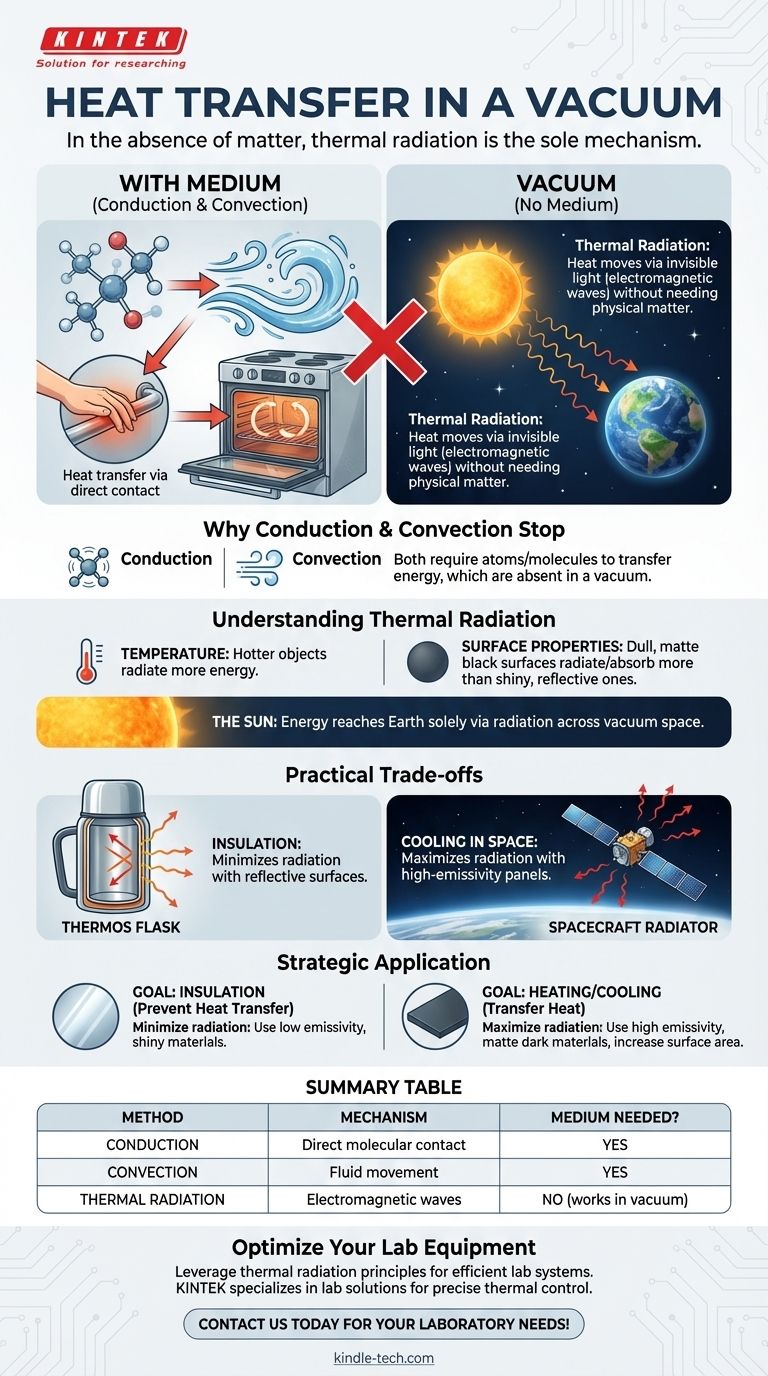
In the absence of matter, heat transfer occurs exclusively through a process called thermal radiation. Unlike conduction or convection, which require a physical medium to transfer energy, radiation moves energy through electromagnetic waves. This is precisely how the sun's warmth travels across the vast vacuum of space to reach Earth.
While we intuitively think of heat transfer through touch (conduction) or moving air (convection), a vacuum eliminates these pathways. This leaves only thermal radiation—the transfer of energy via invisible light—as the sole mechanism for heat to move between objects.

Why Conduction and Convection Stop
The Need for a Medium
Conduction is the transfer of heat through direct molecular contact. Imagine a hot pan handle; the heat travels from one molecule to the next along the metal.
Convection is the transfer of heat through the movement of fluids (gases or liquids). A convection oven, for example, uses a fan to circulate hot air, which then transfers its heat to the food.
A Vacuum's Defining Trait
Both of these methods fundamentally rely on the presence of atoms and molecules to carry the energy. A vacuum, by definition, is a space largely devoid of matter.
Without a medium, there are no molecules to vibrate against each other (for conduction) or to form currents (for convection). Both processes simply cannot occur.
Understanding Thermal Radiation
Heat as an Electromagnetic Wave
Every object with a temperature above absolute zero (-273.15°C or 0K) constantly emits energy in the form of electromagnetic waves. This is thermal radiation.
For most objects we encounter, this radiation is primarily in the infrared part of the spectrum, which is invisible to the human eye but can be felt as heat.
Key Factors in Radiative Transfer
The rate of heat transfer through radiation is governed by two main factors: temperature and surface properties.
A hotter object radiates significantly more energy than a cooler one. Furthermore, a dull, matte black surface will both radiate and absorb heat far more effectively than a shiny, reflective one.
The Ultimate Example: The Sun
The vacuum of space between the sun and Earth is roughly 150 million kilometers. Conduction and convection are impossible across this distance.
The sun’s immense energy reaches us entirely as radiation, demonstrating the power of this heat transfer mechanism.
Understanding the Practical Trade-offs
The Power of Insulation: The Thermos Flask
A thermos is a perfect real-world application of this principle. It consists of two walls separated by a vacuum.
This vacuum layer almost completely stops heat transfer by conduction and convection. The inner walls are also silvered (shiny and reflective) to minimize heat loss or gain from radiation, keeping your drink hot or cold for hours.
The Challenge of Cooling in Space
Getting rid of heat is a critical engineering challenge for spacecraft and satellites. Since there is no air to carry heat away, they cannot use fans for cooling.
Instead, they must rely on large panels called radiators. These are designed with high-emissivity surfaces to efficiently radiate waste heat out into the cold vacuum of space. The size and efficiency of these radiators are often a limiting factor in spacecraft design.
Slower, but Inescapable
In many Earth-based industrial processes, forced convection (using fans or pumps) is a much faster way to heat or cool something than radiation alone.
However, radiation is always present. Even in a room full of air, a hot object is still radiating heat to the cooler objects around it, in addition to heating the air via convection.
Applying This to Your Goal
Understanding how heat behaves in a vacuum is key to designing effective thermal systems. Your strategy will depend entirely on whether you want to contain heat or transfer it.
- If your primary focus is insulation (preventing heat transfer): Your goal is to minimize radiation by using surfaces with low emissivity, such as shiny, reflective materials.
- If your primary focus is heating or cooling an object in a vacuum: Your goal is to maximize radiation by using surfaces with high emissivity, like matte, dark-colored materials, and increasing the object's surface area.
Mastering this single principle of radiative transfer is the foundation for engineering everything from a simple thermos to a deep-space satellite.
Summary Table:
| Heat Transfer Method | Mechanism | Requires a Medium? |
|---|---|---|
| Conduction | Transfer through direct molecular contact | Yes |
| Convection | Transfer through movement of fluids (gas/liquid) | Yes |
| Thermal Radiation | Transfer via electromagnetic waves | No (works in vacuum) |
Need to Optimize Heat Transfer in Your Lab Equipment?
Understanding thermal radiation is crucial for designing efficient lab systems, whether you're working with vacuum furnaces, thermal insulation, or specialized heating applications. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing solutions that leverage these principles for superior performance and reliability.
Let our experts help you achieve precise thermal control—contact us today to discuss your specific laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What materials are used in a vacuum furnace? Selecting the Right Hot Zone for Your Process
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- What is a vacuum furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Contamination-Free Thermal Processing
- How to vacuum out a furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe DIY Maintenance
- What is the leak rate for a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Purity and Repeatability



















