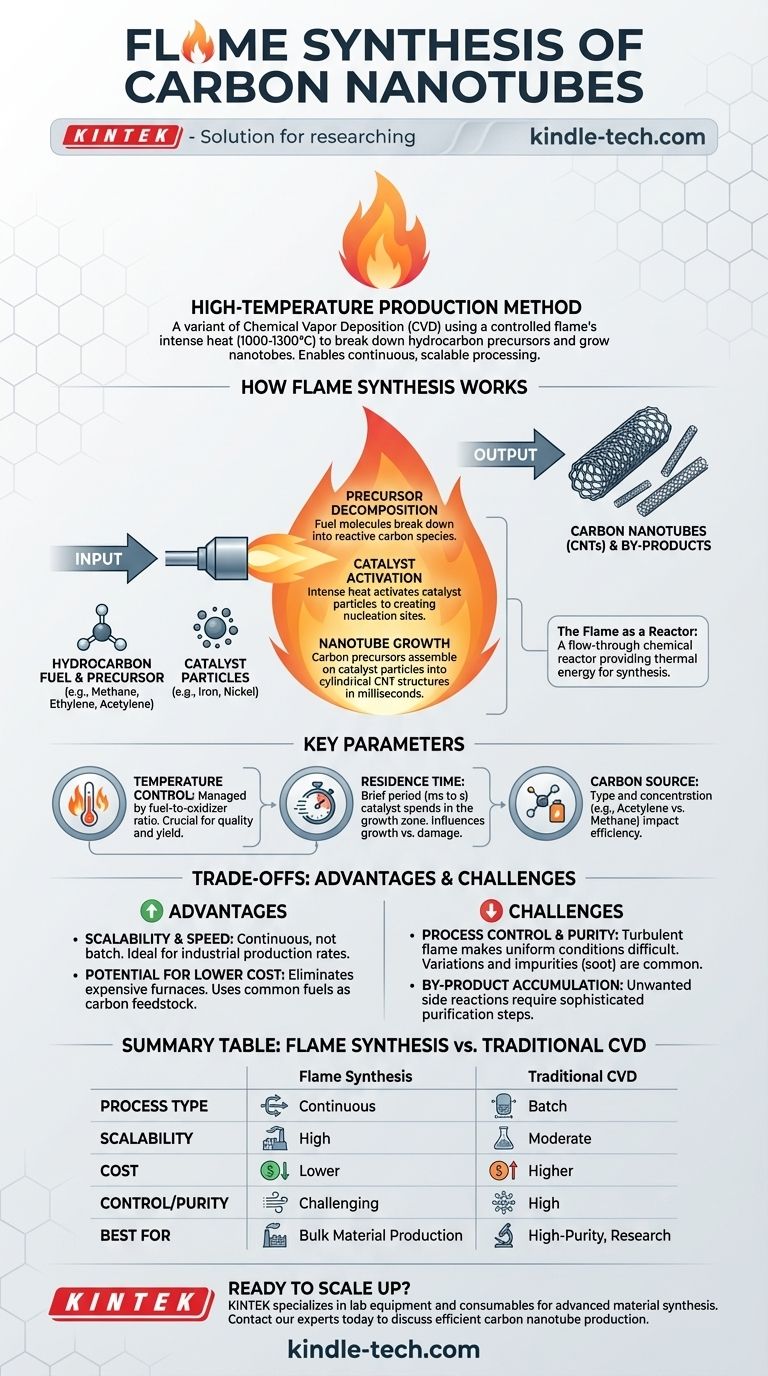
Flame synthesis of carbon nanotubes is a high-temperature production method where the energy from a controlled flame is used to break down hydrocarbon precursors and grow the nanotubes. It is a variant of Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) that leverages combustion for the intense heat required, enabling a continuous and highly scalable process.
Flame synthesis represents a shift from the controlled, enclosed environment of a furnace to the dynamic, high-energy environment of a flame. While it offers immense potential for low-cost, large-scale production, its primary challenge lies in precisely controlling the complex combustion chemistry to achieve high-quality nanotubes.
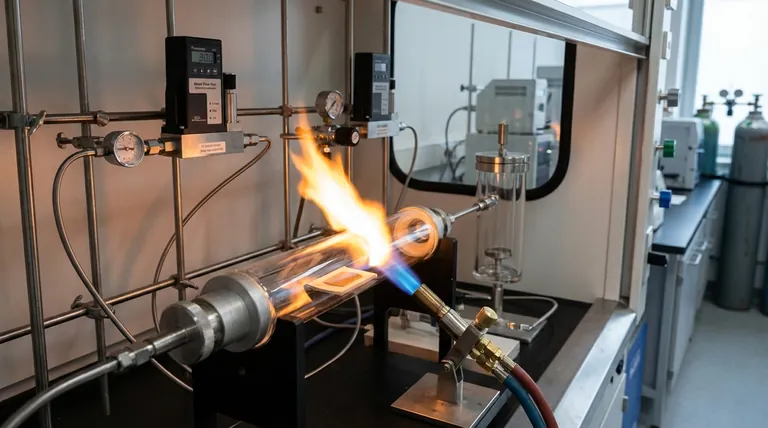

How Flame Synthesis Works
Flame synthesis uses the fundamental principles of CVD but replaces the furnace with a flame as the energy source. The entire process of precursor decomposition, catalyst activation, and nanotube growth occurs within seconds inside the flame itself.
The Role of the Flame as a Reactor
A carefully controlled flame, typically burning a hydrocarbon fuel, creates a high-temperature zone (often 1000-1300°C). This zone acts as a flow-through chemical reactor, providing the thermal energy necessary to initiate the synthesis process.
Carbon Source and Precursor Formation
The fuel for the flame (like methane, ethylene, or acetylene) often doubles as the carbon source for the nanotubes. As mentioned in production principles, different hydrocarbons require different energy levels for conversion. A flame must be hot enough to break these molecules down into reactive carbon species, or "precursors."
Catalyst Activation and Growth
Tiny metallic catalyst particles (e.g., iron, nickel) are introduced into the flame. The intense heat activates these particles, which then serve as nucleation sites. The carbon precursors land on these catalyst particles and assemble into the cylindrical, hexagonal lattice structure of a carbon nanotube.
Key Parameters in a Flame Environment
The critical operating parameters of any CNT synthesis—temperature, carbon source, and residence time—take on unique dimensions in a flame.
Temperature Control
Unlike a furnace with a setpoint, flame temperature is managed by the fuel-to-oxidizer ratio. Adjusting the flow of the hydrocarbon gas and oxygen (or air) changes the flame's temperature profile, which directly impacts the quality and yield of the nanotubes.
Residence Time
Residence time is the brief period (milliseconds to seconds) that the catalyst particles spend in the optimal growth zone of the flame. If the time is too short, growth is insufficient. If it is too long, the nanotubes can be damaged or coated with unwanted by-products like amorphous carbon.
Carbon Source Concentration
The type and concentration of the carbon source are critical. Using a fuel like acetylene can be more efficient as it can act as a direct precursor without needing as much energy for thermal conversion compared to a more stable molecule like methane.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Flame synthesis is a powerful technique, but it involves a distinct set of advantages and challenges compared to more conventional methods.
Advantage: Scalability and Speed
Because the process is continuous and not confined to a batch reactor, flame synthesis is exceptionally scalable. Production rates can be orders of magnitude higher than traditional furnace-based CVD, making it ideal for industrial applications.
Advantage: Potential for Lower Cost
This method eliminates the need for expensive, energy-intensive high-temperature furnaces. Using common fuels as the carbon feedstock can also reduce raw material costs, contributing to more economical production.
Challenge: Process Control and Purity
Flames are turbulent, complex environments. Achieving uniform temperature and chemical composition is significantly harder than in a stable furnace. This can lead to variations in nanotube diameter, length, and the formation of impurities like soot, which can be difficult to separate from the final product.
Challenge: By-product Accumulation
The very nature of combustion means that unwanted side reactions can occur, leading to the creation and accumulation of by-products. This requires sophisticated process control and downstream purification steps to achieve high-purity material.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a synthesis method depends entirely on your end goal, whether it's bulk production or precision engineering.
- If your primary focus is large-scale, low-cost production: Flame synthesis is a leading candidate due to its unmatched speed and potential for continuous, high-volume output.
- If your primary focus is high purity for electronics or research: Traditional furnace CVD or arc-discharge methods offer more precise control over the synthesis environment, often resulting in a higher-quality product with fewer defects.
- If your primary focus is creating hybrid materials: The open-atmosphere nature of flame synthesis allows for the direct incorporation of other additives into the flame to create unique hybrid products in a single step.
Ultimately, mastering flame synthesis empowers you to transform simple fuels directly into advanced nanomaterials at an industrial scale.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Flame Synthesis | Traditional CVD |
|---|---|---|
| Process Type | Continuous | Batch |
| Scalability | High (Industrial) | Moderate (Lab/Pilot) |
| Cost | Lower (Uses fuel as carbon source) | Higher (Energy-intensive furnace) |
| Control/Purity | Challenging (Turbulent flame) | High (Stable furnace environment) |
| Best For | Bulk material production | High-purity, research-grade CNTs |
Ready to scale up your nanomaterial production?
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for advanced material synthesis. Whether you are exploring flame synthesis or optimizing traditional CVD processes, our expertise and products can support your R&D and scale-up goals.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can help you achieve efficient and reliable carbon nanotube production.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the precursors for carbon nanotubes? Optimize Your CNT Synthesis for Cost and Efficiency
- Are carbon nanotubes used in industry? Unlocking High-Performance Materials
- How does diamond like coating work? Unlock Superior Hardness and Low Friction
- What are the major functions of the synthetic graphene? Unlock Next-Gen Electronics and Materials
- What are the limitations of sputtering? High Costs, Slow Speeds, and Material Damage
- What are thin films used for? Unlock Advanced Material Properties for Your Applications
- What are the applications of semiconductor thin films? Powering the Core of Modern Electronics
- How high of temperature do carbon nanotubes in air have the ability to sustain? Understanding the Oxidation Limit



















