The fundamental difference between sintering and melting in additive manufacturing is the state of the material during processing. Sintering fuses material particles together using heat and pressure without fully liquefying them. In contrast, melting-based processes use a focused energy source to heat the material past its melting point, turning it completely liquid before it cools and solidifies.
The choice between a sintering or melting process is not just a technical detail; it is the primary factor that determines the final density, porosity, and mechanical strength of your 3D-printed part.
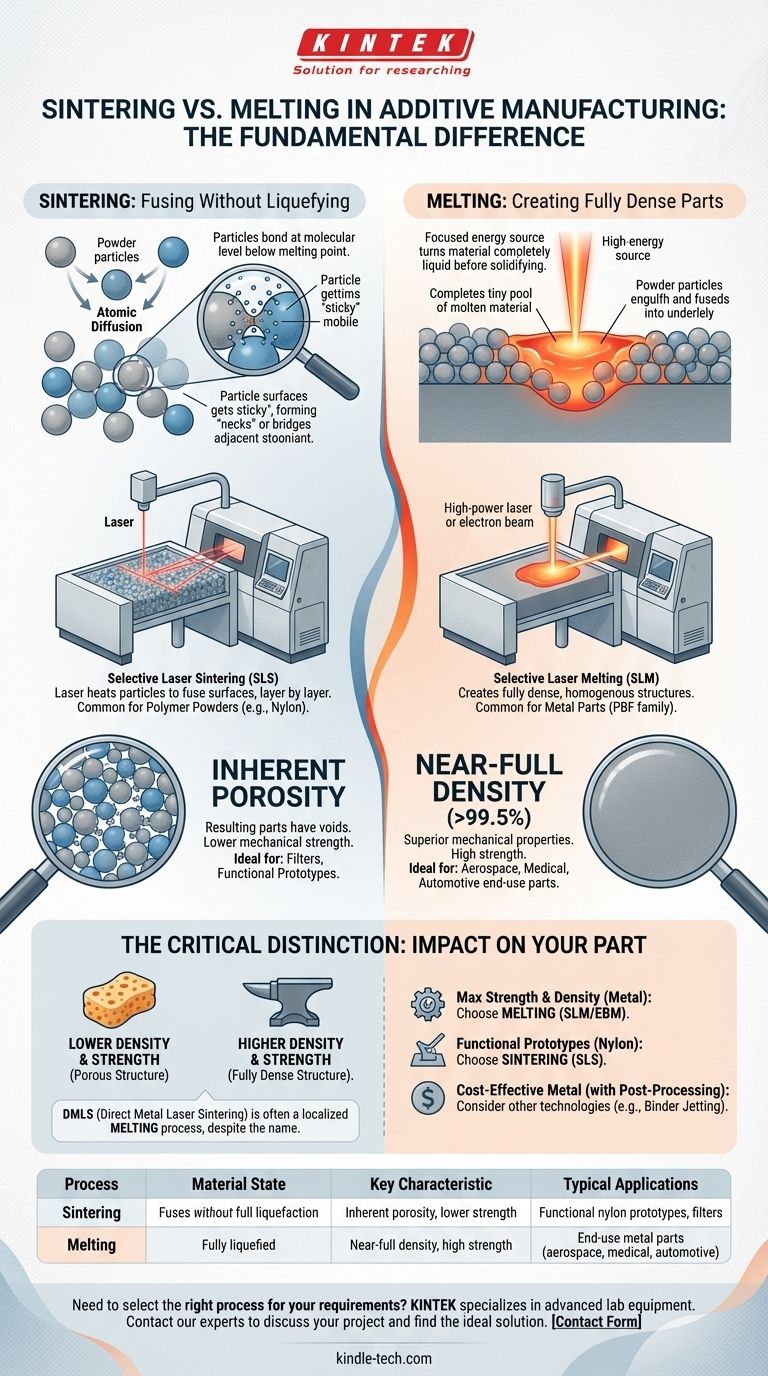
Deconstructing Sintering: Fusing Without Liquefying
Sintering is a thermal process where particles bond at a molecular level, reducing the empty space, or pores, between them. This happens at temperatures below the material's melting point.
The Core Mechanism: Atomic Diffusion
Think of sintering as particles getting "sticky" at high temperatures. The atoms on the surface of adjacent powder particles become mobile and diffuse across the boundaries, creating solid bridges or "necks" where they touch.
Over time, these necks grow, pulling the particles closer together and forming a solid, yet often porous, mass.
How It Works in Practice
The most common example is Selective Laser Sintering (SLS), used primarily with polymer powders like nylon. A laser scans the powder bed, heating the particles just enough for their surfaces to fuse together, layer by layer.
Key Characteristic: Inherent Porosity
Because the material never becomes a complete liquid that can fill all voids, sintered parts typically have some degree of residual porosity. This can be a desired feature for applications like filters, but it often results in lower mechanical strength compared to fully melted parts.
Understanding Melting: Creating Fully Dense Parts
Melting-based processes are the dominant method for producing high-strength metal and high-performance polymer parts. They aim to create components that are as dense as possible.
The Core Mechanism: Complete Liquefaction
In these methods, a high-energy source—like a laser or electron beam—is used to melt the powder particles completely. This creates a tiny pool of molten material that fully fuses with the underlying solid layer.
As the energy source moves on, this molten pool cools and solidifies, forming a dense, homogenous structure with minimal voids.
How It Works in Practice
Technologies like Selective Laser Melting (SLM) and Electron Beam Melting (EBM) are prime examples. They are part of the Powder Bed Fusion (PBF) family of processes and are used to create metal parts with properties that can meet or exceed those made through traditional casting or forging.
The Critical Distinction: Why It Matters for Your Part
The decision to use a process based on sintering versus melting directly impacts the final part's performance characteristics and suitability for a given application.
Impact on Material Density
Melting creates fully dense parts (typically >99.5% density). This is critical for applications where strength, fatigue resistance, and pressure-tightness are non-negotiable.
Sintering results in porous parts. While post-processing steps like infiltration can increase density, the as-printed component will have microscopic voids between the fused particles.
Consequences for Mechanical Strength
Higher density almost always translates to superior mechanical properties. Parts made via melting processes are significantly stronger and more durable than their sintered counterparts, making them suitable for end-use functional components in aerospace, medical, and automotive industries.
A Note on Terminology: The "Sintering" Confusion
In the world of metal 3D printing, the terminology can be misleading. A popular process called Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) actually involves a localized melting of the metal powder, not true solid-state sintering. The term is largely a brand name that has persisted, but for practical purposes, it functions as a melting process to achieve high-density metal parts.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your goal determines the right process.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and density for a functional metal part: You need a melting-based Powder Bed Fusion process like SLM or EBM.
- If your primary focus is producing functional nylon prototypes or parts where some porosity is acceptable: A sintering-based process like SLS is the industry standard and highly effective.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective metal parts where some porosity can be tolerated or fixed in post-processing: Consider a different technology altogether, like binder jetting, which uses sintering as a secondary step.
Ultimately, understanding this core difference empowers you to select the right technology to achieve your desired material properties.
Summary Table:
| Process | Material State | Key Characteristic | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sintering | Particles fuse without full liquefaction | Inherent porosity, lower strength | Functional nylon prototypes, filters |
| Melting | Particles are fully liquefied | Near-full density, high strength | End-use metal parts (aerospace, medical, automotive) |
Need to select the right additive manufacturing process for your specific material and performance requirements? KINTEK specializes in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables for materials research and development. Our experts can help you understand the capabilities of different 3D printing technologies to achieve your desired part density and strength. Contact our team today to discuss your project and find the ideal solution for your laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the sintering temperature of zirconium? A Guide to the 1400°C-1600°C Range for Dental Labs
- What is the temperature of sintering zirconia? Mastering the Protocol for Perfect Dental Restorations
- Can you change the color of zirconia crowns? Understanding the Permanent Nature of Zirconia
- What is the sintering time for zirconia? A Guide to Precise Firing for Optimal Results
- What is a dental oven? The Precision Furnace for Creating Strong, Aesthetic Dental Restorations



















