At its core, a quench furnace is an integrated system designed for the heat treatment of materials, most commonly metals. It consists of a high-temperature heating chamber connected to a tank containing a quenching medium, such as oil, water, or polymer. A key feature, as noted in dual-chamber designs, is an internal mechanism that rapidly transfers the heated part from the furnace into the quench bath to achieve specific metallurgical properties.
The true purpose of a quench furnace isn't just to heat and cool a part. It is to execute a precisely controlled thermal cycle—heating, transferring, and rapidly cooling—to intentionally transform a material's internal structure and lock in desired properties like hardness and strength.
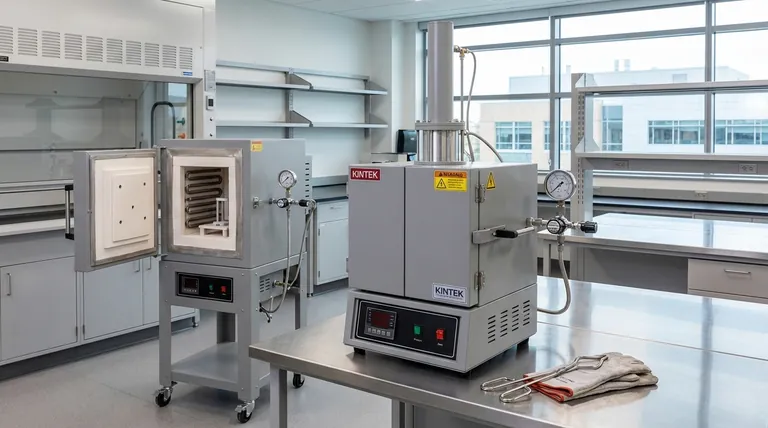

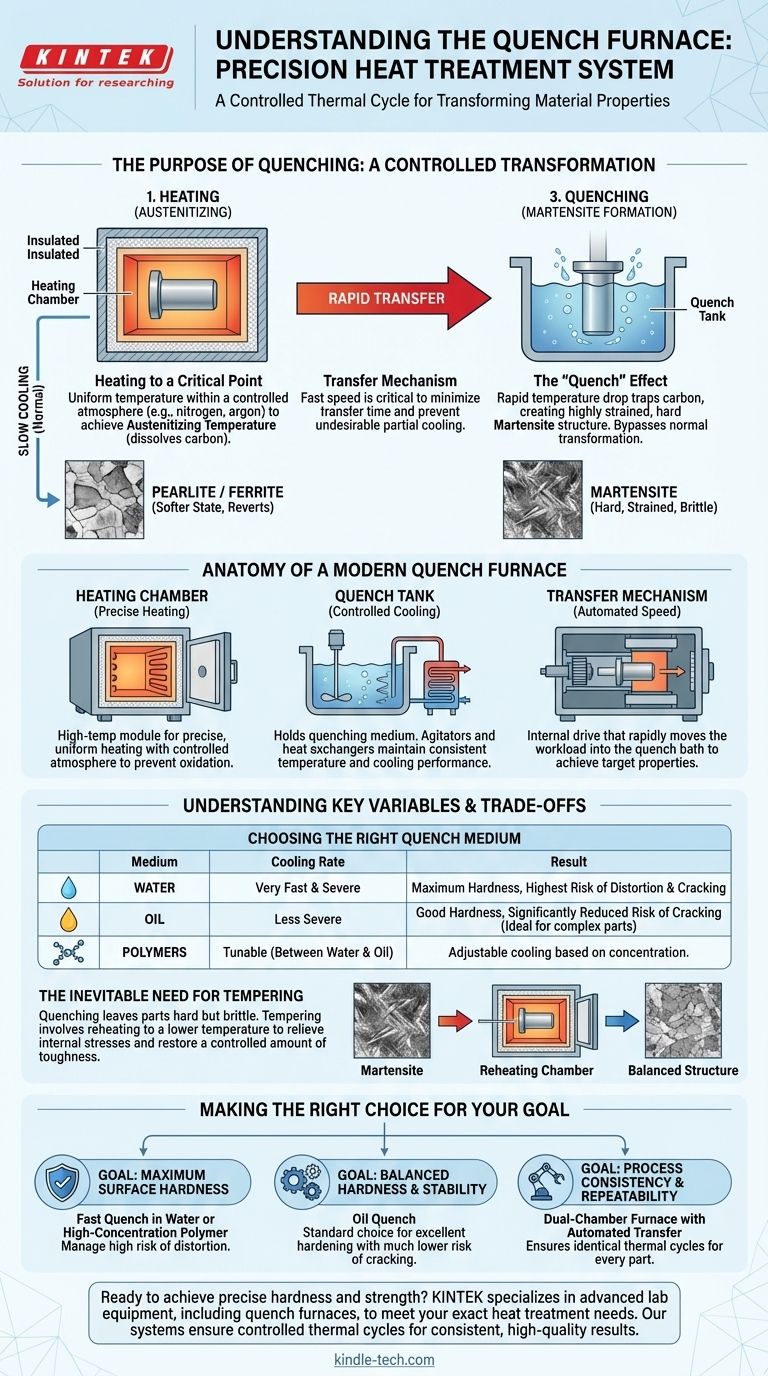
The Purpose of Quenching: A Controlled Transformation
Heat treating in a quench furnace is a process of deliberate material transformation. The goal is to manipulate the crystalline structure of a metal to enhance its mechanical properties.
### Heating to a Critical Point
First, the material is heated to a specific, uniform temperature within the furnace's heating chamber. For steel, this is known as the austenitizing temperature, where its crystal structure changes into a form called austenite, which can dissolve carbon.
### The "Quench" and Its Effect
If the steel were allowed to cool slowly, the structure would simply revert to its softer, pre-heated state.
However, by rapidly cooling or quenching the part, the normal transformation is bypassed. The rapid temperature drop traps the dissolved carbon atoms, forcing the creation of a new, highly strained, and very hard crystal structure called martensite.
Anatomy of a Modern Quench Furnace
The design of a quench furnace is entirely driven by the need for process control and repeatability. The dual-chamber model is a perfect example of this principle in action.
### The Heating Chamber
This is an insulated, high-temperature module designed for precise and uniform heating. It often contains a controlled atmosphere (such as nitrogen or argon) to prevent oxidation and scaling on the part's surface during the heating cycle.
### The Quench Tank
Located adjacent to or below the heating chamber, this tank holds the quenching liquid. The choice of liquid, or quenchant, is one of the most critical variables in the process. The tank often includes agitators to circulate the fluid and heat exchangers to maintain its temperature, ensuring consistent cooling performance.
### The Transfer Mechanism
This is the internal drive that moves the workload. Its most important attribute is speed. The time it takes to move the part from the heat of the furnace into the quench liquid is known as the transfer time, and minimizing it is critical for achieving the desired hardness and preventing undesirable, partial cooling in the open air.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Key Variables
Quenching is a powerful but aggressive process. The dramatic temperature change induces significant internal stress, which must be managed to avoid damaging the part.
### Choosing the Right Quench Medium
The severity of the quench is determined by the cooling medium.
- Water: Provides a very fast and severe quench, producing maximum hardness but also carrying the highest risk of distortion and cracking.
- Oil: Cools much less severely than water. It significantly reduces the risk of cracking, making it ideal for parts with complex geometries or those made from higher-alloy steels.
- Polymers: These are water-based solutions with dissolved polymers. By changing the concentration, their cooling rate can be adjusted to fall between that of water and oil, offering a tunable solution.
### The Inevitable Need for Tempering
A part that has been quenched is in a state of maximum hardness but also maximum brittleness, making it unsuitable for most applications.
Therefore, quenching is almost always followed by a secondary heat treatment process called tempering. This involves reheating the part to a much lower temperature to relieve internal stresses and restore a controlled amount of toughness, reducing its brittleness to a functional level.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The selection of a furnace and process parameters depends entirely on the desired outcome for the finished component.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum surface hardness: A fast quench in water or a high-concentration polymer is necessary, but you must be prepared to manage the high risk of part distortion.
- If your primary focus is balancing hardness with dimensional stability: An oil quench is the standard choice, providing excellent hardening with a much lower risk of cracking, especially for intricate or high-value components.
- If your primary focus is process consistency and repeatability: A dual-chamber furnace with an automated transfer mechanism is essential to ensure every part experiences the exact same thermal cycle.
Understanding that a quench furnace is a complete process-control system allows you to precisely engineer the final properties of your materials.
Summary Table:
| Key Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Heating Chamber | Heats material to a precise, uniform temperature (e.g., austenitizing for steel) |
| Quench Tank | Holds quenching medium (oil, water, polymer) for rapid cooling |
| Transfer Mechanism | Rapidly moves heated parts into quench to minimize transfer time |
| Quench Medium | Determines cooling rate and final material properties (hardness vs. risk of cracking) |
Ready to achieve precise hardness and strength for your metal components? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including quench furnaces, to meet your exact heat treatment needs. Our systems ensure controlled thermal cycles for consistent, high-quality results. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your laboratory's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the process of annealing tubes? Achieve Optimal Softness and Ductility for Your Tubing
- How do you clean a tubular furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Maintenance
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- What temperature is tube annealing? A Guide to Material-Specific Ranges for Optimal Results
- What is a vertical tube furnace? Leverage Gravity for Superior Uniformity and Process Control



















