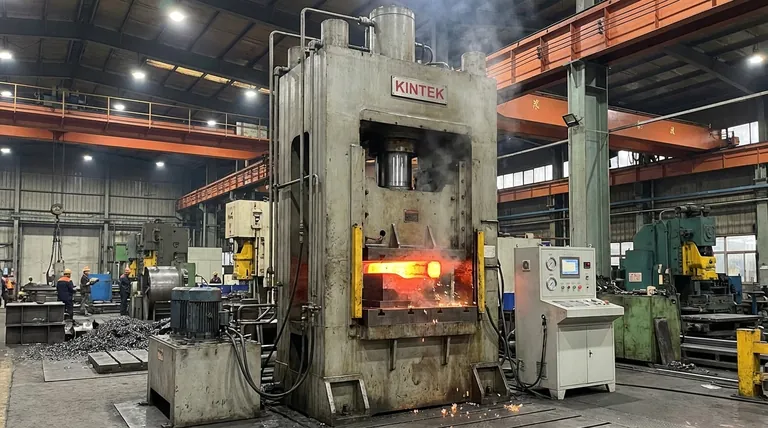
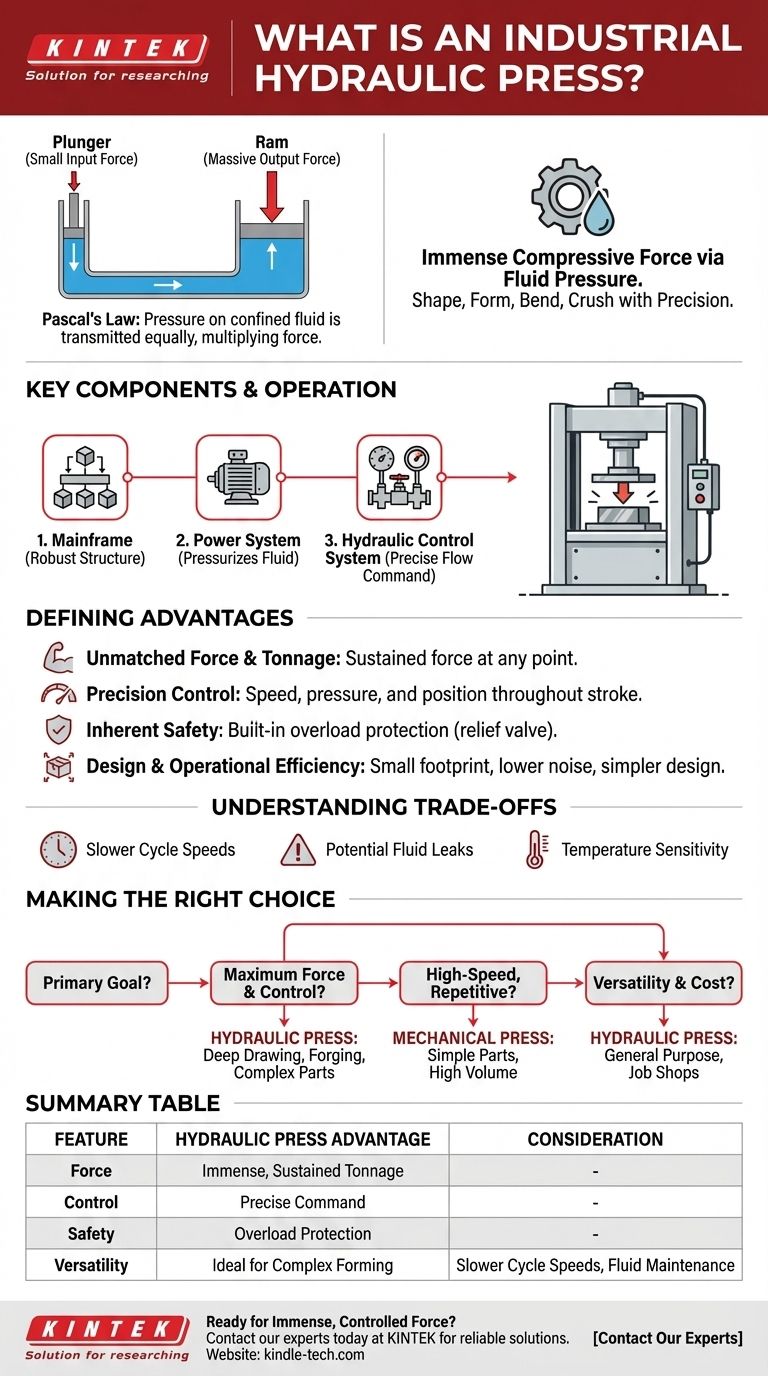
At its core, an industrial hydraulic press is a machine tool that uses hydraulic fluid pressure to generate immense compressive force. It operates based on Pascal's law, where a small force applied to a confined fluid in a small cylinder is multiplied into a massive force in a larger cylinder. This principle allows it to shape, form, bend, and crush even the most robust materials with precision.
A hydraulic press is not just about raw power; it's about control. By leveraging the properties of a confined fluid, it translates a small, manageable input into an enormous, highly controllable output force, making it a cornerstone of modern manufacturing.

How a Hydraulic Press Achieves Immense Force
To understand the value of a hydraulic press, you must first grasp the elegant physics behind its operation. It is a system where components work in unison to multiply force.
The Core Principle: Pascal's Law
A hydraulic press functions on Pascal's law. This fundamental principle of fluid mechanics states that pressure exerted on a confined, incompressible fluid is transmitted equally in all directions throughout the fluid.
Imagine pressing down on a small piston (the plunger) connected to a larger piston (the ram) by a tube filled with oil. The pressure you create under the small piston is transferred without loss to the entire surface of the large piston, generating a proportionally larger output force.
Key Components Working in Unison
An industrial press is typically composed of three primary systems:
- The Mainframe: This is the robust structure that houses the components and withstands the immense forces generated.
- The Power System: This includes the motor and pump responsible for pressurizing the hydraulic fluid.
- The Hydraulic Control System: This consists of valves, pipes, and controls that direct the flow and pressure of the fluid, giving the operator precise command over the press's movement and force.
The Plunger and the Ram
The heart of the force multiplication is the relationship between two cylinders. A small-diameter cylinder, known as the plunger, receives the initial force from the power system. This creates pressure in the hydraulic fluid.
This pressure then acts upon a much larger-diameter cylinder, the ram. Because the surface area of the ram is many times greater than the plunger, the resulting output force is magnified by the same factor, enabling the machine to generate thousands of tons of force.
The Defining Advantages in an Industrial Setting
The hydraulic press is not the only type of press, but its unique characteristics make it indispensable for a wide range of applications.
Unmatched Force and Tonnage
The primary advantage is the ability to generate immense and sustained force. Unlike mechanical presses that deliver maximum force only at the bottom of the stroke, a hydraulic press can deliver its full rated force at any point.
Precision Control Over Speed and Pressure
Operators have complete control over the ram's speed, pressure, and position throughout the stroke. This allows for complex operations like deep drawing or forming unique geometries, where the material must be manipulated carefully to avoid defects.
Inherent Safety and Durability
Hydraulic systems have built-in overload protection. If the force required exceeds the machine's capacity, a pressure relief valve opens, preventing damage to the machine or the tooling. This simple design with fewer moving parts also contributes to a longer tool lifespan.
Design and Operational Efficiency
For the power they produce, hydraulic presses can have a relatively small footprint. Their design is simpler than complex mechanical presses, often resulting in lower initial and maintenance costs. They also operate with significantly less noise.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No technology is without its limitations. Being a trusted advisor means acknowledging the areas where a hydraulic press may not be the optimal choice.
Slower Cycle Speeds
The primary trade-off is speed. The movement of fluid takes time, making hydraulic presses generally slower than their mechanical counterparts. For high-volume, repetitive stamping operations, a mechanical press is often faster.
Potential for Fluid Leaks
As with any hydraulic system, there is a risk of fluid leaks. This requires diligent maintenance to ensure seals and hoses are in good condition to prevent environmental contamination and loss of performance.
Temperature Sensitivity
The viscosity of hydraulic fluid can change with temperature, which can affect the press's performance and consistency. In many industrial applications, hydraulic coolers are integrated to maintain a stable operating temperature.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct press technology depends entirely on your project's specific goals for force, speed, and control.
- If your primary focus is maximum force and control: The hydraulic press is ideal for deep drawing, forging, compression molding, and forming complex parts where sustained pressure is critical.
- If your primary focus is high-speed, repetitive stamping: A mechanical press is likely the superior choice due to its faster cycle times for producing large quantities of simple parts.
- If your primary focus is versatility and cost-effectiveness: The simple design and adaptability of a hydraulic press make it an excellent general-purpose tool for job shops that handle a wide variety of tasks.
Ultimately, understanding the fundamental principle of force multiplication is the key to leveraging a hydraulic press to its full potential.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Hydraulic Press Advantage |
|---|---|
| Force | Delivers immense, sustained tonnage at any point in the stroke |
| Control | Precise command over speed, pressure, and ram position |
| Safety | Built-in overload protection prevents machine damage |
| Versatility | Ideal for deep drawing, forging, molding, and complex part forming |
| Consideration | Slower cycle speeds than mechanical presses; requires fluid maintenance |
Ready to apply immense, controlled force to your manufacturing process?
At KINTEK, we specialize in robust laboratory and industrial equipment, including hydraulic presses designed for precision and durability. Whether you're involved in material testing, sample preparation, or complex part fabrication, our solutions deliver the reliability and control your lab demands.
Contact our experts today to discuss how a KINTEK hydraulic press can enhance your capabilities and efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press Machine for Glove Box
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- 24T 30T 60T Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- What kind of press do blacksmiths use? The Ultimate Guide to Hydraulic Forging Presses
- What is a BARS press? Discover the Engineering Secrets to Growing Large, Gem-Quality Diamonds
- How much PSI does a hydraulic actuator usually operate at? A Guide to Industrial & High-Pressure Ranges
- What is the function of a laboratory hydraulic press in nanocellulose prep? Unlock Ultra-High Strength Materials
- What is an automatic press machine? High-Precision Force for Modern Manufacturing
- Is KBr used in IR spectroscopy? The Essential Guide to Solid Sample Analysis
- What is the function of a laboratory hydraulic press and a 15 mm circular mold? Create Dense Oxygen Membrane Green Bodies
- What role does a laboratory hydraulic press play in sulfide-based solid-state batteries? Achieve Optimal Densification



















