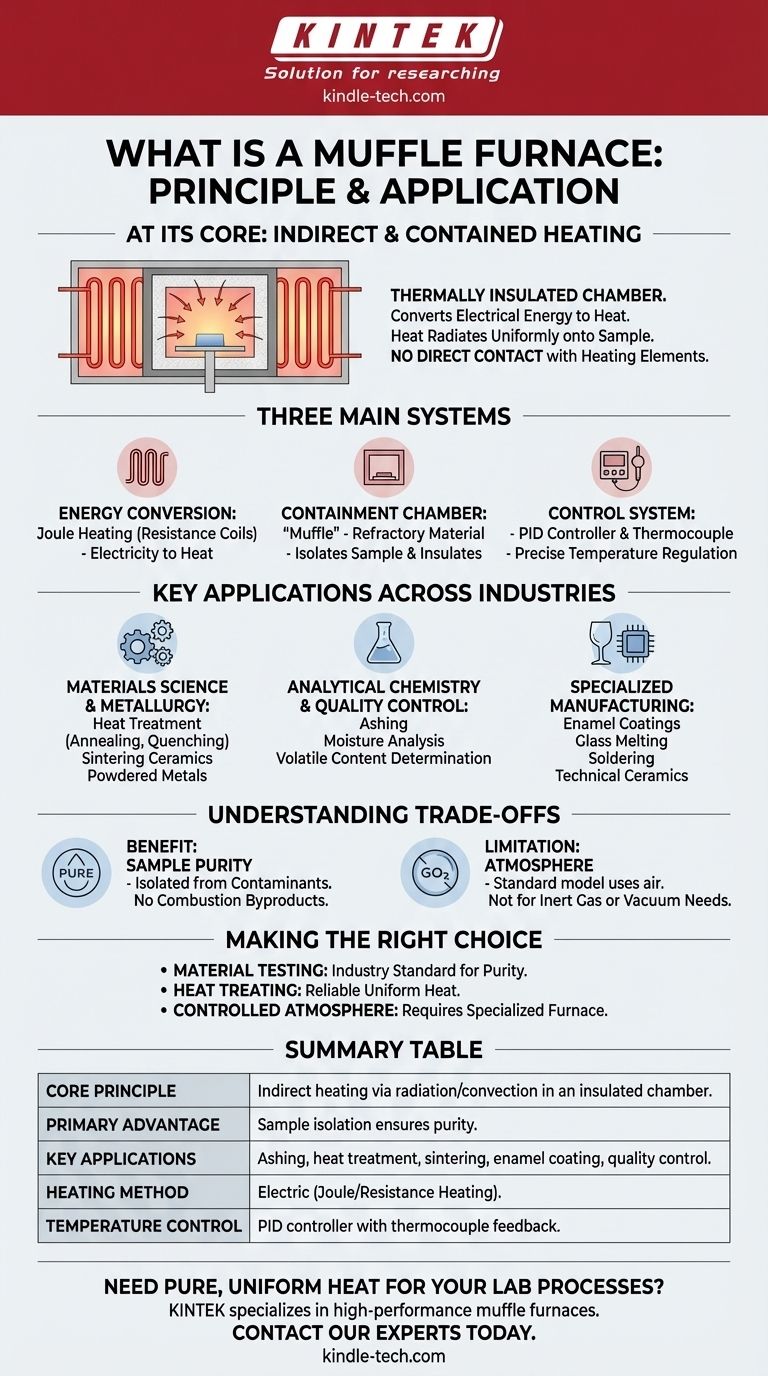
At its core, a muffle furnace operates on the principle of indirect heating within a thermally insulated chamber. It converts electrical energy into heat, which is then radiated uniformly onto a sample without the heating elements making direct contact. This method is essential for applications ranging from heat-treating metals and sintering ceramics to performing highly sensitive chemical analyses like determining the ash content of a material.
The defining characteristic of a muffle furnace is not just high heat, but sample isolation. Its design separates the material being heated from the raw heating elements and external contaminants, ensuring both uniform temperature and high sample purity.
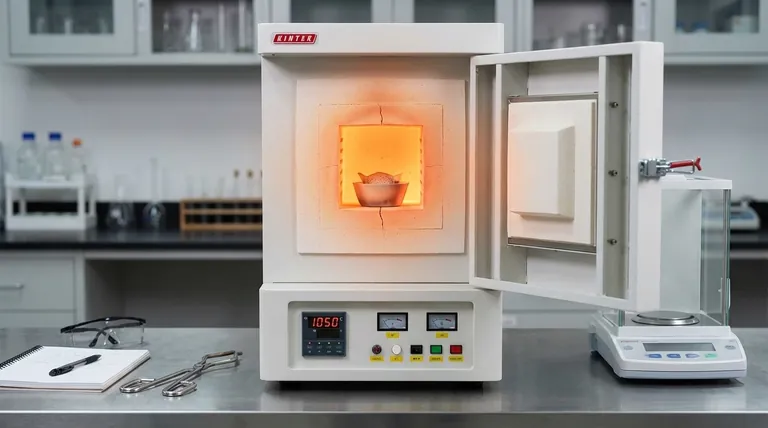

The Core Principle: Indirect and Contained Heating
Understanding how a muffle furnace works requires looking at its three main systems: the energy conversion system, the containment chamber, and the control system.
From Electrical Energy to Thermal Energy
A modern muffle furnace is an electric furnace. It operates on the principle of Joule heating, also known as resistance heating.
High-resistance heating coils, often made of materials like Nichrome or Kanthal, are mounted along the walls of the furnace. When a high electric current passes through these coils, their resistance causes them to become extremely hot, converting electrical energy directly into thermal energy.
The "Muffle" Chamber
This is the key component that gives the furnace its name. The "muffle" is the inner chamber that holds the sample.
It is constructed from high-temperature refractory materials, such as dense ceramic bricks. This chamber serves two critical purposes: it separates the sample from the glowing-hot heating elements and provides exceptional thermal insulation to prevent heat from escaping.
Heat Transfer and Uniformity
The sample inside the chamber is not heated directly by the coils. Instead, the coils heat the walls of the muffle chamber.
These hot walls then transfer thermal energy to the sample primarily through radiation and convection. This indirect method ensures a highly uniform temperature distribution across the entire workpiece, which is critical for consistent results.
Precision Temperature Control
A muffle furnace is not simply a hot box; it is a precision instrument. A thermocouple acts as a temperature sensor inside the chamber.
This sensor continuously sends feedback to a PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) controller, which intelligently regulates the power sent to the heating coils to maintain a precise temperature setpoint with minimal fluctuation.
Key Applications Across Industries
The principle of isolated, uniform heating makes the muffle furnace an indispensable tool in a wide range of scientific and industrial fields.
Materials Science and Metallurgy
The controlled heating environment is ideal for modifying the physical properties of materials. This includes heat treatment of metals like annealing, quenching, and tempering, as well as the high-temperature sintering of ceramics and powdered metals to create dense, solid components.
Analytical Chemistry and Quality Control
Muffle furnaces are fundamental in laboratories for preparing or analyzing samples where high temperatures are required. Common uses include ashing, which burns off organic matter to determine the non-combustible ash content of a sample, and determining moisture or volatile content.
Specialized Manufacturing
Industries rely on muffle furnaces for processes that demand precision and purity. This includes creating enamel coatings on metal, melting small batches of glass, soldering and brazing complex parts, and producing technical ceramics for dental or electronic applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a muffle furnace is not the universal solution for all high-temperature needs. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
The Benefit of Purity
The primary advantage is sample integrity. Because the sample is isolated from the heating elements, there is no risk of contamination from the coils or, in older fuel-fired designs, from the byproducts of combustion. This is non-negotiable for analytical work.
The Limitation of Atmosphere
A standard muffle furnace operates with the air that is inside the chamber. It does not inherently control the atmosphere. For processes that require an inert gas (like argon) or a vacuum to prevent oxidation, a more specialized tube furnace or vacuum furnace is necessary.
The Consideration of Speed
The indirect heating method that ensures uniformity can sometimes result in slower heating and cooling cycles compared to direct heating methods. For high-throughput applications, this may be a factor to consider.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct heating instrument depends entirely on your end goal. The muffle furnace is a specialized tool designed for purity and uniformity.
- If your primary focus is material testing (e.g., ashing or moisture analysis): The muffle furnace is the industry standard due to its precise temperature control and prevention of sample contamination.
- If your primary focus is heat treating common metals and alloys: The uniform, indirect heat of a muffle furnace provides reliable and repeatable results for processes like annealing and tempering.
- If your primary focus requires a controlled, non-air atmosphere: A standard muffle furnace is insufficient; your application demands a specialized tube, vacuum, or retort furnace.
Understanding this core principle of isolated heating empowers you to select the right tool for achieving pure and precise high-temperature results.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Core Principle | Indirect heating via radiation/convection in an insulated chamber |
| Primary Advantage | Sample isolation ensures purity and prevents contamination |
| Key Applications | Ashing, heat treatment, sintering, enamel coating, quality control |
| Heating Method | Electric (Joule/Resistance Heating) |
| Temperature Control | PID controller with thermocouple feedback for precision |
| Ideal For | Processes requiring uniform heat and sample integrity in air |
Need pure, uniform heat for your lab processes?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including muffle furnaces designed for precision ashing, heat treatment, and sintering. Our furnaces ensure sample integrity and consistent results for your laboratory's most demanding applications.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect heating solution for your needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the different types of laboratory furnaces? Find the Perfect Fit for Your Application
- What is the difference between a furnace and oven? Understanding Their Unique Heating Purposes
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of muffle furnace? Achieve Absolute Purity and Control in Your Lab
- What is the operating range of a muffle furnace? Unlock the Key to Your High-Temperature Tasks
- What is the temperature of heat treatment? It Depends on Your Metal and Desired Properties



















