At its core, a high-temperature furnace is a specialized tool used to transform materials. These furnaces are employed across scientific research and industrial production for processes like sintering technical ceramics, melting metals to create alloys, and performing critical heat treatments that alter a material's fundamental properties. They achieve this by creating a precisely controlled environment at extreme temperatures, often exceeding 1500° C.
The true purpose of a high-temperature furnace is not simply to heat an object, but to fundamentally change its chemical and physical structure. It is an instrument for materials engineering, enabling the creation of advanced materials with specific, high-performance characteristics.
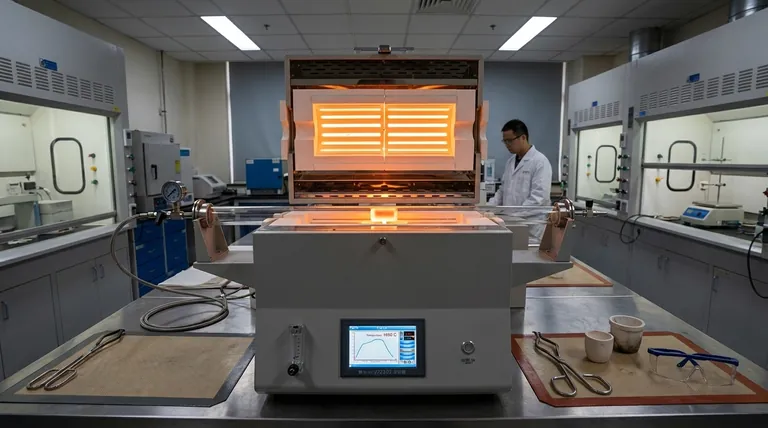

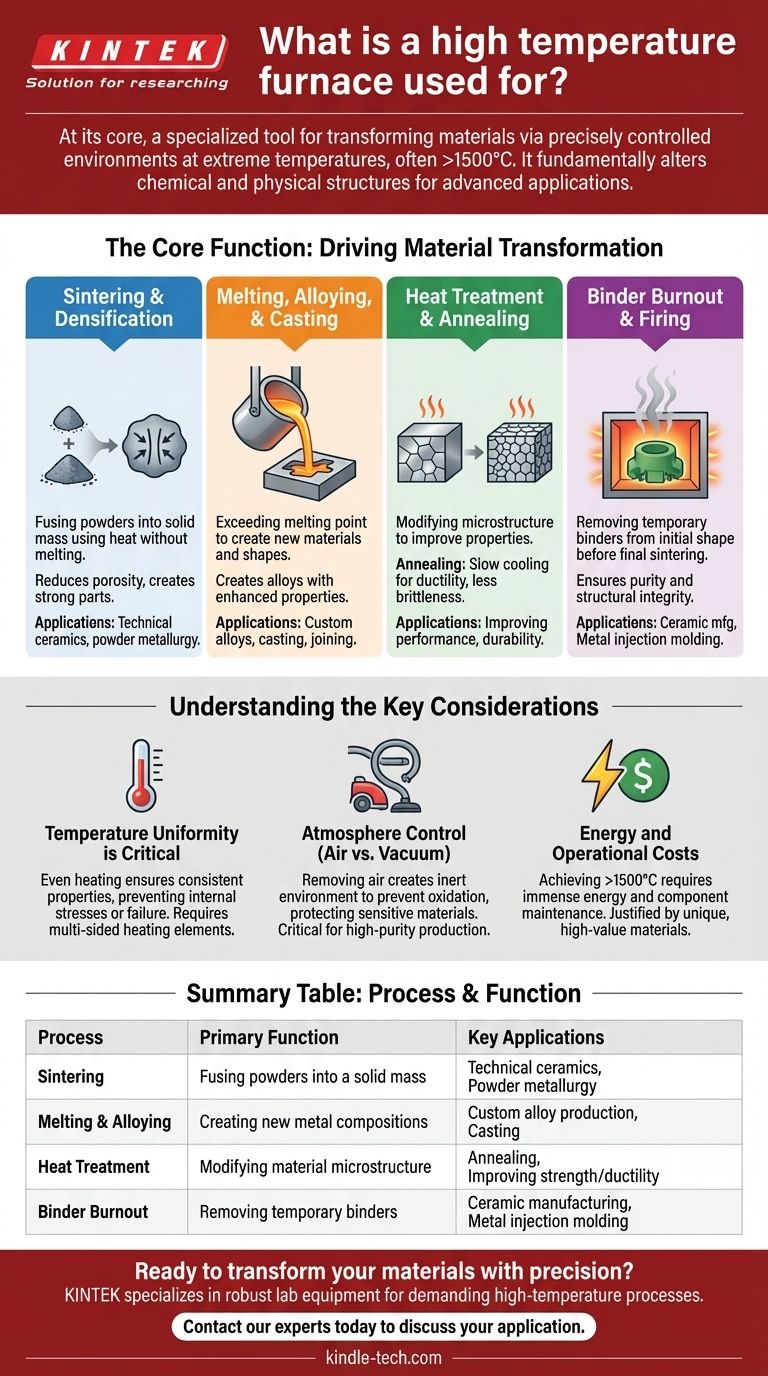
The Core Function: Driving Material Transformation
A high-temperature furnace provides the energy needed to rearrange the atomic and molecular structure of a material. This enables several key industrial and scientific processes.
Sintering and Densification
Sintering is the process of fusing powders into a solid, dense mass using heat, but without melting them completely. This is a cornerstone of modern materials science.
High-temperature furnaces provide the necessary thermal energy to bond the particles together, reducing porosity and creating a strong, coherent part. This is essential for producing technical ceramics and parts via powder metallurgy.
Melting, Alloying, and Casting
For metals, these furnaces are used to exceed the material's melting point. This allows for the creation of new materials and shapes.
By melting different metals together, manufacturers can create alloys with enhanced properties like superior strength or corrosion resistance. The molten material can then be cast into a specific form or used in other high-temperature joining processes.
Heat Treatment and Annealing
Heat treating modifies the microstructure of a material to improve its properties. Annealing, for example, involves heating a metal and then slowly cooling it to make it less brittle and more ductile.
These processes don't change the shape of the material but refine its internal structure, improving performance and durability for demanding applications.
Binder Burnout and Firing
In processes like ceramic manufacturing or metal injection molding, a temporary "binder" is used to hold the material's shape in its initial, or "green," state.
A high-temperature furnace is used in a preliminary stage to carefully burn out this binder material before the final firing or sintering stage, ensuring the final part is pure and structurally sound.
Understanding the Key Considerations
While powerful, operating a high-temperature furnace requires careful control over several variables. The success of any process depends on managing these factors precisely.
Temperature Uniformity is Critical
For a material to have consistent properties throughout, it must be heated evenly. High-quality furnaces use heating elements on multiple sides of the chamber to ensure excellent thermal uniformity.
Any significant temperature variation can lead to internal stresses, weak spots, or a failed part, making uniformity a non-negotiable requirement for high-performance materials.
Atmosphere Control (Air vs. Vacuum)
Many materials will react with oxygen at high temperatures, leading to unwanted oxidation that degrades their properties.
This is why high-temperature vacuum furnaces are critical. By removing the air, they create an inert environment that protects sensitive materials during processing, enabling the production of high-purity metals and advanced ceramics.
Energy and Operational Costs
Achieving and maintaining temperatures above 1500° C requires an immense amount of energy. The operational cost, both in terms of power consumption and the maintenance of sophisticated components, is a significant factor.
This high cost is justified by the unique capabilities and high-value materials that these furnaces produce.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The specific process you use depends entirely on your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is creating dense, solid parts from powders: Sintering is the correct process for ceramics and powder metallurgy applications.
- If your primary focus is creating new metal compositions: Melting and alloying are the essential processes for developing custom alloys.
- If your primary focus is improving the properties of an existing solid part: Heat treatment processes like annealing will modify the material's internal structure.
- If your primary focus is foundational materials research: A versatile lab furnace that allows for precise control over temperature and atmosphere is the essential tool for innovation.
Mastering high-temperature processes is fundamental to advancing the field of materials science and engineering.
Summary Table:
| Process | Primary Function | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Sintering | Fusing powders into a solid mass | Technical ceramics, Powder metallurgy |
| Melting & Alloying | Creating new metal compositions | Custom alloy production, Casting |
| Heat Treatment | Modifying material microstructure | Annealing, Improving strength/ductility |
| Binder Burnout | Removing temporary binders | Ceramic manufacturing, Metal injection molding |
Ready to transform your materials with precision?
Whether your goal is sintering advanced ceramics, developing new alloys, or precise heat treatment, the right high-temperature furnace is critical to your success. KINTEK specializes in providing robust lab equipment and consumables designed for demanding high-temperature processes.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application needs. We'll help you select the perfect furnace to achieve superior thermal uniformity, atmosphere control, and the material properties you require.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing
- Why is a quartz tube furnace utilized in the thermal oxidation of MnCr2O4 coatings? Unlock Precise Selective Oxidation
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide for Safe and Effective Maintenance
- How do a quartz tube reactor and atmosphere furnace collaborate in Co@NC pyrolysis? Master Precision Synthesis
- What are the applications of tube furnace? Unlock Precise High-Temperature Processing



















