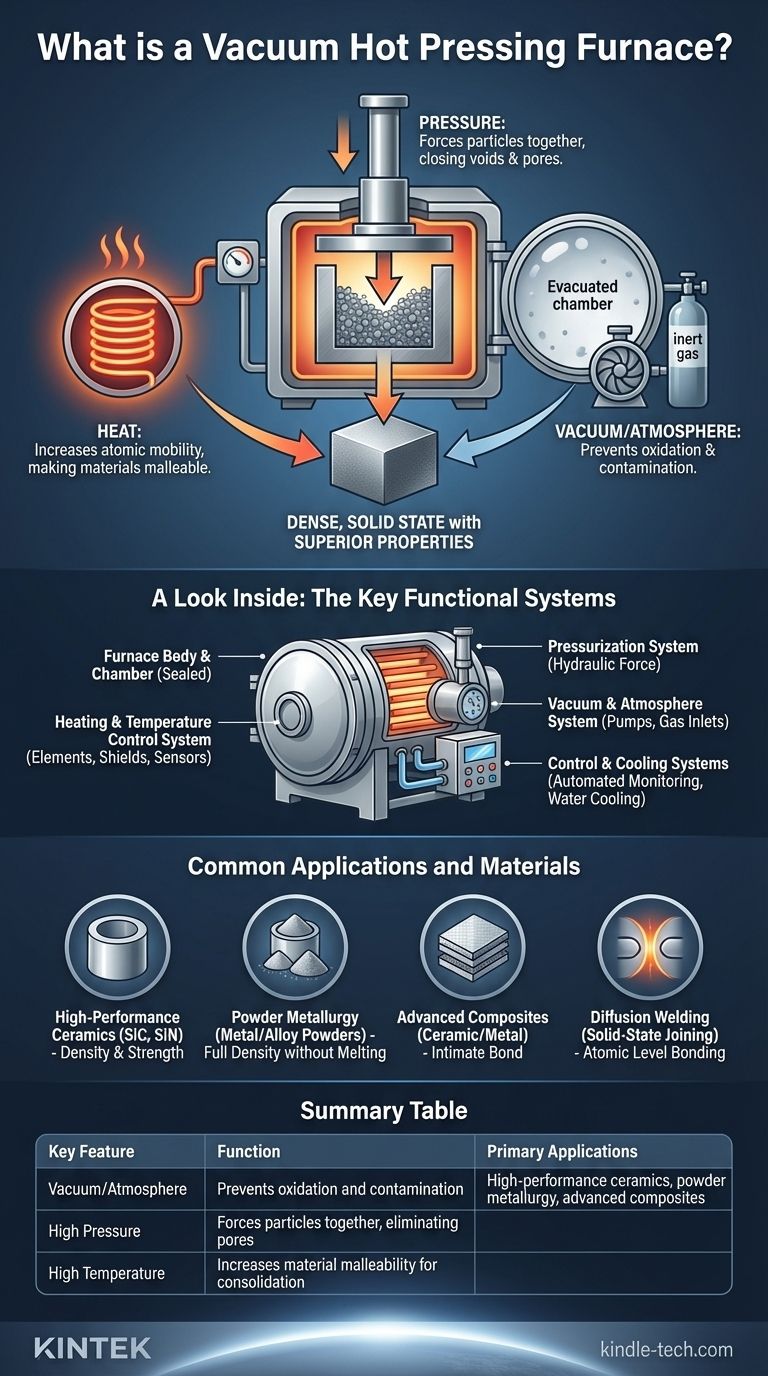
A vacuum hot pressing furnace is a complete set of equipment designed to simultaneously apply high temperature and high pressure to materials within a vacuum or a controlled atmosphere. This combination of forces is used to consolidate powders or bond materials, forming them into a dense, solid state with superior properties.
The core function of a vacuum hot pressing furnace is to eliminate porosity and achieve maximum material density. It combines heat to make materials malleable, pressure to force particles together, and a controlled atmosphere to prevent unwanted chemical reactions.

The Core Principle: How It Works
A vacuum hot press furnace operates on the synergy of three critical elements: heat, pressure, and a controlled atmosphere. This process is fundamentally different from simply heating a material (sintering) or pressing it at room temperature.
The Role of Heat
The furnace's heating system raises the material's temperature, often just below its melting point. This thermal energy increases atomic mobility, making the material soft and pliable enough for consolidation.
The Role of Pressure
Simultaneously, a pressurization system, typically hydraulic, applies a strong mechanical force. This pressure physically forces the material's particles together, closing up internal voids and pores far more effectively than heat alone.
The Role of Vacuum or Controlled Atmosphere
The entire process occurs inside a sealed chamber. A vacuum system removes air and other reactive gases, preventing oxidation and contamination of sensitive materials. Alternatively, the chamber can be filled with a specific inert gas to create a protective atmosphere for certain processes.
A Look Inside: The Key Functional Systems
While designs vary, all vacuum hot pressing furnaces are built around several essential systems that work in concert.
The Furnace Body and Chamber
This is the main structural component, including the sealed furnace body, cover, and bottom. It is designed to withstand extreme temperatures, high pressure, and the vacuum environment.
The Heating and Temperature Control System
This system consists of heating elements (like graphite or refractory metals) and heat shields or insulation layers. A precise temperature measurement and control system ensures the material reaches and maintains the target temperature accurately.
The Pressurization System
This is the "hot press" component, almost always a hydraulic system. It applies a controlled, powerful force onto the material inside the furnace, driving the densification process.
The Vacuum and Atmosphere System
This is composed of vacuum pumps that evacuate the furnace chamber. It may also include an automatic charging and deflating system to introduce specific gases (like argon or nitrogen) when an inert atmosphere is required instead of a pure vacuum.
The Control and Cooling Systems
A central control system automates and monitors all parameters—temperature, pressure, vacuum level, and process time. A robust water cooling system is critical for protecting the furnace shell, seals, and other components from the intense internal heat.
Common Applications and Materials
The unique capabilities of this technology make it essential for creating advanced materials that cannot be produced by other means.
High-Performance Ceramics
The furnace is widely used for the hot press sintering of industrial and functional ceramics, such as silicon carbide (SiC) and silicon nitride (SiN). This process achieves a density and strength that is impossible with conventional sintering.
Powder Metallurgy
It is used to consolidate metal and alloy powders, especially those involving refractory metals. The process creates fully dense parts from powder without having to melt the material completely.
Advanced Composites
The furnace is critical for preparing ceramic/metal composites and intermetallic compounds. The pressure and heat ensure an intimate bond between the different material phases.
Diffusion Welding
The equipment can also be used for diffusion welding, a solid-state joining process where pressure and heat cause two separate pieces to bond at the atomic level without any melting.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Deciding to use a vacuum hot pressing furnace depends entirely on the specific properties you need to achieve in your final material.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum density and eliminating porosity: This is the most effective technology for creating fully dense ceramic or metallic parts from powders.
- If your primary focus is processing oxygen-sensitive materials: The vacuum or inert gas environment is essential for working with refractory metals, certain alloys, and non-oxide ceramics without contamination.
- If your primary focus is developing novel composites or bonded materials: The combination of heat and pressure is ideal for ensuring strong metallurgical or ceramic bonding between dissimilar materials.
- If your primary focus is maintaining fine-grained microstructures: Hot pressing allows for densification at lower temperatures and for shorter times than conventional sintering, which helps prevent unwanted grain growth and preserves material strength.
This technology is a powerful tool for pushing the boundaries of material performance and manufacturing.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Function |
|---|---|
| Vacuum/Atmosphere | Prevents oxidation and contamination |
| High Pressure | Forces particles together, eliminating pores |
| High Temperature | Increases material malleability for consolidation |
| Primary Applications | High-performance ceramics, powder metallurgy, advanced composites |
Ready to achieve maximum density and superior performance for your advanced materials?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including vacuum hot pressing furnaces designed for researchers and manufacturers working with ceramics, metal powders, and composites. Our solutions provide the precise control and robust performance needed to push the boundaries of material science.
Contact our experts today to discuss how a vacuum hot press furnace can meet your specific R&D or production goals.
Visual Guide
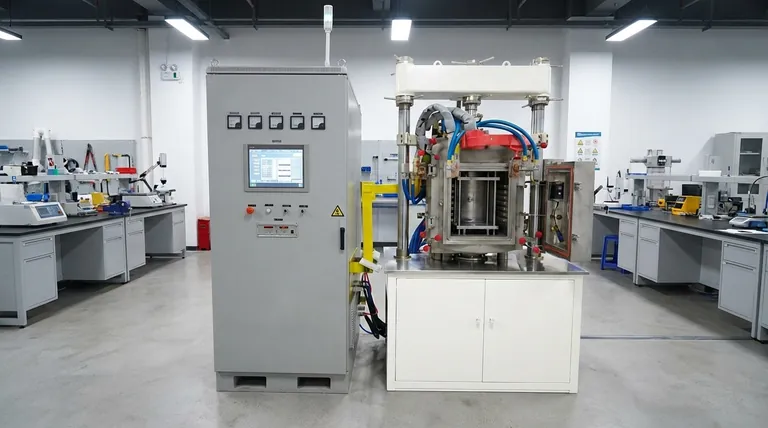
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Electric Heated Hydraulic Vacuum Heat Press for Lab
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Vacuum Box Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- Why is precise temperature control necessary for SiC/Cu Vacuum Hot Pressing? Mastering the Cu9Si Interface Phase
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot press for CuCr50? Achieve Superior Density & Purity in Alloy Production
- What is the significance of precise temperature control in melt infiltration? Achieve High-Performance Li-Alloy Electrodes
- How does the uniaxial pressing function of a vacuum hot press furnace influence the microstructure of ZrC-SiC ceramics?
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot press sintering furnace? Achieve 99.1% Density in CuW30 Composites



















