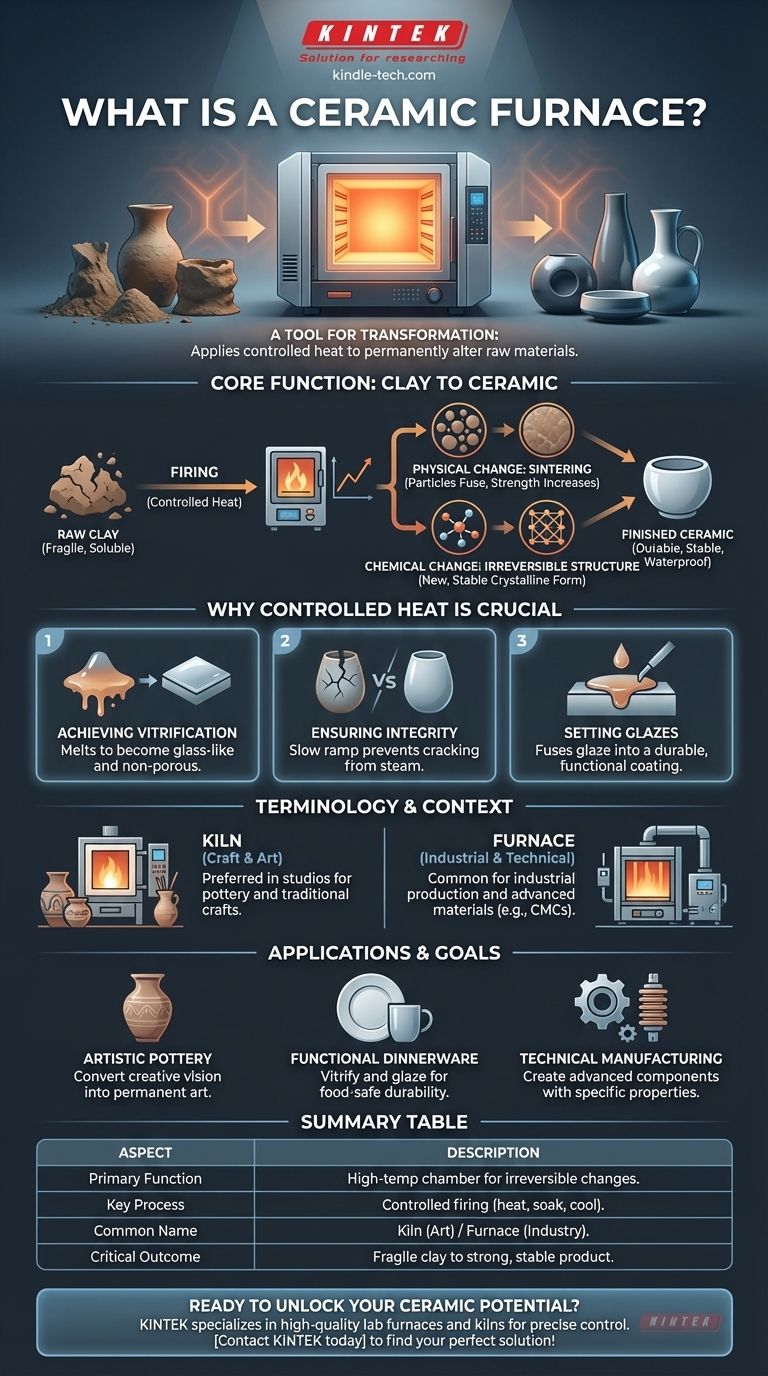
In essence, a ceramic furnace is a high-temperature, thermally insulated chamber used to transform raw materials like clay into hard, durable ceramic objects. Often called a kiln, its core purpose is to apply controlled heat in a process known as firing, which causes permanent chemical and physical changes in the material.
A ceramic furnace isn't merely an oven; it's a tool for transformation. Its critical function is to apply a precise heating schedule that turns a fragile, water-soluble material into a strong, stable, and often waterproof final product.
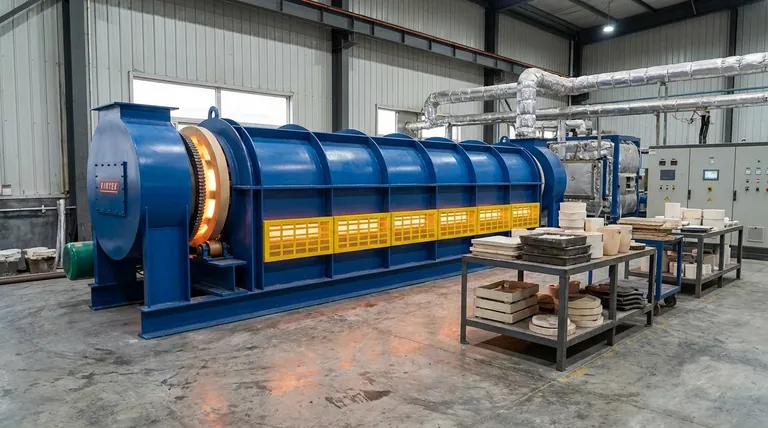

The Core Function: From Clay to Ceramic
A furnace facilitates a fundamental change in material properties. Without this controlled heating process, a clay object would remain fragile and would disintegrate in water.
The Process of 'Firing'
Firing is the technical term for heating ceramics in a furnace or kiln. This is not simple heating; it involves a carefully managed schedule of temperature increases, holds (called soaks), and cooling periods.
Physical Transformation
As the temperature rises, all remaining water is driven out of the clay. At higher temperatures, the clay particles begin to fuse together in a process called sintering. This fusion is what gives the finished piece its strength and hardness.
Chemical Transformation
The intense heat alters the molecular structure of the clay minerals. This chemical change is irreversible, locking the particles into a new, stable, and permanent crystalline structure that makes the object durable and impervious to water.
Why Controlled Heat is Crucial
The precision of a ceramic furnace is what separates a successful firing from a shattered failure. The rate of heating and cooling is as important as the maximum temperature reached.
Achieving Vitrification
For many types of ceramics, the goal is vitrification. This is the point where the material melts enough to become glass-like and non-porous. A furnace allows the user to reach and hold this specific temperature without overheating and deforming the object.
Ensuring Structural Integrity
If clay is heated too quickly, any trapped water can turn to steam and cause the object to crack or even explode. A slow, controlled temperature ramp, managed by the furnace's controller, is essential for allowing moisture to escape safely.
Setting Glazes
Glazes are essentially a form of glass applied to the surface of a ceramic piece. The furnace melts these powdered minerals into a smooth, liquid coating that fuses to the clay body, creating a decorative and functional surface.
Understanding the Terminology: Furnace vs. Kiln
While the terms are often used interchangeably, context can create a subtle distinction. Understanding this helps clarify their application.
Common Usage in Crafts
In the world of pottery, art, and traditional ceramics, the term kiln is overwhelmingly preferred. This is the word you will hear most often in studios and classrooms.
Industrial and Technical Context
The term furnace is more common in industrial and scientific settings. It is often used when discussing the production of advanced materials like Ceramic Matrix Composites (CMCs), insulators, or other technical components where precise engineering properties are paramount.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
The purpose of a ceramic furnace is consistent, but its role feels different depending on your objective.
- If your primary focus is artistic pottery: You need a kiln to convert your creative vision from fragile clay into a permanent work of art.
- If your primary focus is functional dinnerware: The furnace is essential for vitrifying the clay and melting the glaze, which makes your pieces food-safe, waterproof, and durable enough for daily use.
- If your primary focus is technical manufacturing: A high-temperature furnace is a critical industrial tool for creating advanced ceramic components with specific heat-resistant and structural properties.
Ultimately, a ceramic furnace is the essential instrument that unlocks the final, permanent form and function of any ceramic object.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | A high-temperature chamber for firing ceramics, causing irreversible chemical and physical changes. |
| Key Process | Controlled heating (firing) to drive out water, sinter clay particles, and achieve vitrification. |
| Common Name | Kiln (in art/craft contexts); Furnace (in industrial/technical contexts). |
| Critical Outcome | Transforms fragile, water-soluble clay into strong, stable, and often waterproof final products. |
Ready to unlock the potential of your ceramic projects?
Whether you are an artist creating pottery, a manufacturer producing functional dinnerware, or an engineer developing advanced technical ceramics, the right furnace is critical to your success. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab furnaces and kilns designed for precise temperature control and reliable performance.
We provide the essential tools for sintering, vitrification, and glaze firing, ensuring your materials achieve the desired strength, durability, and properties. Let our expertise in laboratory equipment support your creative or industrial process from start to finish.
Contact KINTEK today to find the perfect ceramic furnace solution for your specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Mesh belt controlled atmosphere furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of a calciner? Boost Efficiency in High-Temperature Processing
- What biomass is used in pyrolysis? Selecting the Optimal Feedstock for Your Goals
- What are the products of pyrolysis of wood? A Guide to Biochar, Bio-oil, and Syngas Yields
- What are the zones in rotary kiln in cement production? Master the Core Process for High-Quality Clinker
- What are the industrial applications of pyrolysis? Transform Waste into Energy and Valuable Products



















