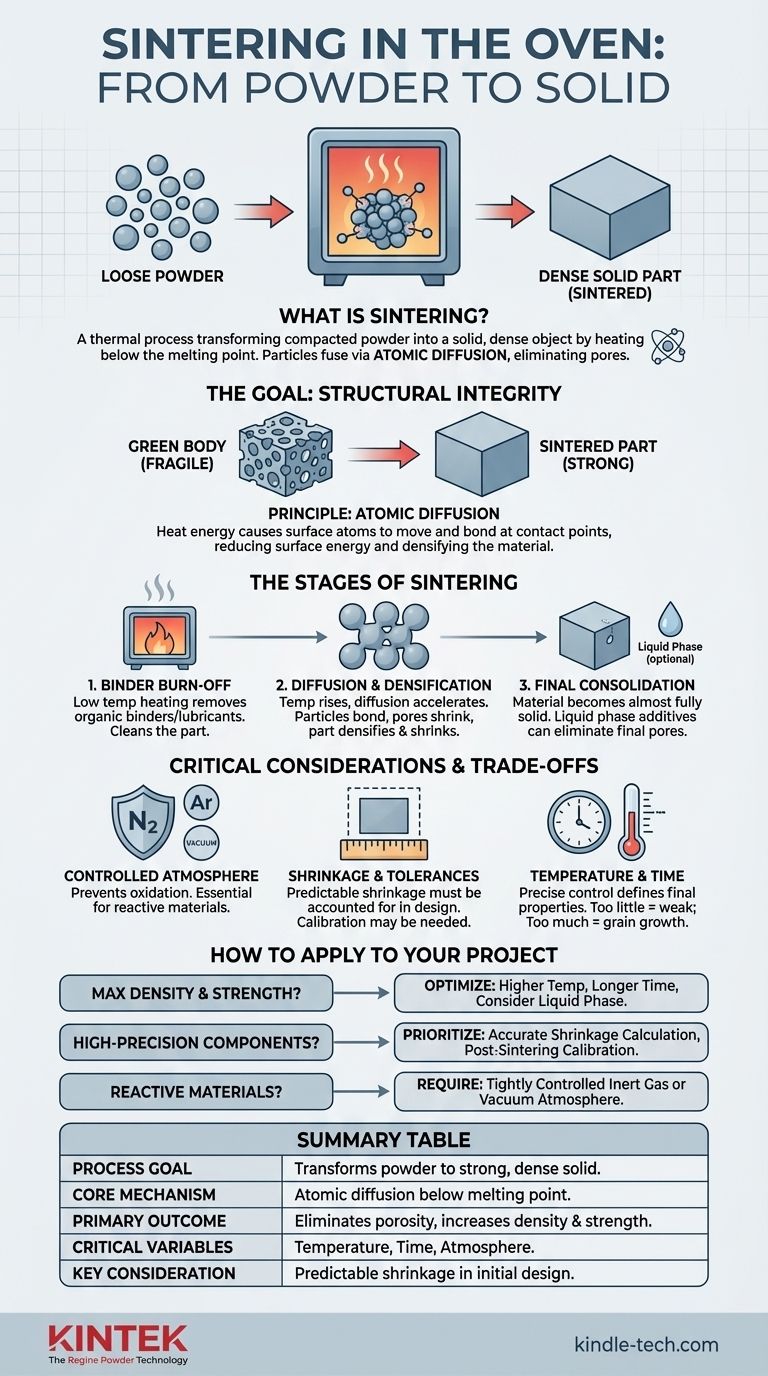
In essence, sintering is a thermal process that transforms a compacted powder into a solid, dense object by heating it in an oven or furnace to a temperature just below its melting point. Instead of melting, the individual powder particles fuse together through atomic diffusion. This process eliminates the empty spaces, or pores, between the particles, resulting in a strong, coherent mass with significantly improved mechanical properties.
The core challenge in powder-based manufacturing is converting a fragile, porous shape into a robust, solid part. Sintering solves this not by melting the material, but by using controlled heat to encourage individual particles to bond and merge, effectively squeezing out internal voids and creating a dense, unified structure.

The Goal of Sintering: From Powder to Solid
Sintering is the critical step that provides structural integrity to parts made from ceramic or metallic powders. The entire process is a journey from a loose collection of particles to a high-performance, engineered component.
The 'Green Body' Starting Point
Before entering the furnace, the raw powder is first pressed into a desired shape using a mold and die. This initial part, known as a "green body" or compact, has the correct geometry but is mechanically fragile and highly porous.
The Principle of Atomic Diffusion
The magic of sintering happens below the material's melting point. The high heat provides energy for atoms on the surfaces of adjacent particles to move and diffusion bond at their points of contact. Think of it like a cluster of soap bubbles merging to reduce their total surface area; the particles fuse to lower their overall surface energy.
The Result: Increased Density and Strength
As particles bond and pull closer together, the gaps and pores between them shrink and eventually close. This densification is the primary goal. By eliminating porosity, the final part becomes significantly stronger, harder, and less permeable than its "green" counterpart.
A Journey Through the Furnace: The Stages of Sintering
When the green body is placed in the furnace, it undergoes a precisely controlled thermal cycle designed to achieve optimal densification.
Stage 1: Binder Burn-Off
In the initial heating phase, at lower temperatures, any organic binders or lubricants used during the pressing stage are burned off. This "cleaning" step is crucial to prevent defects in the final part.
Stage 2: Diffusion Bonding and Densification
As the temperature rises toward the target sintering point, diffusion accelerates. The contact points between particles grow into "necks," pulling the particle centers together. This is where the bulk of shrinkage and pore elimination occurs as the part densifies.
Stage 3: Final Consolidation
In the final stage, the material is almost fully solid, with only isolated, closed-off pores remaining. To eliminate these last voids, the process might involve a technique called liquid phase sintering, where a small amount of an additive melts and flows into the pores, effectively "welding" the structure together from the inside.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
Sintering is a powerful process, but it requires precise control to achieve the desired outcome. Its success depends on managing several critical variables.
Controlled Atmospheres are Crucial
Sintering furnaces often use a controlled atmosphere (e.g., nitrogen, argon, or a vacuum). This is essential to prevent oxidation or other unwanted chemical reactions with the hot material, which could compromise its final properties.
The Challenge of Shrinkage and Tolerances
Because densification involves the elimination of pores, the part will inevitably shrink during sintering. This shrinkage must be accurately predicted and accounted for in the initial design of the green body's tooling. For parts requiring extremely tight tolerances, a post-sintering calibration step (re-pressing the part) may be necessary.
Temperature and Time Define the Outcome
The final properties of a sintered part are directly dependent on the sintering temperature and the time spent in the furnace. Too little heat or time results in incomplete densification and a weak part. Too much can cause unwanted grain growth, which can also degrade mechanical properties.
How to Apply This to Your Project
The specific parameters of your sintering process should be dictated by the end goal for your component.
- If your primary focus is maximum density and strength: You will need to optimize for higher temperatures and longer sintering times, potentially utilizing liquid phase additives to eliminate final porosity.
- If your primary focus is high-precision components: You must prioritize accurate shrinkage calculation in your initial mold design and consider a final calibration step after sintering.
- If you are working with reactive materials (like certain metals): Your chief concern must be the furnace environment, requiring a tightly controlled inert gas or vacuum atmosphere to prevent oxidation.
Ultimately, mastering sintering is about precisely controlling heat, time, and atmosphere to transform simple powder into a high-performance, engineered component.
Summary Table:
| Sintering Aspect | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| Process Goal | Transforms fragile powder compacts into strong, dense solids. |
| Core Mechanism | Atomic diffusion bonds particles below the melting point. |
| Primary Outcome | Eliminates porosity, increases density, and improves mechanical properties. |
| Critical Variables | Temperature, time, and furnace atmosphere (e.g., vacuum, inert gas). |
| Key Consideration | Predictable shrinkage must be accounted for in initial part design. |
Ready to transform your material powders into high-performance components?
Mastering the sintering process is key to achieving the density, strength, and precision your projects demand. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the advanced lab furnaces and expert support you need to perfect your sintering cycle.
We serve laboratories and manufacturers who require precise thermal processing for metals, ceramics, and other materials. Our equipment ensures the controlled atmospheres and exact temperatures critical for successful sintering outcomes.
Contact our thermal processing experts today to discuss how our sintering solutions can bring strength and integrity to your next project.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
People Also Ask
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis
- What is quartz tube heating? Achieve Instant, Targeted Heat with Infrared Radiation
- Why is a quartz tube furnace utilized in the thermal oxidation of MnCr2O4 coatings? Unlock Precise Selective Oxidation
- What is the technical value of using a quartz tube reaction chamber for static corrosion testing? Achieve Precision.
- What materials are used for the tubes in tube furnaces? A Guide to Selecting the Right Tube for Your Process



















