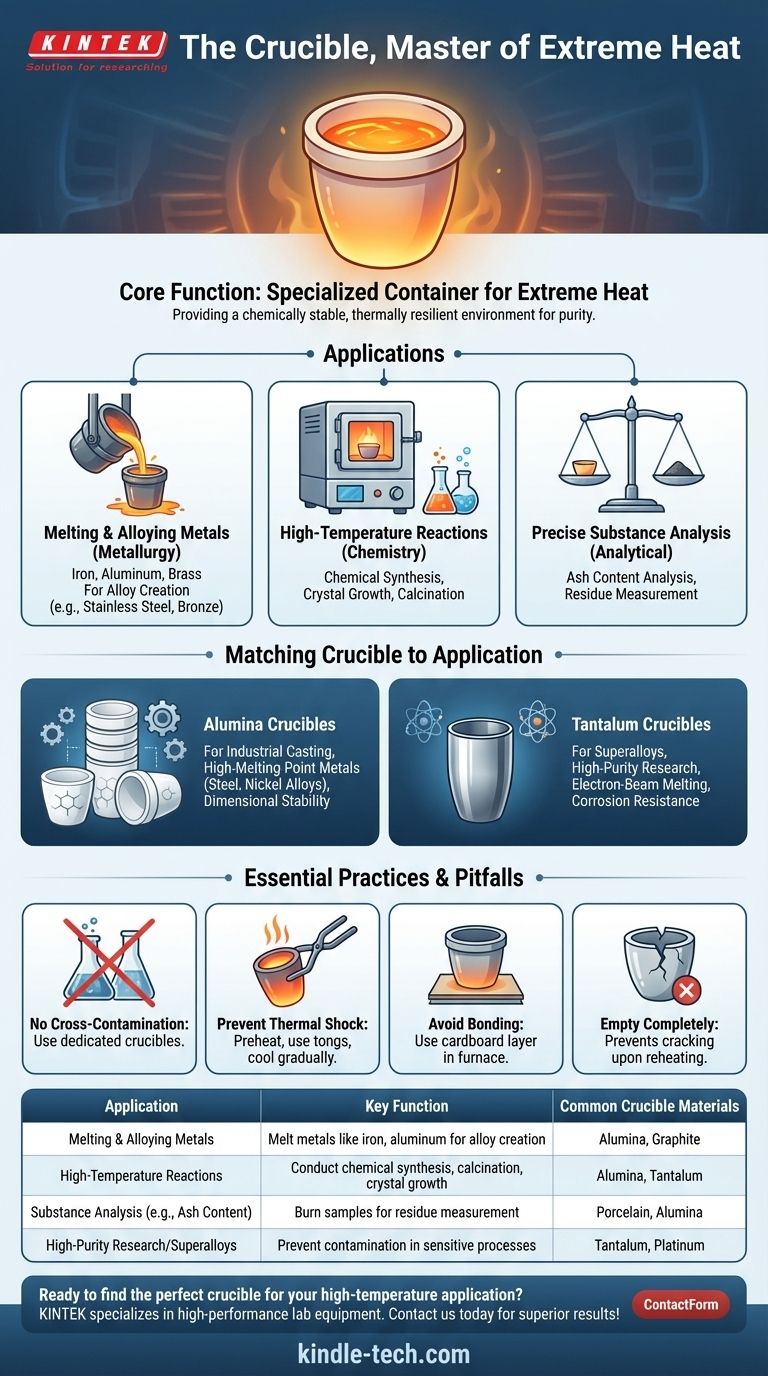
At its core, a crucible is a specialized container engineered to withstand extremely high temperatures. It is an essential tool used across metallurgy, chemistry, and materials science for melting metals, conducting high-temperature reactions, and performing precise substance analysis where conventional containers would fail.
The primary function of a crucible is not merely to hold a substance, but to provide a chemically stable and thermally resilient environment, ensuring the purity and integrity of the material being heated.
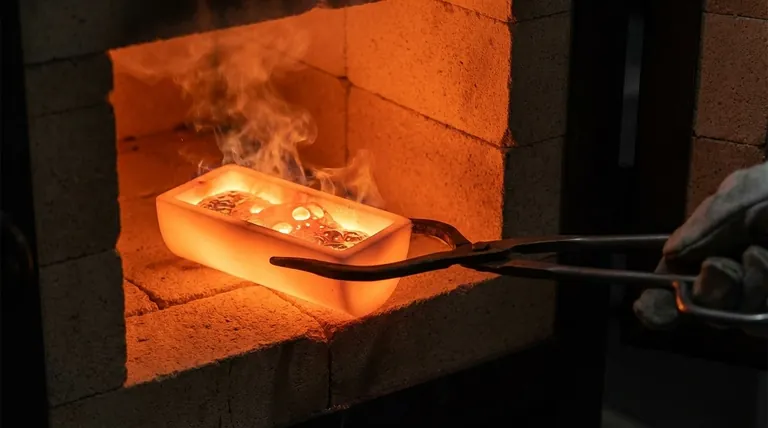

The Core Function: Containing Extreme Heat
A crucible's design and material composition are entirely focused on one goal: maintaining structural integrity and remaining non-reactive when subjected to temperatures that can melt steel, glass, and other robust materials.
Melting and Alloying Metals
In metallurgy and foundries, crucibles are indispensable. They are used within furnaces to melt down raw metals like iron, aluminum, or brass into a liquid state.
This process is the first step in creating alloys, where different metals are combined to produce materials with specific properties, such as stainless steel or bronze.
High-Temperature Chemical Reactions
In chemistry and materials science labs, crucibles serve as vessels for reactions that only occur at high temperatures.
This could involve synthesizing new ceramic compounds, growing crystals, or calcining materials to remove volatile substances. The crucible ensures the reaction is contained and uncontaminated.
Precise Substance Analysis
Certain analytical techniques, like ash content analysis, require a sample to be burned at a controlled high temperature until only non-combustible material remains.
A crucible provides a stable, pre-weighed container for this process, allowing for highly accurate measurements of the residue.
Matching the Crucible to the Application
The material of the crucible itself is a critical variable. Choosing the wrong type can lead to contamination of the sample, or even the destruction of the crucible.
Alumina Crucibles for Industrial Casting
Alumina (aluminum oxide) crucibles are widely used in industrial settings for melting materials like steel, nickel alloys, and other high-melting-point metals.
Their high thermal expansion properties also make them suitable for casting and molding processes where dimensional stability during heating is important.
Tantalum Crucibles for Superalloys and Research
Tantalum is used for more specialized, high-purity applications. It's often found in laboratory equipment and is used in the manufacturing of superalloys and electron-beam melting.
Its high cost is justified by its exceptional resistance to chemical corrosion at extreme temperatures, sometimes serving as a substitute for platinum.
Essential Practices and Common Pitfalls
Using a crucible correctly is just as important as choosing the right one. Mishandling can compromise results and create safety hazards.
The Risk of Cross-Contamination
You must use different crucibles for different metals or compounds. Porous ceramic materials can absorb trace amounts of a substance, which can then leach out and contaminate the next batch.
Preventing Thermal Shock
Crucibles should be handled with properly fitting tongs, and they should be heated and cooled gradually whenever possible to prevent cracking from thermal shock.
Before placing a crucible into a hot furnace, it's good practice to preheat it to reduce the temperature differential.
Avoiding Crucible-to-Furnace Bonding
In some furnace types, a crucible can fuse to the furnace floor at very high temperatures. Placing a thin piece of cardboard underneath the crucible, which will burn away, can prevent this bonding.
The Danger of Leftover Material
Always empty a crucible completely after use. Any remaining metal will solidify and can expand with significant force upon reheating, potentially cracking or destroying the crucible.
Making the Right Choice for Your Task
Your specific goal dictates the type of crucible and the procedures you must follow.
- If your primary focus is industrial metallurgy or casting: An alumina crucible is likely the most cost-effective and durable choice for melting steel, iron, and other common alloys.
- If your primary focus is high-purity research or superalloy development: A specialized material like tantalum or platinum is necessary to prevent any reaction or contamination with your sample.
- If your primary focus is small-scale laboratory analysis: The key is to maintain a dedicated, clean crucible for each substance to ensure the accuracy and reliability of your results.
Ultimately, a crucible is a precision instrument for high-temperature work, and treating it as such is the key to achieving successful outcomes.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Function | Common Crucible Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Melting & Alloying Metals | Melt metals like iron, aluminum for alloy creation | Alumina, Graphite |
| High-Temperature Reactions | Conduct chemical synthesis, calcination, crystal growth | Alumina, Tantalum |
| Substance Analysis (e.g., Ash Content) | Burn samples for residue measurement | Porcelain, Alumina |
| High-Purity Research/Superalloys | Prevent contamination in sensitive processes | Tantalum, Platinum |
Ready to find the perfect crucible for your high-temperature application?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, providing crucibles made from materials like alumina and tantalum to meet the demanding needs of metallurgy, chemistry, and materials science laboratories. Our products ensure chemical stability, thermal resilience, and purity for your melting, alloying, and analysis tasks.
Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and let our experts help you select the ideal crucible for superior results and safety in your lab!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible Semicircle Boat with Lid for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible for Laboratory Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is an alumina crucible selected for SiC coatings? Achieve Superior Purity in Molten Salt Bath Synthesis
- What is the temperature range of alumina crucibles? Key Factors for Safe High-Temp Use
- Can you melt gold in a crucible? Yes, with the right crucible, heat source, and safety process.
- What can I use as a melting crucible? Select the Right Material for Your Application
- What factors are considered when choosing Glassy Carbon or Alumina crucibles? Optimize Molten Salt Corrosion Studies
- What is a porcelain crucible? Your Essential Guide to High-Temp Lab Work
- Can a crucible crack? Prevent Thermal Shock and Extend Crucible Life
- What is a crucible furnace? A Guide to Simple, Controlled Material Melting



















