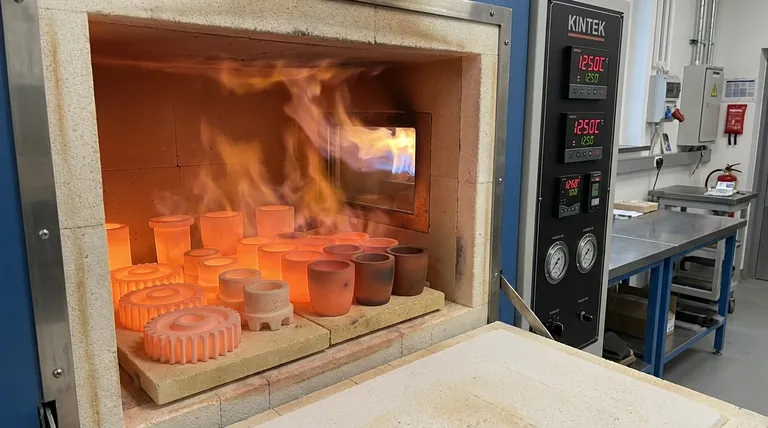
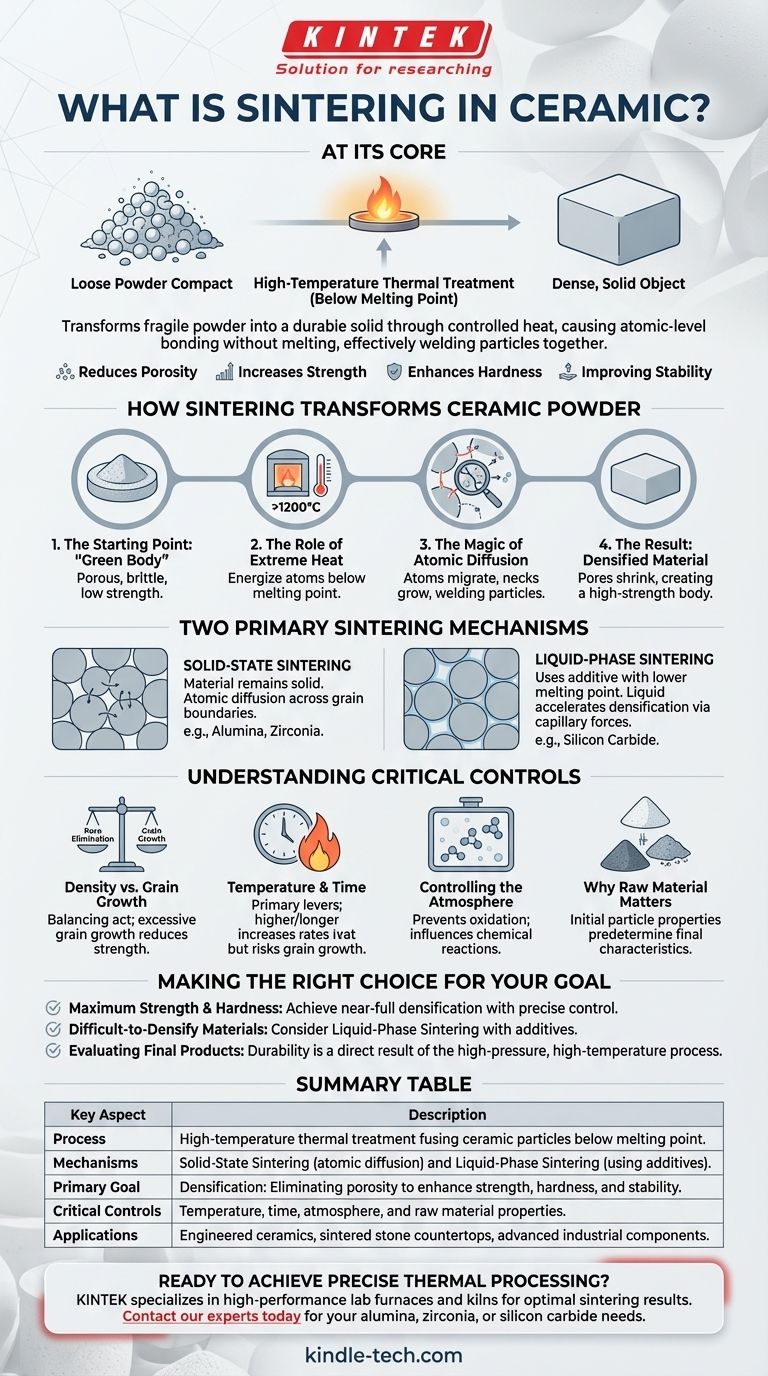
At its core, ceramic sintering is a high-temperature thermal treatment that transforms a compact of loose ceramic powder into a dense, solid object. Through a combination of heat and sometimes pressure, individual particles fuse together—without ever melting—to drastically reduce porosity and significantly increase the material's strength, hardness, and stability.
The fundamental challenge in ceramics is turning a fragile powder into a durable, high-performance solid. Sintering solves this by using controlled heat to drive atomic-level bonding between particles, effectively welding them into a unified, dense structure.

How Sintering Fundamentally Transforms Ceramic Powder
Sintering is not merely drying or baking; it is a sophisticated process of material transformation that dictates the final properties of the ceramic.
The Starting Point: The "Green Body"
The process begins with a "green body," which is ceramic powder (like silica, clay, or zirconia) that has been pressed or formed into the desired shape. At this stage, the object is porous, brittle, and has very low mechanical strength.
The Role of Extreme Heat
The green body is placed in a kiln and heated to a very high temperature, often above 1200°C. Crucially, this temperature is kept below the material's melting point. The goal is not to liquefy the ceramic, but to energize its atoms.
The Magic of Atomic Diffusion
At these elevated temperatures, atoms at the contact points between powder particles become highly mobile. They begin to migrate, or diffuse, across the boundaries of adjacent particles. This movement causes the necks between particles to grow, effectively welding them together.
The Result: A Densified, High-Strength Material
As the particles fuse, the empty spaces (pores) between them shrink and are gradually eliminated. This process, known as densification, is the primary objective of sintering. The resulting object is a solid, non-porous body with the high strength, hardness, and thermal stability characteristic of engineered ceramics.
The Two Primary Sintering Mechanisms
The exact method of sintering depends on the specific ceramic material being processed.
Solid-State Sintering
This is the most common form, used for materials like alumina and zirconia. The entire process occurs while the material remains in a solid state. Material transport happens exclusively through atomic diffusion across the grain boundaries of the particles.
Liquid-Phase Sintering
This method is used for materials that are very difficult to densify, such as silicon carbide. A small amount of an additive is mixed with the primary ceramic powder. This additive has a lower melting point and forms a liquid at the sintering temperature.
This liquid wets the solid particles and pulls them together through capillary forces, dramatically accelerating the densification process before solidifying upon cooling.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Critical Controls
Optimizing the sintering process is essential for achieving the desired physical properties. It is a balancing act of several key parameters.
The Balance Between Density and Grain Growth
While the goal is to eliminate pores, leaving the ceramic at high temperatures for too long can cause the individual crystals, or "grains," to grow excessively large. Overly large grains can create internal stress and actually reduce the material's final strength and fracture toughness.
The Impact of Temperature and Time
Temperature and time are the primary levers for controlling the process. A higher temperature or longer duration increases the rate of diffusion and densification, but also increases the risk of unwanted grain growth. These parameters are carefully engineered for each specific material.
Controlling the Atmosphere
The gas environment inside the kiln can influence the chemical reactions occurring during sintering. A controlled atmosphere (e.g., inert gas, vacuum, or reactive gas) is often used to prevent oxidation or other undesirable effects.
Why Raw Material Matters
The process starts with the powder. The size, shape, and chemical composition of the initial particles (including materials like silica, feldspars, and mineral pigments) predetermine the final properties, such as hardness, chemical stability, and even color.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the principles of sintering allows you to connect a product's properties directly to its manufacturing process.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and hardness: The goal is to achieve near-full densification while tightly controlling grain growth, which demands precise control over the temperature, time, and atmosphere of the sintering cycle.
- If you are working with difficult-to-densify materials: Consider liquid-phase sintering, as the right additive can dramatically improve densification rates and unlock superior final properties that are otherwise unattainable.
- If you are evaluating a final product (like a "sintered stone" countertop): Recognize that its exceptional durability, non-porous nature, and resistance to staining are a direct result of this high-pressure, high-temperature fusion process.
Ultimately, mastering the science of sintering is what transforms humble powders into some of the most advanced and resilient materials in modern use.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Process | High-temperature thermal treatment fusing ceramic particles below melting point. |
| Mechanisms | Solid-State Sintering (atomic diffusion) and Liquid-Phase Sintering (using additives). |
| Primary Goal | Densification: Eliminating porosity to enhance strength, hardness, and stability. |
| Critical Controls | Temperature, time, atmosphere, and raw material properties. |
| Applications | Engineered ceramics, sintered stone countertops, advanced industrial components. |
Ready to achieve precise thermal processing for your ceramic materials? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab furnaces and kilns designed for optimal sintering results. Whether you're working with alumina, zirconia, or silicon carbide, our equipment ensures controlled temperature profiles and atmospheres for maximum densification and material performance. Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your ceramic sintering process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Mesh belt controlled atmosphere furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between calcining and roasting? A Guide to High-Temperature Processing
- What equipment is used in pyrolysis? Choosing the Right Reactor for Your Feedstock and Products
- What are the products of pyrolysis of wood? A Guide to Biochar, Bio-oil, and Syngas Yields
- What biomass is used in pyrolysis? Selecting the Optimal Feedstock for Your Goals
- What is the purpose of a calciner? Boost Efficiency in High-Temperature Processing



















