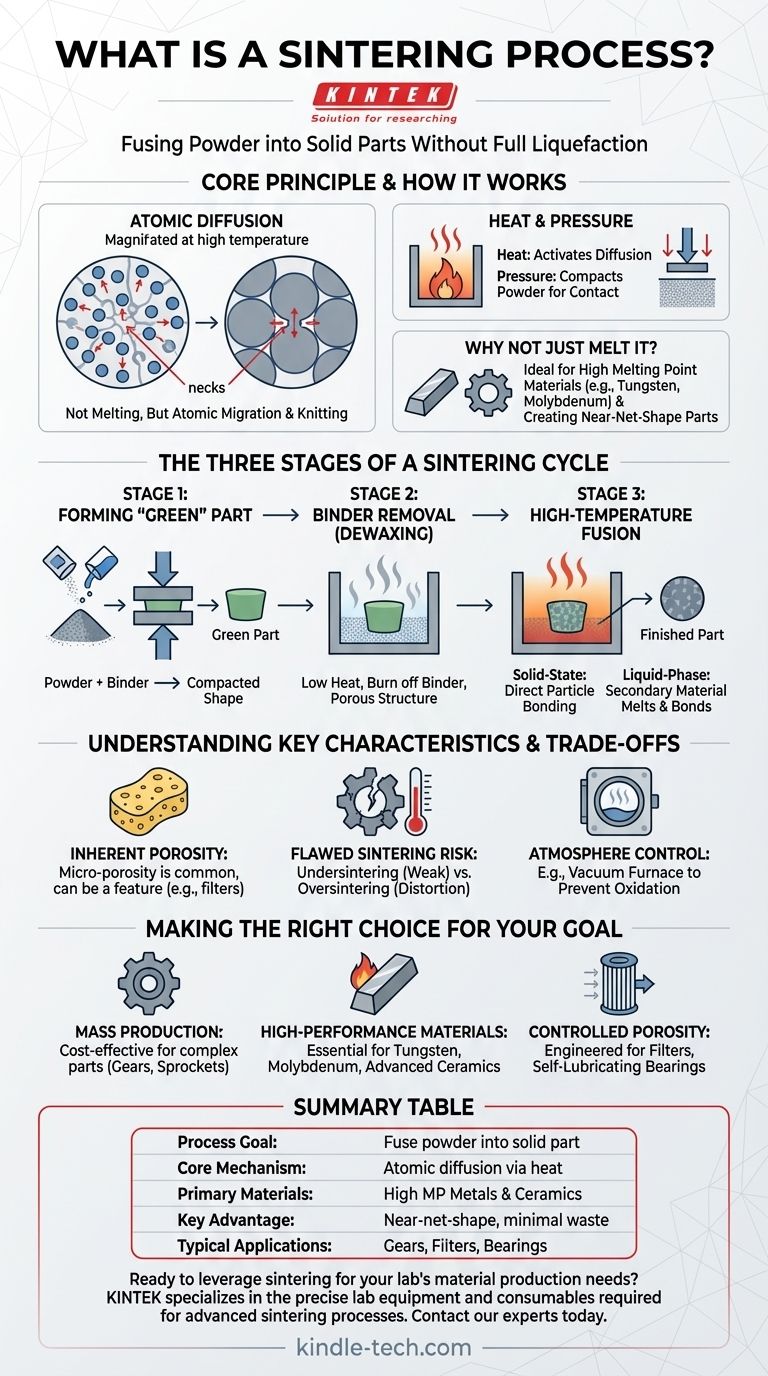
Sintering is a manufacturing process that uses heat and pressure to fuse powdered materials into a solid, functional part. Critically, this is achieved without melting the primary material to the point of liquefaction, making it an efficient method for creating components from metals and ceramics with very high melting points.
The core principle of sintering is not melting, but atomic diffusion. By heating a compressed powder, you give the atoms enough energy to migrate across the boundaries of individual particles, effectively knitting them together into a single, solid piece with precise dimensions.

How Sintering Fundamentally Works
Sintering transforms loose powder into a cohesive object by manipulating atomic behavior. This approach offers unique advantages over traditional melting and casting, particularly for certain materials and applications.
The Core Principle: Atomic Diffusion
At its heart, sintering relies on diffusion. When particles are pressed together and heated, the atoms at the contact points become agitated and begin to move across the particle boundaries.
This atomic movement closes the gaps, or pores, between the particles. The points of contact grow into "necks," gradually eliminating the voids and increasing the density and strength of the material.
The Role of Heat and Pressure
Heat provides the thermal energy necessary to activate atomic diffusion. It energizes the atoms, allowing them to break their bonds and move.
Pressure serves to compact the powder, ensuring the particles are in intimate contact. This proximity is essential for diffusion to occur effectively across their surfaces.
Why Not Just Melt It?
Sintering is often the preferred or only viable method for materials with exceptionally high melting points, like tungsten and molybdenum. Melting these materials is extremely energy-intensive and difficult to control.
Furthermore, sintering allows for the creation of "near-net-shape" parts, which require little to no finishing or machining. This significantly reduces waste and production costs, especially for complex components.
The Three Stages of a Typical Sintering Cycle
Most industrial sintering processes follow a clear, three-stage progression from a loose powder to a finished, solid component.
Stage 1: Forming the "Green" Part
First, the primary material powder is mixed with a temporary bonding agent, such as wax or a polymer. This mixture is then compacted in a die to form the desired shape.
This initial, fragile piece is known as a "green" part. It has the correct geometry but lacks the mechanical strength of the final product.
Stage 2: Binder Removal (Dewaxing)
The green part is placed in a furnace and heated at a relatively low temperature. During this phase, the bonding agent is systematically burned off or evaporated.
This leaves a porous structure composed solely of the primary material particles, now ready for the final fusion stage.
Stage 3: High-Temperature Fusion
The temperature is increased to the material's specific sintering point. Here, atomic diffusion accelerates, and the particles fuse together. This can happen in two primary ways:
- Solid-State Sintering: The primary material particles bond directly to one another at their surfaces.
- Liquid-Phase Sintering: A secondary material with a lower melting point is included in the powder mix. This material melts, flows into the pores, and acts as a cement to bond the primary particles.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Key Characteristics
While powerful, sintering produces parts with distinct properties and requires careful process control to avoid defects.
Inherent Porosity
Sintered parts almost always retain a certain degree of micro-porosity. While this can be a limitation for applications requiring perfect density, it can also be a desired feature for parts like self-lubricating bearings, where the pores hold oil.
The Risk of Flawed Sintering
Proper control of temperature and time is critical. Undersintering occurs when the heat is insufficient, resulting in weak bonds and a fragile part. Oversintering happens when the temperature is too high, which can cause slumping, distortion, or unwanted melting.
The Importance of Atmosphere Control
Many sintering processes are performed in a controlled atmosphere, such as a vacuum furnace. Removing atmospheric gases like oxygen prevents oxidation and other unwanted chemical reactions that could compromise the strength and integrity of the final component.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Sintering is not a one-size-fits-all solution. Its value is tied directly to the specific requirements of the material and the final part.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective mass production of complex parts: Sintering is a leading choice for creating near-net-shape components like gears, sprockets, and pulleys with minimal waste and post-processing.
- If your primary focus is working with high-performance, high-melting-point materials: Sintering is often the only practical manufacturing method for materials like tungsten, molybdenum, and many advanced ceramics.
- If your primary focus is creating parts with controlled porosity: Sintering is uniquely capable of engineering specific levels of porosity for applications such as filters and self-lubricating components.
Ultimately, sintering provides a powerful and precise method for turning simple powders into complex, high-performance components.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Process Goal | Fuse powdered materials into a solid part without full liquefaction. |
| Core Mechanism | Atomic diffusion across particle boundaries, driven by heat. |
| Primary Materials | Metals (e.g., tungsten, molybdenum) and ceramics with high melting points. |
| Key Advantage | Creates complex, near-net-shape parts with minimal waste. |
| Typical Applications | Gears, filters, bearings, and high-performance industrial components. |
Ready to leverage sintering for your lab's material production needs?
KINTEK specializes in the precise lab equipment and consumables required for advanced sintering processes. Whether you are developing new high-performance alloys, ceramic components, or complex metal parts, our expertise and reliable products ensure your sintering cycles are controlled, efficient, and successful.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific sintering applications and help you achieve superior results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Warm Isostatic Press WIP Workstation 300Mpa for High Pressure Applications
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
- Warm Isostatic Press for Solid State Battery Research
People Also Ask
- What technical conditions does a heated hydraulic press provide for PEO batteries? Optimize Solid-State Interfaces
- How much force can a hydraulic press exert? Understanding its immense power and design limits.
- Does a hydraulic press have heat? How Heated Platens Unlock Advanced Molding and Curing
- Why do you need to follow the safety procedure in using hydraulic tools? Prevent Catastrophic Failure and Injury
- Why are hydraulic presses dangerous to operate? Uncover the Silent, Deceptive Risks



















