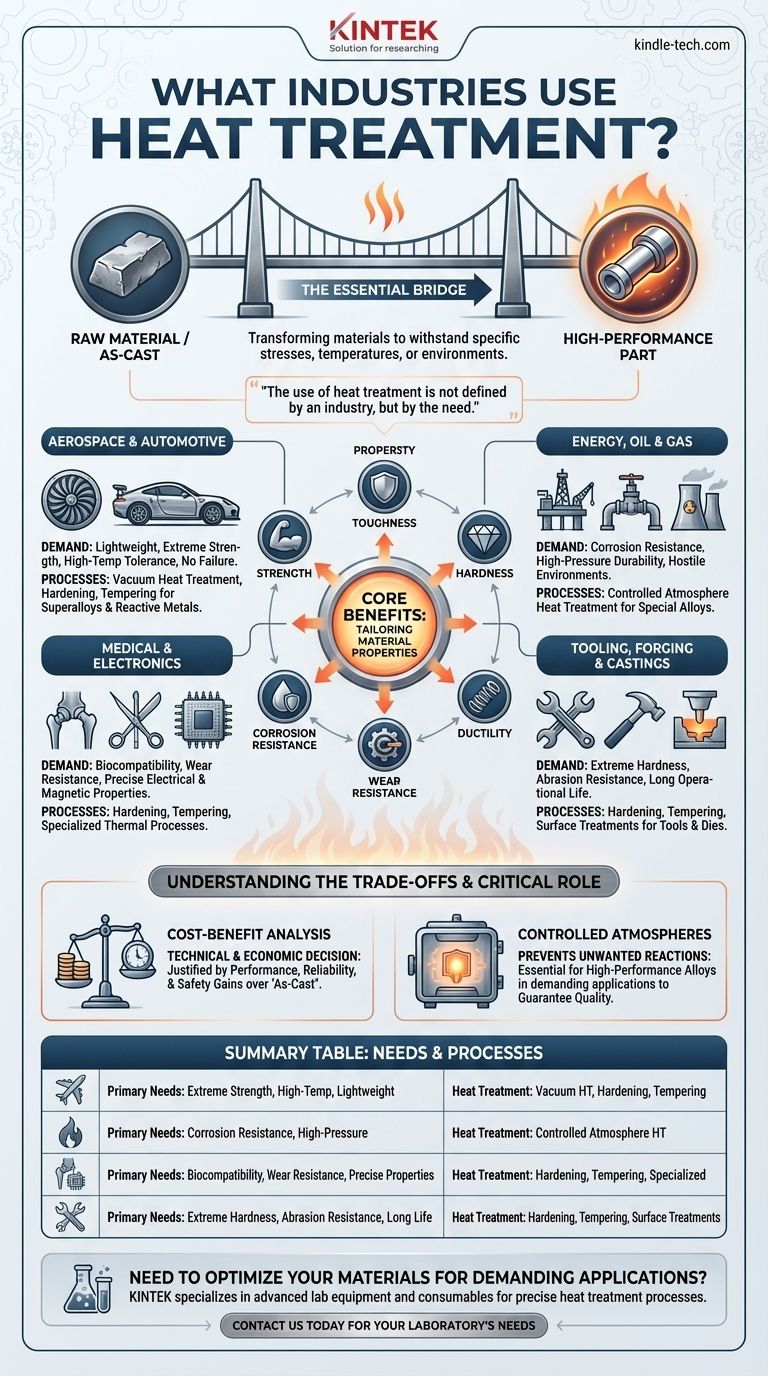
At its core, heat treatment is a fundamental process used across nearly every major industrial sector that works with metals. This includes aerospace, automotive, energy, oil and gas, medical, military, and electronics, where the precise control of a material's properties is critical for performance and safety.
The use of heat treatment is not defined by an industry, but by the need. It is the essential bridge between a raw material and a final component that can withstand specific stresses, temperatures, or corrosive environments.

Why Heat Treatment is a Critical Manufacturing Step
Heat treatment is a group of controlled heating and cooling processes used to intentionally alter the physical, and sometimes chemical, properties of a material. The goal is to change the material's internal crystalline structure, known as its microstructure.
Tailoring Material Properties
By manipulating the microstructure, manufacturers can precisely dial in desired characteristics. This allows them to enhance a material's strength, toughness, hardness, ductility, or wear resistance to meet the exact demands of an application.
From Raw Material to Finished Component
A metal component straight from a forge or a casting mold often does not have the optimal properties for its end use. Heat treatment is the crucial post-processing step that transforms it into a reliable, high-performance part.
A Closer Look at Key Industries and Their Needs
Different industries leverage heat treatment to solve very specific engineering challenges. The process is chosen based on the material and the environment the final part will operate in.
Aerospace and Automotive
These sectors demand materials that are both lightweight and incredibly strong, with an absolute intolerance for failure. Components like turbine blades, landing gear, and engine parts must withstand extreme stress and high temperatures.
Processes like vacuum heat treatment are essential here. They allow for the precise treatment of high-performance superalloys (like iron-nickel or cobalt-nickel) and reactive metals (like titanium) without introducing impurities that could compromise the part's integrity.
Energy, Petrochemical, and Oil & Gas
Components in these industries operate in some of the most hostile environments, facing high pressures, extreme temperatures, and corrosive substances.
Controlled atmosphere heat treatment is critical for ensuring that special alloys used for pipes, valves, and reactor components retain their high-temperature strength and corrosion resistance. The controlled atmosphere prevents oxidation and other contamination during heating, preserving the material's carefully engineered properties.
Medical and Electronics
In the medical field, heat treatment is used on surgical instruments and implants. The process ensures they have the required hardness, wear resistance, and can be formed into complex shapes while remaining biocompatible.
For electronics and semiconductors, heat treatment helps achieve specific magnetic and electrical properties in components used in transformers, motors, and other sensitive devices.
Tooling, Forging, and Castings
For an industry that makes tools, the tools must be harder and more durable than the materials they cut, press, or shape.
Heat treatment processes like hardening and tempering are used to give tools, dies, and molds exceptional hardness and abrasion resistance. This ensures a long operational life and consistent performance.
Understanding the Trade-offs: When is Heat Treatment Necessary?
While incredibly powerful, heat treatment is not a default step for every metal part. It represents an additional investment in time, energy, and cost.
The 'As-Cast' or 'As-Forged' Condition
Some components are designed for applications where the material's natural properties are sufficient. These parts can be used directly "as-cast" or "as-forged," providing a perfectly functional and more cost-effective solution for less demanding roles.
The Cost-Benefit Analysis
The decision to heat treat is a technical and economic one. If an application requires properties that the base material does not possess—such as extreme hardness for a cutting tool or fatigue resistance for an engine part—then heat treatment is non-negotiable. The cost is justified by the performance, reliability, and safety gains.
The Critical Role of Controlled Atmospheres
For the most demanding applications, simply heating a part is not enough. Heating metal in open air can cause it to react with oxygen, forming a scale on the surface and altering its properties.
Controlled atmospheres (including vacuums) prevent these unwanted reactions. This is why industries like aerospace and nuclear power, which rely on specialized and expensive alloys, almost always require this level of process control to guarantee quality.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use heat treatment hinges on the performance requirements of the final component.
- If your primary focus is maximum performance and reliability: Advanced processes like vacuum or controlled atmosphere heat treatment are essential to protect material integrity, especially for superalloys.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness for general applications: First, assess if the component's 'as-cast' or 'as-forged' state is sufficient before adding the cost and complexity of heat treatment.
- If your primary focus is extreme durability and wear resistance: Specific hardening and tempering processes are necessary to achieve the hardness required for tools, dies, and high-wear industrial components.
Ultimately, heat treatment is the engineering tool that allows you to tailor a material's performance to perfectly match its purpose.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Primary Needs | Common Heat Treatment Processes |
|---|---|---|
| Aerospace & Automotive | Extreme strength, high-temperature resistance, lightweight | Vacuum heat treatment, hardening, tempering |
| Energy, Oil & Gas | Corrosion resistance, high-pressure durability | Controlled atmosphere heat treatment |
| Medical & Electronics | Biocompatibility, wear resistance, precise electrical properties | Hardening, tempering, specialized thermal processes |
| Tooling & Forging | Extreme hardness, abrasion resistance, long tool life | Hardening, tempering, surface treatments |
Need to optimize your materials for demanding applications? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for precise heat treatment processes. Whether you're working with superalloys, reactive metals, or tool steels, our solutions help you achieve the exact material properties your industry requires. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's heat treatment needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is gold coating SEM for? Prevent Charging & Get Clearer SEM Images
- What is the best solvent for FTIR? Master Solvent Selection for Clear, Accurate Spectra
- What should be considered when performing melting point determination? Ensure Accurate Compound Identification and Purity Assessment
- How is in-situ Raman spectroscopy utilized to evaluate the stability of anti-corrosion coatings? Precision Real-Time Monitoring
- What are the types of sintering furnace? A Guide to Heating, Handling & Atmosphere
- What is slow pyrolysis? A Guide to Maximizing Biochar Production from Biomass
- What is the temperature range for pyrolysis? Optimize for Biochar, Bio-oil, or Syngas
- What are the limitations of XRF? Understanding Its Boundaries for Accurate Elemental Analysis



















