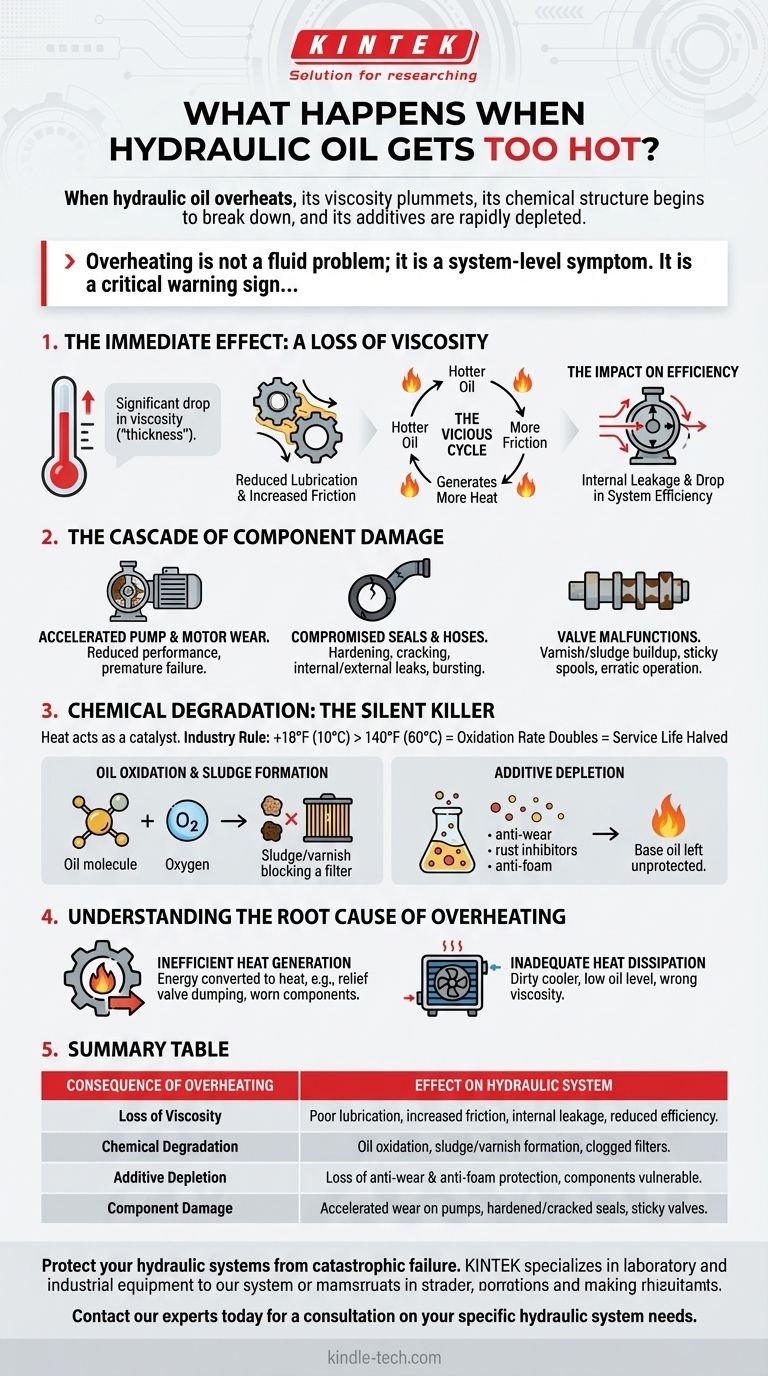
When hydraulic oil overheats, its viscosity plummets, its chemical structure begins to break down, and its additives are rapidly depleted. This triple threat compromises the system's ability to lubricate parts and transmit power, leading to a cascade of accelerated wear on pumps, seals, and valves that can culminate in catastrophic failure.
Overheating is not a fluid problem; it is a system-level symptom. It is a critical warning sign that your hydraulic system is either generating excessive heat through inefficiency or failing to dissipate the heat it is designed to produce.

The Immediate Effect: A Loss of Viscosity
The most direct and immediate consequence of overheating hydraulic oil is a significant drop in viscosity. Viscosity is a measure of the oil's resistance to flow—its "thickness."
Why Viscosity is Critical
Proper viscosity is essential for maintaining a protective film of oil between moving metal surfaces. This film prevents direct metal-on-metal contact, which is the primary cause of wear in hydraulic components.
The Vicious Cycle of Low Viscosity
As the oil thins, its ability to lubricate diminishes. This allows for more friction between parts, which in turn generates even more heat. This creates a dangerous feedback loop where hotter oil leads to more friction, which leads to even hotter oil, accelerating wear exponentially.
The Impact on Efficiency
Thinner oil is more likely to leak past the tight clearances in pumps, motors, and cylinders. This internal leakage means the component must work harder (and generate more heat) to produce the same amount of output, causing a significant drop in overall system efficiency.
The Cascade of Component Damage
This loss of viscosity and chemical integrity triggers a system-wide decline in health, directly damaging expensive components.
Accelerated Pump and Motor Wear
Pumps and motors are typically the most expensive and critical components. Without an adequate lubricating film, the precision-machined surfaces inside will wear down rapidly, reducing performance and leading to premature failure.
Compromised Seals and Hoses
Excessive heat hardens and cracks elastomeric seals. This loss of flexibility prevents them from sealing effectively, causing both internal and external leaks. Hoses are also susceptible to heat damage, which can lead to bursting under pressure.
Valve Malfunctions
The chemical breakdown of hot oil creates varnish and sludge. These deposits can coat the inside of control valves, causing spools to stick or respond sluggishly. This leads to erratic machine operation and loss of control.
Chemical Degradation: The Silent Killer
Beyond the physical thinning, heat acts as a catalyst for destructive chemical reactions within the oil. The industry rule of thumb is that for every 18°F (10°C) increase above 140°F (60°C), the oxidation rate of the oil doubles, effectively halving its service life.
Oil Oxidation and Sludge Formation
Oxidation is the reaction of oil molecules with oxygen, a process massively accelerated by heat. It creates insoluble byproducts that form sludge, which can block filters, and varnish, which coats internal surfaces and acts as an insulator, further trapping heat.
Additive Depletion
Hydraulic oil is fortified with a package of additives, including anti-wear agents, rust inhibitors, and anti-foam agents. High temperatures cause these additives to "burn out" and deplete far more quickly, leaving the base oil unprotected and unable to perform its critical functions.
Understanding the Root Cause of Overheating
Treating overheated oil with a larger cooler without understanding the cause is treating a symptom, not the disease. The heat comes from one of two sources: inefficiency in the system or a failure to remove heat.
Inefficient Heat Generation
This occurs when hydraulic energy is converted to heat instead of doing useful work. Common causes include a relief valve constantly dumping pressure, a pump operating far from its peak efficiency, or excessive internal leakage in worn components.
Inadequate Heat Dissipation
This occurs when the system cannot get rid of the heat it normally generates. Common culprits are a dirty or blocked oil cooler, a cooler that is undersized for the application, low oil level in the reservoir, or using an oil with the wrong viscosity grade for the ambient conditions.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Moving from diagnosis to action requires a clear understanding of your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is preventative maintenance: Regularly monitor fluid temperature and conduct periodic oil analysis to detect increased oxidation and additive depletion before they cause component damage.
- If your primary focus is troubleshooting an existing overheating problem: First, confirm the heat dissipation system is working correctly (clean cooler, correct reservoir level) before investigating inefficient heat generation from components like relief valves or worn pumps.
- If your primary focus is designing or modifying a system: Ensure your heat-load calculations are accurate and size your reservoir and cooling circuit with a sufficient safety margin to handle the worst-case operating conditions.
Ultimately, treating your hydraulic fluid's temperature as a primary vital sign is the key to ensuring long-term system reliability and performance.
Summary Table:
| Consequence of Overheating | Effect on Hydraulic System |
|---|---|
| Loss of Viscosity | Poor lubrication, increased friction, internal leakage, and reduced efficiency. |
| Chemical Degradation | Oil oxidation, sludge/varnish formation, and clogged filters. |
| Additive Depletion | Loss of anti-wear and anti-foam protection, leaving components vulnerable. |
| Component Damage | Accelerated wear on pumps, hardened/cracked seals, and sticky valves. |
Protect your hydraulic systems from catastrophic failure. Overheating is a major cause of unplanned downtime and expensive repairs. KINTEK specializes in laboratory and industrial equipment, providing the expertise and solutions to maintain your system's health. Our team can help you select the right fluids and implement monitoring strategies to extend equipment life and maximize performance.
Contact our experts today for a consultation on your specific hydraulic system needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Manual Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Manual Lab Heat Press
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Integrated Manual Heated Plates for Lab Use
- Hydraulic Diaphragm Lab Filter Press for Laboratory Filtration
- Oil Free Diaphragm Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- What is a hydraulic hot press? Unlock the Power of Heat and Pressure for Advanced Materials
- What is the role of a hydraulic press with heating plates in copper welding tests? Analyze Stress & Thermal Cycles
- Does a hydraulic press have heat? How Heated Platens Unlock Advanced Molding and Curing
- What is the purpose of using a laboratory hydraulic press for LGVO synthesis? Achieve High-Purity Solid Electrolytes
- What is a hydraulic hot press machine? A Guide to Force and Heat for Material Transformation
















