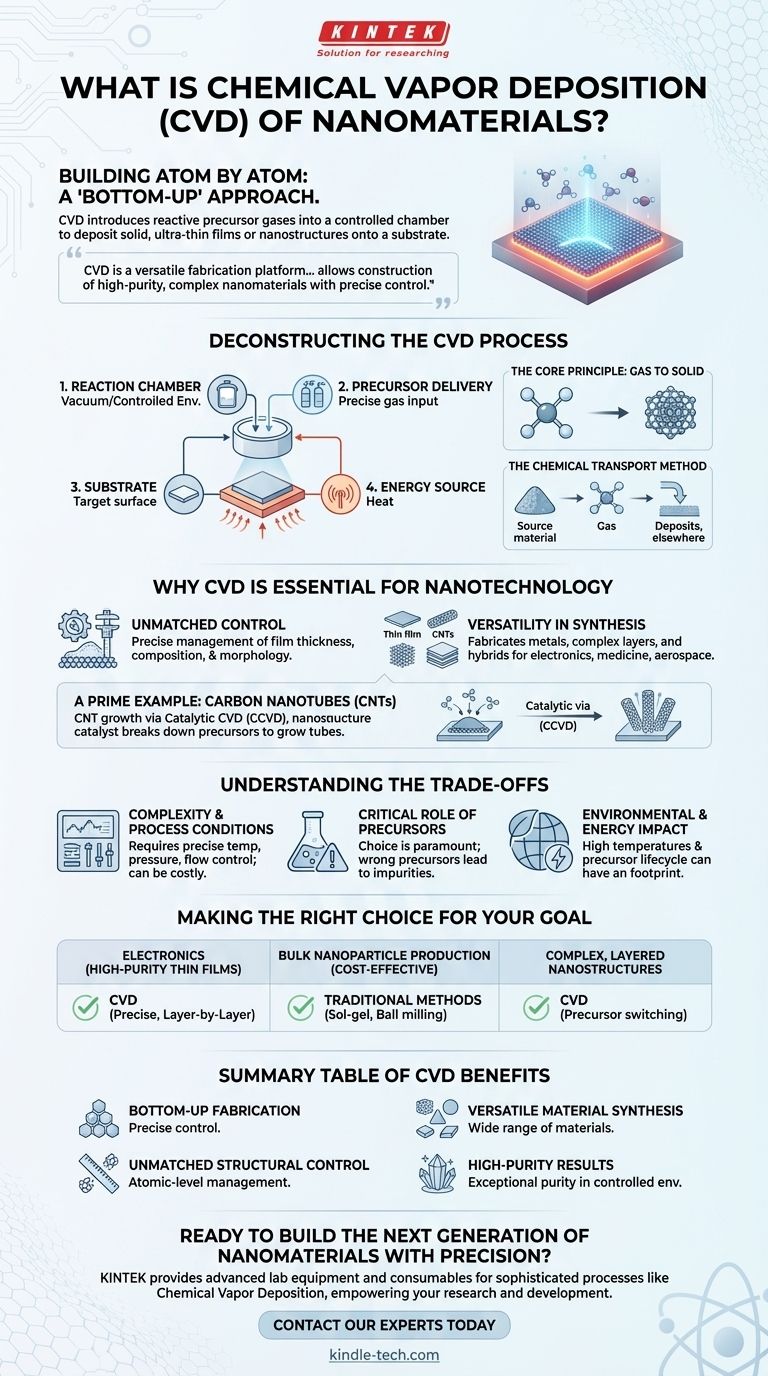
In the simplest terms, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a method for building nanomaterials atom by atom or molecule by molecule. It works by introducing reactive gases, known as precursors, into a controlled chamber where they react and deposit a solid, ultra-thin film or nanostructure onto a target surface, called a substrate. This "bottom-up" approach offers exceptional control over the material's final properties.
Chemical Vapor Deposition is not merely a coating technique; it is a versatile fabrication platform. Its true value lies in its ability to construct a vast range of high-purity, complex nanomaterials with precise structural control, which is often difficult to achieve with traditional chemical synthesis methods.

Deconstructing the CVD Process
To understand CVD, it's best to break it down into its fundamental principles and components. The process is a carefully orchestrated chemical reaction occurring on a surface, not in a beaker.
The Core Principle: Gas to Solid
The foundation of CVD is a phase transformation. Volatile chemical precursors in a gaseous state are delivered into a reaction chamber. When these gases come into contact with a heated substrate, they undergo a chemical reaction that results in the formation of a solid material, which is then deposited onto that substrate's surface.
Key Components of a CVD System
A typical CVD setup involves four critical elements:
- Reaction Chamber: A controlled environment, often under a vacuum, that contains the reaction.
- Precursor Delivery: A system that introduces precise amounts of the reactive gases into the chamber.
- Substrate: The material or workpiece onto which the new nanomaterial will be grown.
- Energy Source: Most commonly heat, which provides the necessary energy to drive the chemical reaction on the substrate surface.
A Deeper Look: The Chemical Transport Method
One variation of CVD is the chemical transport method. In this technique, a source material first reacts to become a gas. This gas is then transported to a different area of the chamber containing the substrate, where an opposite reaction is triggered, causing the desired material to deposit and grow.
Why CVD is Essential for Nanotechnology
While methods like sol-gel or hydrothermal synthesis exist, CVD has become a cornerstone of modern nanotechnology due to its unique advantages in control and versatility.
Unmatched Control Over Structure
Traditional synthesis methods can be complex and offer limited control over the final shape and size of nanoparticles. CVD excels here, allowing for precise management of film thickness, composition, and morphology down to the atomic level.
Versatility in Material Synthesis
CVD is not limited to simple materials. It is used to fabricate a wide array of structures, from basic thin films of metals to complex, multi-component layers and hybrid materials. This makes it indispensable for applications in nanoelectronics, power electronics, medicine, and aerospace.
A Prime Example: Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs)
The synthesis of carbon nanotubes is a perfect illustration of CVD's power. Catalytic Chemical Vapor Deposition (CCVD) is the dominant method used for producing high-quality CNTs. In this process, a catalyst on the substrate helps break down a carbon-containing precursor gas, enabling the controlled growth of nanotube structures.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
No method is without its challenges. Being a trusted advisor means acknowledging the full picture, including the potential drawbacks.
Complexity and Process Conditions
CVD systems require careful control over temperature, pressure, and gas flow rates. The need for vacuum equipment and precise controls can make the initial setup more complex and costly than some traditional wet-chemical methods.
The Critical Role of Precursors
The choice of precursor chemicals is paramount. They must be volatile enough to be transported as a gas but reactive enough to deposit on the substrate at a reasonable temperature. The wrong precursors can lead to impurities or poor material quality.
Environmental and Energy Impact
As seen with CNT synthesis, the CVD process can be energy-intensive due to the high temperatures required. Furthermore, the lifecycle of the chemical precursors—from their creation to their disposal—carries a potential environmental footprint that must be managed to limit ecotoxicity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a fabrication method depends entirely on your end goal. CVD is a powerful tool, but its application must be strategic.
- If your primary focus is high-purity, uniform thin films for electronics: CVD is a superior choice due to its precise, layer-by-layer deposition control.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective, bulk nanoparticle production: Traditional methods like sol-gel or ball milling might be more economical, though they offer less structural precision.
- If your primary focus is creating complex, layered nanostructures: CVD's ability to switch precursors mid-process makes it an indispensable tool for advanced device fabrication.
Ultimately, Chemical Vapor Deposition empowers engineers and scientists to design and build the foundational materials of future technology from the ground up.
Summary Table:
| CVD Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Bottom-Up Fabrication | Builds materials atom-by-atom or molecule-by-molecule for precise control. |
| Unmatched Structural Control | Allows management of film thickness, composition, and morphology down to the atomic level. |
| Versatile Material Synthesis | Fabricates a wide range of materials, from simple thin films to complex, multi-layer structures. |
| High-Purity Results | Produces ultra-thin films and nanostructures with exceptional purity in a controlled environment. |
Ready to build the next generation of nanomaterials with precision?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables needed for sophisticated processes like Chemical Vapor Deposition. Our expertise can help you achieve the high-purity, uniform thin films and complex nanostructures essential for breakthroughs in nanoelectronics, medicine, and aerospace.
Let's discuss how our solutions can empower your research and development. Contact our experts today to find the perfect equipment for your nanomaterial fabrication goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does applying an amorphous carbon layer via CVD affect electro-Fenton catalysts? Enhance H2O2 Selectivity Today
- What equipment is used to grow lab diamonds? HPHT & CVD Diamond Growth Systems Explained
- What are the benefits and applications of Atomic Layer Chemical Vapour Deposition (ALCVD)? Unlock Atomic Precision
- How does CVD work? A Step-by-Step Guide to Chemical Vapor Deposition
- How does chemical vapor deposition work in diamonds? Grow High-Purity Diamonds Layer by Layer
- What is sputtering in metal deposition techniques? Achieve Superior Thin-Film Coatings
- What are the advantages of chemical vapour deposition method for synthesis of nanomaterials? Precision Engineering at the Nanoscale
- What role does a gas control system play in the formation of alternating metal-ceramic structures? Master Cermet Coating



















