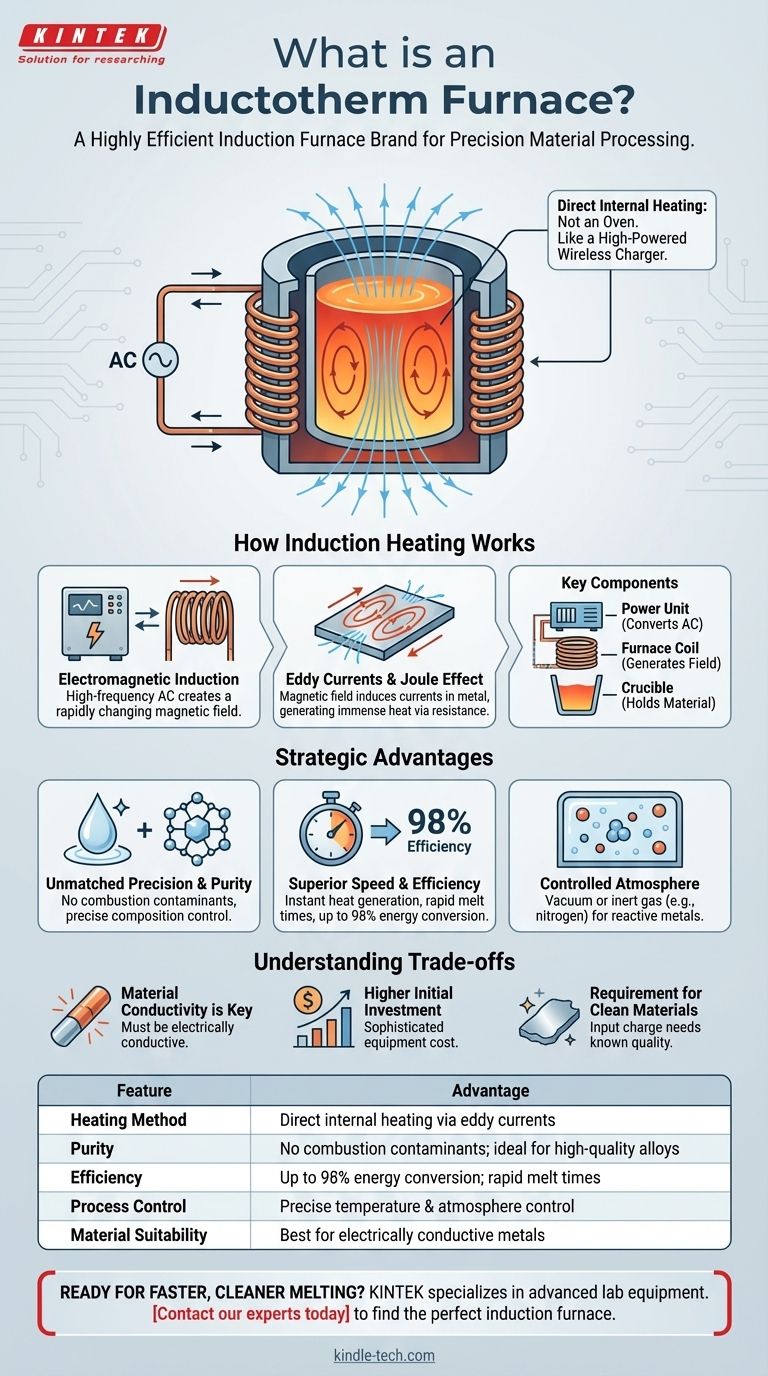
At its core, an Inductotherm furnace is a brand of induction furnace, a highly efficient system that uses electromagnetic principles to melt metal and other conductive materials. Unlike a traditional furnace that uses flames or external heating elements, an induction furnace generates heat directly within the material itself. This is achieved by passing a powerful alternating current through a copper coil, which creates a fluctuating magnetic field that induces electrical currents inside the metal, causing it to rapidly heat up and melt from the inside out.
The crucial concept to understand is that an induction furnace is not an oven. It functions more like a high-powered wireless charger, using an electromagnetic field to transfer energy directly into the metal charge, which results in exceptionally fast, clean, and controllable heating.

How Induction Heating Works
The technology behind an induction furnace is both elegant and powerful, relying on a fundamental principle of physics to achieve its results.
The Principle of Electromagnetic Induction
An induction furnace operates by sending a high-frequency alternating current (AC) through a large, water-cooled copper coil. This coil surrounds a container, known as a crucible, which holds the metal to be melted. The flow of AC electricity through the coil generates a powerful and rapidly changing magnetic field around the crucible.
The Role of Eddy Currents
This magnetic field penetrates the conductive metal inside the crucible, inducing circulating electrical currents within it. These currents are known as eddy currents. The metal has a natural resistance to the flow of these eddy currents, and this resistance generates immense heat—a phenomenon known as the Joule effect. This is what melts the metal, all without any direct contact from a heat source.
Key Furnace Components
While designs vary, the core system consists of three main parts:
- The Power Unit: This component converts mains electricity into the high-frequency, high-power current needed to drive the process.
- The Furnace Coil: A hollow copper coil through which water flows for cooling. This coil generates the critical magnetic field.
- The Crucible: A refractory-lined container that holds the metal charge. It must withstand extreme temperatures while being non-reactive with the molten material.
The Strategic Advantages of Induction
The unique heating method of an induction furnace provides several distinct operational advantages over traditional fuel-fired or arc furnaces.
Unmatched Precision and Purity
Because there is no combustion of fuel, there are no impurities introduced into the melt. This makes induction furnaces ideal for producing high-quality alloys with a very precise and repeatable chemical composition. The electromagnetic field also creates a natural stirring action in the molten metal, ensuring a homogenous mixture.
Superior Speed and Efficiency
Heat is generated instantly and directly within the metal charge. There is no need to first heat a chamber or wait for heat to transfer through a container wall. This results in significantly faster melt times and a very high power efficiency, with some designs reaching up to 98% efficiency in converting electrical energy to heat.
Controlled Atmosphere Processing
Induction furnaces can be easily enclosed and operated under a vacuum or with an inert gas atmosphere, such as nitrogen. This is critical when working with metals that readily oxidize or for specialized processes like carburizing (a type of surface hardening) and sintering advanced technical ceramics.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, induction technology is not universally applicable. Understanding its limitations is key to making an informed decision.
Material Conductivity is Key
The primary requirement for induction heating is that the material itself must be electrically conductive. While non-conductive materials like ceramics can be processed, it often requires using a conductive crucible to act as the heating element, which then transfers heat to the material through conventional means.
Higher Initial Investment
Induction furnace systems are sophisticated pieces of equipment involving advanced power electronics. Consequently, their initial capital cost is typically higher than that of simpler, fuel-fired furnace technologies.
Requirement for Clean Materials
The process relies on melting a charge of known quality. While the stirring effect promotes homogeneity, it is not as effective at removing slag or impurities as some other melting methods. Therefore, the input material (scrap metal or charge) generally needs to be cleaner.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right furnace technology depends entirely on your operational priorities and the materials you are working with.
- If your primary focus is high-purity alloys and exact composition: Induction is the superior choice for its clean, non-contaminating melting and precise temperature control.
- If your primary focus is speed and energy efficiency: The direct, instant heating of induction offers unmatched performance for melting conductive metals quickly.
- If your primary focus is specialized heat treatment or reactive metals: The ability to precisely control the atmosphere makes induction ideal for applications beyond simple melting.
Ultimately, an induction furnace leverages fundamental physics to provide a clean, fast, and highly controllable method for transforming materials with heat.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Advantage |
|---|---|
| Heating Method | Direct internal heating via eddy currents (Joule effect) |
| Purity | No combustion contaminants; ideal for high-quality alloys |
| Efficiency | Up to 98% energy conversion; rapid melt times |
| Process Control | Precise temperature & atmosphere control (vacuum/inert gas) |
| Material Suitability | Best for electrically conductive metals |
Ready to achieve faster, cleaner, and more precise melting in your lab?
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including induction furnaces. Our solutions are designed to enhance your material processing with superior efficiency and control, ensuring high-purity results for your most demanding applications.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect induction furnace for your laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide for Safe and Effective Maintenance
- How does a quartz tube vacuum furnace contribute to the crystallization process of Ag-doped Li-argyrodite electrolytes?
- How do a quartz tube reactor and atmosphere furnace collaborate in Co@NC pyrolysis? Master Precision Synthesis
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing
- Why is a quartz tube furnace utilized in the thermal oxidation of MnCr2O4 coatings? Unlock Precise Selective Oxidation



















