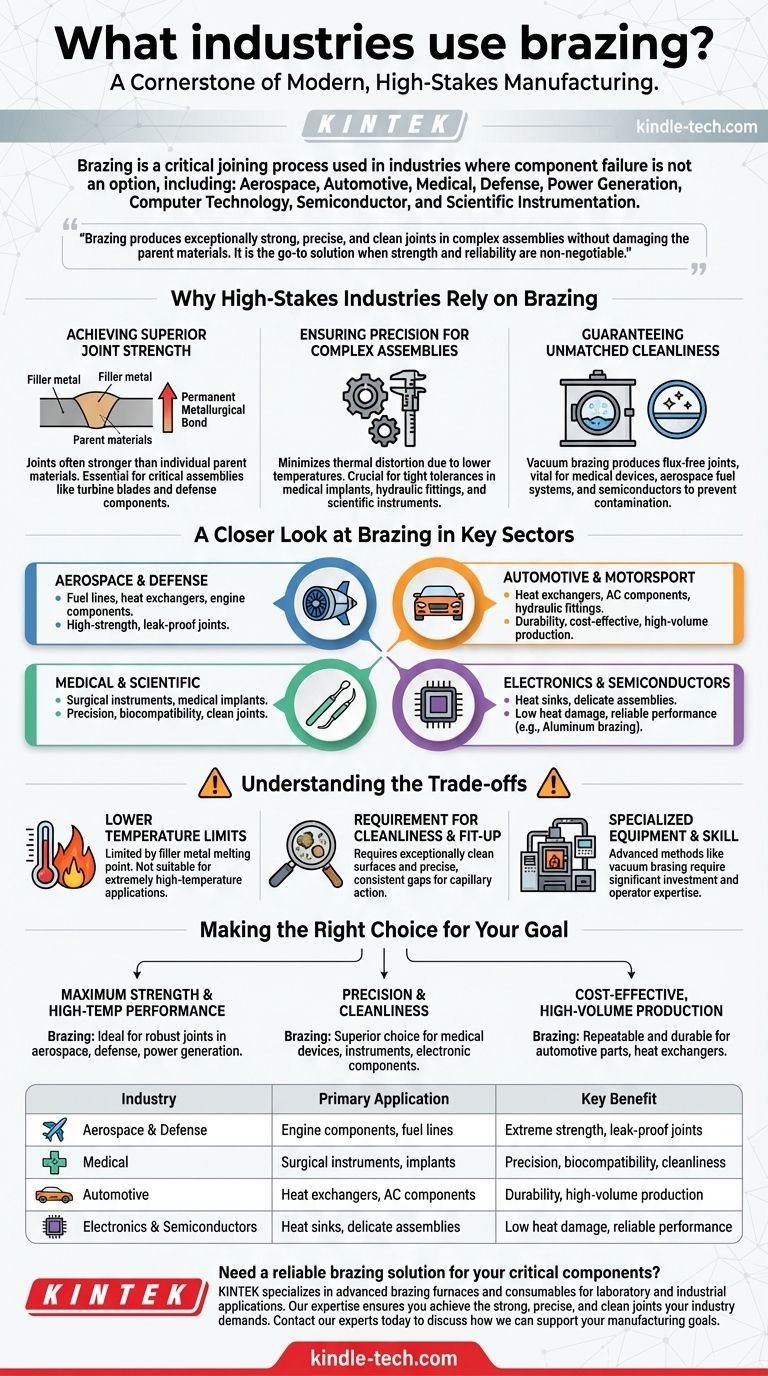
Brazing is a cornerstone of modern, high-stakes manufacturing. It is a critical joining process used extensively in industries where component failure is not an option, including aerospace, automotive, medical, defense, and power generation. Other significant sectors that rely on brazing include computer technology, semiconductor manufacturing, and scientific instrumentation.
The core reason these demanding industries choose brazing is its unique ability to produce exceptionally strong, precise, and clean joints in complex assemblies without damaging the parent materials. It is the go-to solution when strength and reliability are non-negotiable.
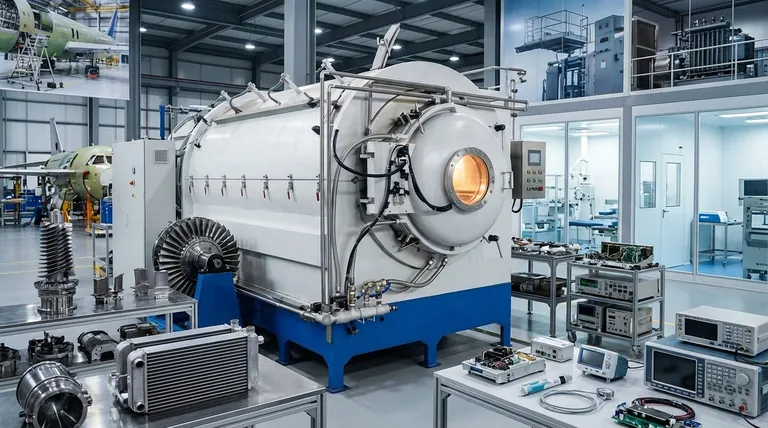

Why High-Stakes Industries Rely on Brazing
Brazing is not just an alternative to welding; it is a specialized solution chosen for specific engineering advantages. The process involves melting a filler metal that is drawn into a joint via capillary action, creating a powerful metallurgical bond well below the melting point of the components being joined.
Achieving Superior Joint Strength
Brazing creates a permanent, high-strength metallurgical bond. The resulting joint is often stronger than the individual parent materials themselves.
This level of integrity is essential for parts like turbine blades in a jet engine or critical assemblies in defense applications, where the joint must withstand extreme stress.
Ensuring Precision for Complex Assemblies
Because brazing occurs at lower temperatures than welding, it minimizes the risk of thermal distortion.
This is crucial for manufacturing intricate parts with tight tolerances, such as medical implants, hydraulic fittings, or components for scientific instruments, where even minor warping would lead to failure.
Guaranteeing Unmatched Cleanliness
Processes like vacuum brazing produce exceptionally clean, flux-free joints. This is a non-negotiable requirement in many advanced applications.
For medical devices, aerospace fuel systems, or semiconductor manufacturing equipment, any contamination or residue within the joint could have catastrophic consequences.
A Closer Look at Brazing in Key Sectors
The unique benefits of brazing make it the ideal choice for specific challenges across various industries.
Aerospace and Defense
In aerospace and defense, components must perform flawlessly under extreme temperatures and pressures. Brazing is used to manufacture fuel lines, heat exchangers, and engine components that require high-strength, leak-proof joints.
Automotive and Motorsport
The automotive industry uses brazing for both durability and cost-effective, high-volume production. It's essential for creating parts like heat exchangers, air conditioning components, and hydraulic fittings that must withstand constant vibration and thermal cycling.
Medical and Scientific
The medical field demands absolute precision and biocompatibility. Brazing is used to assemble surgical instruments and medical implants where clean, strong, and smooth joints are critical to performance and patient safety.
Electronics and Semiconductors
In electronics, brazing is used to join delicate components without causing heat damage. Aluminum brazing, for example, is vital for manufacturing heat sinks and other parts for the semiconductor and computer technology industries.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, brazing is a specific tool for specific jobs, and it's important to understand its operational requirements.
Lower Temperature Limits than Welding
A brazed joint's maximum service temperature is limited by the melting point of the filler metal. For applications requiring performance at extremely high temperatures, a welded joint may be more suitable.
Requirement for Cleanliness and Fit-Up
Brazing relies on capillary action to draw the filler metal into the joint. This process demands that component surfaces be exceptionally clean and that the gap between them (the fit-up) is precise and consistent.
Specialized Equipment and Skill
Advanced methods like vacuum brazing require a significant investment in specialized furnaces and a high level of operator skill. This makes it less accessible for low-volume or general-purpose fabrication compared to other joining methods.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use brazing is driven by the specific demands of the final component.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and high-temperature performance: Brazing is ideal for creating robust, reliable joints in critical components for the aerospace, defense, and power generation sectors.
- If your primary focus is precision and cleanliness: Brazing is the superior choice for medical devices, scientific instruments, and electronic components where thermal distortion and contamination must be avoided.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective, high-volume production: Brazing provides a repeatable and durable method for manufacturing parts like automotive components and heat exchangers.
Ultimately, brazing is the engineering solution for joining materials when strength, precision, and reliability cannot be compromised.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Primary Application | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Aerospace & Defense | Engine components, fuel lines | Extreme strength, leak-proof joints |
| Medical | Surgical instruments, implants | Precision, biocompatibility, cleanliness |
| Automotive | Heat exchangers, AC components | Durability, high-volume production |
| Electronics & Semiconductors | Heat sinks, delicate assemblies | Low heat damage, reliable performance |
Need a reliable brazing solution for your critical components? KINTEK specializes in advanced brazing furnaces and consumables for laboratory and industrial applications. Our expertise ensures you achieve the strong, precise, and clean joints your industry demands. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your manufacturing goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- What is a vacuum furnace used for? Unlock Purity in High-Temperature Processing
- What are vacuum furnaces used for? Unlock Ultimate Material Purity and Performance
- What is the cost of a vacuum brazing furnace? A guide to key factors and investment strategy
- What is brazing in heat treatment? Achieve Superior Joint Quality and Efficiency
- What are the different types of brazing welding? A Guide to Choosing the Right Heat Source



















