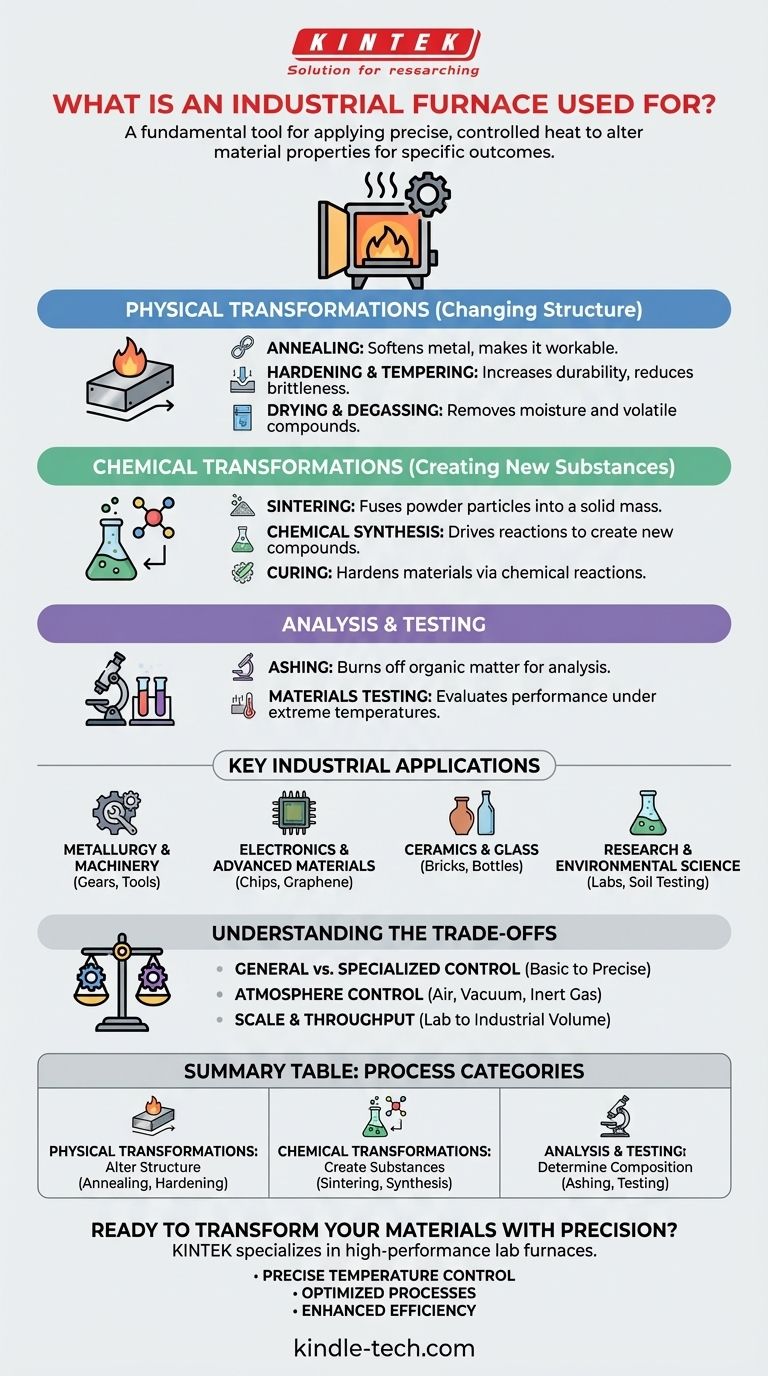
In an industrial context, a furnace is a fundamental piece of equipment used to apply precise and controlled heat to a material. Its purpose is to intentionally alter that material's physical or chemical properties to achieve a specific outcome, such as hardening steel, firing ceramics, synthesizing new chemical compounds, or preparing samples for scientific analysis.
The core function of an industrial furnace is not merely to generate heat, but to act as a tool for material transformation. By precisely managing temperature, a furnace can change a material's internal structure, trigger chemical reactions, or enable detailed analysis.

The Core Function: Transforming Materials with Heat
A furnace's value lies in its ability to facilitate predictable and desirable changes in a wide range of materials. These changes generally fall into two categories: physical transformations and chemical transformations.
Physical Transformations (Changing Structure)
Many processes use heat to alter a material's physical structure and mechanical properties without changing its chemical identity.
Annealing involves heating and then slowly cooling a material, typically metal, to make it softer and more workable.
Hardening and tempering are multi-step processes where a material is heated to a high temperature and then rapidly cooled (quenched) to increase its hardness, followed by a lower-temperature heating to reduce brittleness.
Drying and degassing use controlled heat to remove moisture or other volatile compounds from a material, which is critical in preparing everything from building materials to components for vacuum systems.
Chemical Transformations (Creating New Substances)
In other applications, heat acts as the catalyst for chemical reactions, creating entirely new materials or bonding different elements together.
Sintering is a process that uses heat to fuse particles of powder together, forming a solid, coherent mass. This is essential for manufacturing ceramics, certain metal parts, and refractories.
Chemical synthesis relies on a furnace to provide the necessary energy to drive reactions, creating new compounds for industries ranging from electronics to pharmaceuticals.
Curing uses heat to trigger a chemical reaction that hardens a material, such as with polymers, composites, or specialized adhesives.
Analysis and Testing
Furnaces are also indispensable tools in laboratory and quality control settings.
Ashing involves using a furnace to burn off all organic matter from a sample, leaving behind only the inorganic residue for analysis. This is common in food science, environmental testing, and geological research.
Materials testing for industries like aerospace requires furnaces to see how new alloys or ceramics perform under extreme temperatures, simulating their operational environment.
Key Industrial Applications
The versatility of heat treatment means furnaces are found in nearly every major industrial and research sector.
Metallurgy and Machinery
Furnaces are the backbone of the metal industry. They are used for annealing raw metal to make it workable, hardening machine parts and tools to make them durable, and sintering powdered metals to create complex components.
Electronics and Advanced Materials
The production of modern electronics is heavily reliant on highly specialized tube furnaces. They create the controlled, high-temperature environments needed for producing semiconductors, solid oxide fuel cells, and advanced materials like graphene and polymer composites.
Ceramics, Glass, and Building Materials
This is a traditional but critical application. Furnaces are used for firing clay to create ceramics and brick, melting raw materials to form glass, and roasting powders to produce cement.
Research and Environmental Science
In universities and research institutes, furnaces enable high-temperature experiments for materials science and engineering. They are also used in environmental labs for water, waste, and soil testing, as well as in the energy sector for oil and gas analysis.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a furnace involves more than just picking a maximum temperature; it requires matching the equipment to the process.
General Purpose vs. Specialized Control
A simple box furnace might be sufficient for basic drying or ashing. However, manufacturing a semiconductor requires a highly specialized tube furnace with exceptionally precise temperature uniformity and programmable heating and cooling cycles.
Atmosphere Control
Many advanced processes cannot be performed in normal air. Processes like vacuum brazing or sintering sensitive materials require the furnace chamber to be either a vacuum or filled with an inert gas like argon to prevent oxidation and unwanted chemical reactions. This adds significant complexity and cost.
Scale and Throughput
A small tube furnace in a research lab may only process a few grams of material at a time. In contrast, an industrial furnace for annealing steel coils or firing bricks is a massive installation designed for continuous, high-volume production.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your objective determines the type of furnace process you need.
- If your primary focus is improving a material's mechanical properties: You will be using processes like annealing, hardening, and tempering to make it stronger, softer, or more durable.
- If your primary focus is creating a new solid object or compound: You will rely on sintering, chemical synthesis, or curing to bond particles and molecules together.
- If your primary focus is analyzing a sample's composition: You will use a furnace for processes like ashing or high-temperature materials testing to understand its fundamental makeup.
Ultimately, the industrial furnace is a powerful and precise instrument for changing the very nature of matter.
Summary Table:
| Process Category | Key Processes | Primary Goal |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Transformations | Annealing, Hardening, Drying | Alter material structure & properties |
| Chemical Transformations | Sintering, Synthesis, Curing | Create new substances or bonds |
| Analysis & Testing | Ashing, Materials Testing | Determine composition or performance |
Ready to transform your materials with precision?
Whether your goal is to harden a metal alloy, sinter a ceramic component, or prepare samples for critical analysis, the right furnace is key to your success. KINTEK specializes in providing high-performance lab furnaces and equipment tailored to your specific industrial or research needs.
We help you achieve:
- Precise Temperature Control for consistent, reliable results.
- Optimized Processes for annealing, sintering, ashing, and more.
- Enhanced Efficiency in your laboratory or production line.
Let's discuss your application. Contact our experts today to find the perfect furnace solution for your laboratory's challenges.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the high temperature of a muffle furnace? From 1100°C to 1700°C+ for Your Lab Needs
- What type of furnace is a muffle furnace? A Guide to High-Purity, Contamination-Free Heating
- What is a muffle furnace for laboratory use? A Guide to Contaminant-Free High-Temperature Processing
- Why is the metal melting temperature important? The Key to Manufacturing & Performance
- What heat can a muffle furnace produce? Achieve Precise High Temperatures Up to 1800°C



















