating acts as a multifunctional interface. It simultaneously protects the core material from unwanted chemical reactions, holds it together during physical stress, and creates a conductive highway for energy transfer, but its benefits must be balanced against its inherent trade-offs.
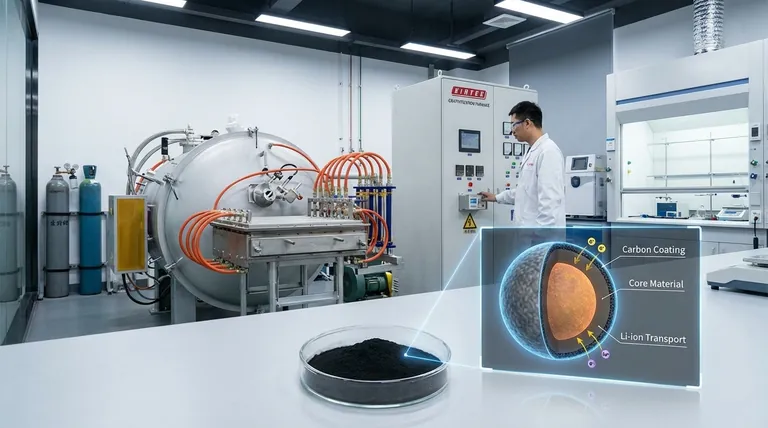

The Core Functions of a Carbon Coating
At its heart, carbon coating is a strategy to compensate for the inherent weaknesses of many high-performance materials, particularly within batteries. It addresses three critical areas.
Modifying Surface Chemical Stability
Many advanced electrode materials are highly reactive with the liquid electrolyte inside a battery.
This reactivity leads to unwanted side reactions, forming an unstable layer known as the Solid Electrolyte Interphase (SEI). An unstable SEI consumes active lithium and degrades battery life.
A carbon coating acts as a chemically inert barrier, physically separating the active material from the electrolyte. This creates a more stable and controlled interface, dramatically reducing parasitic reactions and extending the material's cycle life.
Enhancing Structural Stability
Certain high-capacity materials, like silicon or metal oxides, undergo massive volume expansion and contraction during charging and discharging.
This repeated stress can cause the material particles to crack, pulverize, and lose electrical contact with the rest of the electrode, leading to rapid capacity fade.
The carbon coating functions like a flexible, conductive net. It mechanically holds the particles together, accommodates the volume changes, and ensures the electrical pathways remain intact even after hundreds of cycles.
Improving Electrical and Ionic Transport
Many promising battery materials are poor electrical conductors, essentially acting as insulators. This limits how quickly a battery can charge and discharge.
Carbon, in forms like amorphous carbon or graphite, is an excellent electrical conductor. The coating provides a continuous, conductive pathway for electrons to reach the active material, drastically improving the rate capability, or power output.
Furthermore, a well-designed porous carbon coating can facilitate the movement of lithium ions (Li-ion diffusion) from the electrolyte to the surface of the active material, ensuring the entire particle is utilized efficiently.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, applying a carbon coating is a delicate balancing act with clear downsides if implemented incorrectly.
Reduced Energy Density
The carbon coating itself does not store energy. It is considered an "inactive" component.
Every bit of mass dedicated to the coating is mass that is not being used by the "active" energy-storing material. An overly thick coating will increase stability but will reduce the battery's overall energy density (the amount of energy stored per unit of weight or volume).
Potential for Blocking Ion Pathways
The primary goal is to improve performance, but a poor coating can do the opposite.
If the carbon layer is too dense or non-porous, it can act as a barrier that physically blocks lithium ions from reaching the active material. This increases internal resistance and cripples the battery's power performance.
Added Cost and Complexity
Applying a uniform, high-quality carbon coating is an additional, energy-intensive step in the manufacturing process.
This inevitably adds cost and complexity, which must be justified by a significant improvement in performance and lifespan.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The ideal carbon coating strategy depends entirely on the primary performance target for the material.
- If your primary focus is longevity and cycle life: A robust coating that prioritizes chemical and structural stability is the correct choice, even at a slight cost to energy density.
- If your primary focus is high power and fast charging: The key is a thin, highly conductive, and porous coating that maximizes electron and ion transport.
- If your primary focus is maximum energy density: You must use the thinnest possible coating that still provides the minimum required stability and conductivity to avoid excessive "dead weight."
Ultimately, carbon coating is a powerful tool for unlocking the potential of next-generation materials by turning their inherent weaknesses into strengths.
Summary Table:
| Function | Key Benefit | Key Trade-off |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Stability | Creates a stable interface, reduces side reactions | Adds inactive mass, can reduce energy density |
| Structural Stability | Holds particles together during volume changes | Complex and costly manufacturing process |
| Electrical/Ionic Transport | Enhances conductivity for fast charging/discharging | Poor coating can block ion pathways, increasing resistance |
Ready to optimize your battery materials with a precise carbon coating strategy?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables needed for developing and testing high-performance coatings. Whether your goal is maximizing cycle life, achieving high power, or optimizing energy density, our solutions can help you achieve the perfect balance.
Contact our experts today via our Contact Form to discuss how we can support your research and development in materials science.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is synthetic graphite manufactured? A Deep Dive into the High-Temperature Process
- What is the maximum working temperature of graphite? Unlock High-Temp Performance with the Right Atmosphere
- Can graphite withstand high-temperature? Maximizing Performance in Controlled Atmospheres
- Is graphite affected by heat? Discover Its Remarkable Strength and Stability at High Temperatures
- Is graphite good for high temperature? Unlock Its Full Potential in Controlled Atmospheres



















