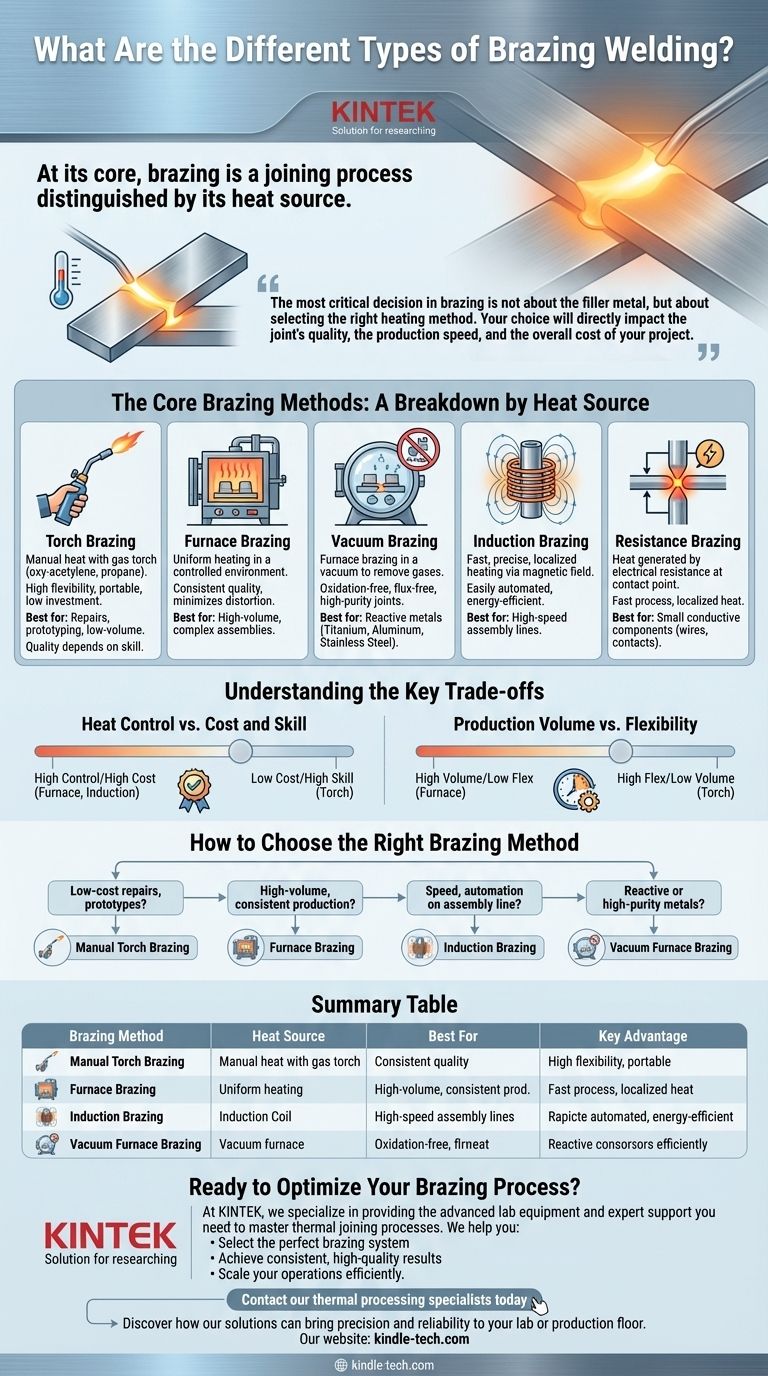
At its core, brazing is a joining process distinguished by its heat source. While often confused with welding, brazing joins metals using a filler metal that melts at a lower temperature than the base materials, allowing for strong bonds without melting the parts themselves. The primary types of brazing are defined by the method used to apply this heat, including torch, furnace, induction, and resistance brazing.
The most critical decision in brazing is not about the filler metal, but about selecting the right heating method. Your choice will directly impact the joint's quality, the production speed, and the overall cost of your project.

The Core Brazing Methods: A Breakdown by Heat Source
Brazing methods are almost always categorized by how they generate and apply heat. Each approach offers a unique profile of speed, cost, precision, and suitability for different materials and production volumes.
Torch Brazing
This is the most common and versatile form of brazing. It involves using a gas-fueled torch (like oxy-acetylene or propane) to manually heat the parts and melt the filler alloy into the joint.
It is highly portable and requires a low initial investment, making it ideal for repairs, prototyping, and low-volume production. However, quality is highly dependent on operator skill.
Furnace Brazing
In furnace brazing, the components (with the filler metal pre-placed) are loaded into a high-temperature furnace. The entire assembly is heated uniformly in a controlled environment to the brazing temperature.
This method is perfect for high-volume production of complex assemblies, as it produces consistent, high-quality joints with minimal distortion. It ensures that even hard-to-reach joints are heated evenly.
Vacuum Brazing
Vacuum brazing is a specialized type of furnace brazing. The process takes place inside a vacuum, which removes oxygen and other gases that could contaminate or oxidize the metals.
This is essential for joining reactive metals like titanium, aluminum, and stainless steels, as well as for creating a clean, flux-free joint. It is a standard in the aerospace, medical, and semiconductor industries.
Induction Brazing
This method uses an alternating magnetic field generated by an induction coil to heat the conductive metal parts. The heating is extremely fast, precise, and localized to the joint area.
Induction brazing is easily automated and highly repeatable, making it a top choice for high-speed assembly lines. It is also energy-efficient, as it only heats the portion of the part that needs to be joined.
Resistance Brazing
Resistance brazing generates heat using the electrical resistance of the joint as current passes through it, typically via carbon electrodes. The heat is concentrated at the point of contact.
It is a fast process suitable for joining small, highly conductive components. It is commonly used for attaching electrical contacts and wires where localized heating is critical.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
Choosing a brazing method involves balancing competing priorities. Understanding these trade-offs is crucial for making an informed decision that aligns with your technical and business goals.
Heat Control vs. Cost and Skill
Precise heat control is the single most important factor for a quality braze joint.
Furnace and induction brazing offer exceptional, automated control but come with high capital costs. Torch brazing is inexpensive but places the responsibility for heat management entirely on a skilled operator.
Production Volume vs. Flexibility
Your required output dictates your choice. Furnace brazing is built for mass production of identical parts but is very inefficient for one-off jobs due to long heating and cooling cycles.
Torch brazing offers maximum flexibility for unique repairs or prototypes but cannot match the speed and repeatability of automated methods for large volumes.
Material and Atmosphere Purity
The base materials you are joining can immediately disqualify certain methods. Many high-strength alloys and reactive metals will be weakened or damaged by exposure to oxygen at high temperatures.
For these materials, torch brazing is not an option. A controlled atmosphere is required, making furnace brazing in a vacuum or with an inert gas (like nitrogen or argon) the only viable choice.
How to Choose the Right Brazing Method
Your specific application and goals will point you to the correct method. Use these guidelines to narrow your options.
- If your primary focus is low-cost repairs or one-off prototypes: Manual torch brazing offers the best combination of flexibility and low initial investment.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, consistent production: Furnace brazing is the industry standard for creating reliable joints on a massive scale.
- If your primary focus is speed and automation on an assembly line: Induction brazing provides unmatched speed and precise, repeatable localized heating.
- If your primary focus is joining reactive or high-purity metals (e.g., titanium, stainless steel): Vacuum furnace brazing is non-negotiable to prevent oxidation and ensure joint integrity.
Ultimately, mastering the selection of your heat source is the most critical step toward a successful brazing operation.
Summary Table:
| Brazing Method | Heat Source | Best For | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Torch Brazing | Gas-fueled torch | Repairs, prototyping, low-volume | Low cost, high flexibility |
| Furnace Brazing | Controlled furnace | High-volume, complex assemblies | Consistent quality, uniform heating |
| Vacuum Brazing | Vacuum furnace | Reactive metals (titanium, stainless steel) | Oxidation-free, high-purity joints |
| Induction Brazing | Electromagnetic induction | Automated assembly lines | Fast, precise, localized heating |
| Resistance Brazing | Electrical resistance | Small conductive components | Localized heat, fast process |
Ready to Optimize Your Brazing Process?
Choosing the right brazing method is critical for achieving strong, reliable joints in your metal components. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the advanced lab equipment and expert support you need to master thermal joining processes.
We help you:
- Select the perfect brazing system for your specific materials and production volume
- Achieve consistent, high-quality results with precise temperature control and atmosphere management
- Scale your operations efficiently from prototyping to high-volume production
Whether you're working with reactive alloys or need automated solutions, KINTEK has the equipment and expertise to elevate your brazing capabilities.
Contact our thermal processing specialists today to discuss your project requirements and discover how our solutions can bring precision and reliability to your lab or production floor.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is vacuum brazing? The Ultimate Guide to High-Purity, Flux-Free Metal Joining
- What is a vacuum furnace used for? Unlock Purity in High-Temperature Processing
- What are vacuum furnaces used for? Unlock Ultimate Material Purity and Performance
- What is the difference between welding and vacuum brazing? Choose the Right Joining Method for Your Project
- What is brazing in heat treatment? Achieve Superior Joint Quality and Efficiency



















