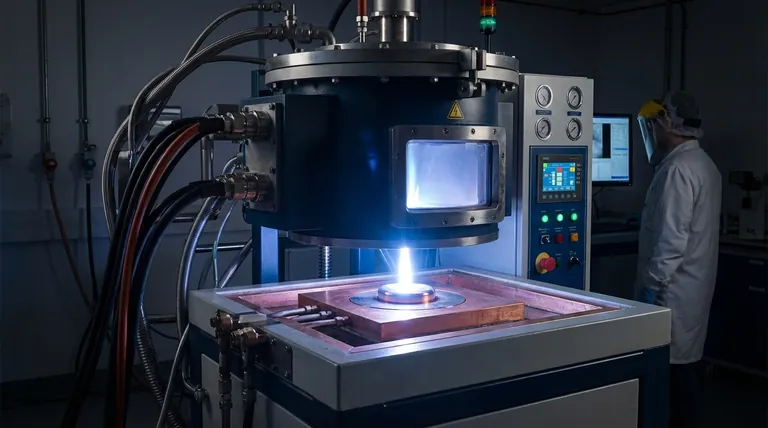
In short, arc melting is a process that uses the intense heat from an electric arc to melt metals. This arc, which is essentially a controlled, high-energy spark or plasma discharge between two electrodes, can generate temperatures high enough to liquefy even the most heat-resistant materials, such as refractory metals and specialized alloys.
The core purpose of arc melting is not just to melt metal, but to achieve the extreme temperatures required for processing high-performance materials that are impossible to handle with more common heating methods.

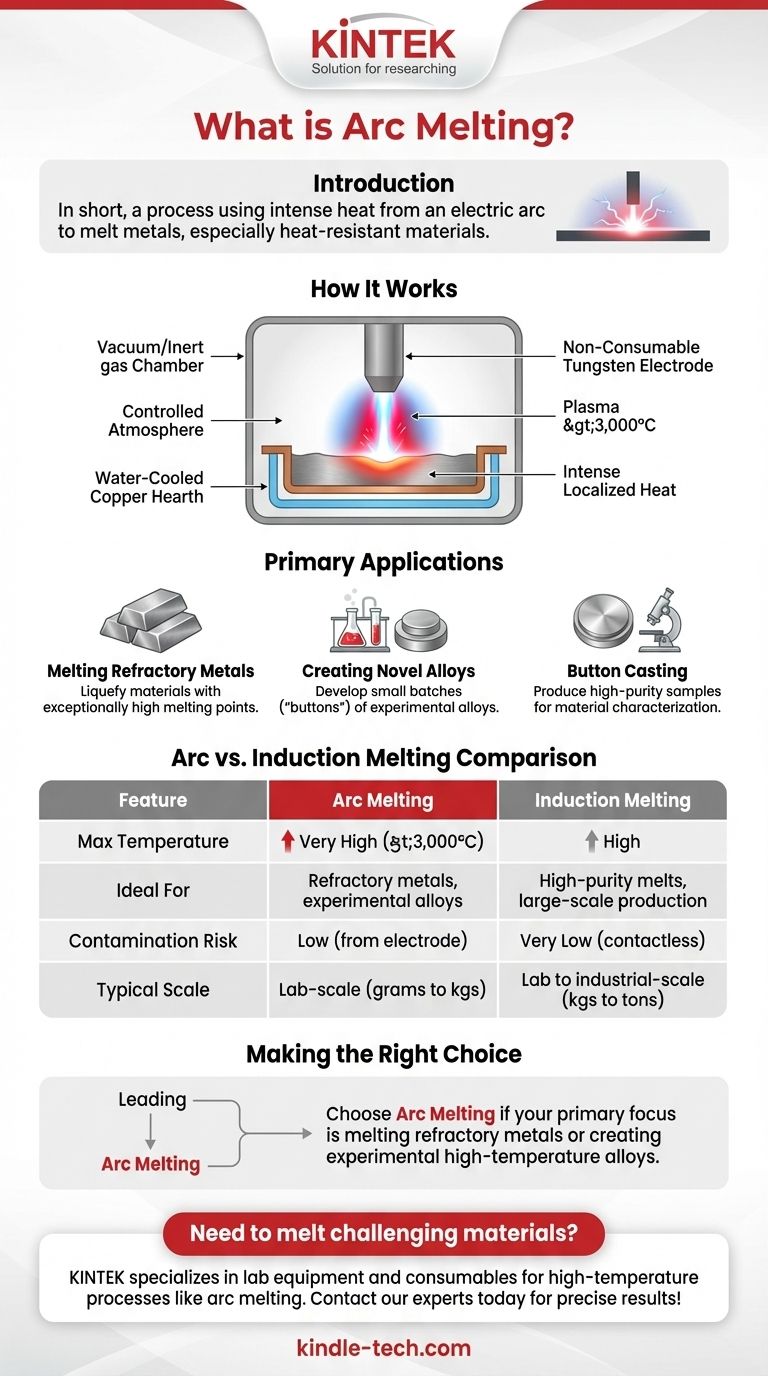
How Arc Melting Works
Arc melting is fundamentally different from conventional heating. Instead of relying on combustion or resistance heating, it harnesses the power of electrical plasma.
The Electric Arc as a Heat Source
An electric arc is formed when a high-voltage current jumps a gap between two conductive electrodes. This process ionizes the gas in the gap (often an inert gas like argon), creating a channel of plasma.
This plasma channel can reach temperatures exceeding 3,000°C (5,400°F). This intense, localized heat is transferred directly to the metal charge, causing it to liquefy rapidly.
Key Components of an Arc Melter
A typical arc melting system consists of a water-cooled copper hearth (or crucible), one or more electrodes (often made of non-consumable tungsten), a power supply, and a vacuum or inert gas chamber.
The chamber is crucial for preventing the molten metal from reacting with oxygen or nitrogen in the air, which would otherwise form unwanted oxides and nitrides, compromising the material's purity and properties.
Primary Applications for Arc Melting
Arc melting is not a general-purpose tool; it is a specialized process used when extremely high temperatures and a controlled atmosphere are non-negotiable.
Melting Refractory Metals
Materials like tungsten, tantalum, molybdenum, and niobium have exceptionally high melting points. Arc melting is one of the few practical methods available to liquefy them for alloying or shaping.
Creating Novel Alloys
In materials science research, scientists use arc melters to create small batches, or "buttons," of new and experimental alloys. The rapid melting and solidification cycles allow for precise control over the final composition.
Button Casting and Sample Preparation
The process is ideal for producing small, high-purity samples for material characterization and testing. The resulting solidified "button" can then be analyzed or further processed.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Arc vs. Induction Melting
While arc melting is powerful, it's essential to compare it with other advanced methods, such as induction melting, to understand its specific advantages and disadvantages.
Temperature and Capability
Arc melting's primary advantage is its ability to reach higher temperatures than induction systems. This makes it the superior choice for materials with the highest melting points.
Induction melting, which uses electromagnetic fields to heat the metal from within, is highly efficient but is typically limited to lower temperatures than arc melting.
Purity and Contamination
A potential drawback of arc melting is the risk of contamination from the electrode. While tungsten electrodes are chosen for their high melting point, microscopic amounts can still transfer to the molten metal.
Induction melting is a "contactless" process. Since the heat is generated directly within the metal by an external magnetic field, there is no risk of contamination from a heating element, making it ideal for applications demanding the absolute highest purity.
Batch Size and Scalability
Arc melting is typically used for small, laboratory-scale batches, from a few grams to a few kilograms. It is not easily scaled for large industrial production.
Induction furnaces, in contrast, can be built to handle many tons of metal, making them a cornerstone of the modern steel and foundry industries.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct melting process depends entirely on your material and your objective.
- If your primary focus is melting refractory metals or creating experimental high-temperature alloys: Arc melting is the definitive tool for achieving the necessary temperatures in a controlled environment.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible purity for reactive metals like titanium: Vacuum arc remelting (a variant of this process) or cold-hearth induction melting are superior choices.
- If your primary focus is efficient, large-scale melting of standard steels and alloys: Induction melting is almost always the more practical and cost-effective industrial solution.
Ultimately, understanding the distinct capabilities of each melting technology empowers you to select the right tool for the job.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Arc Melting | Induction Melting |
|---|---|---|
| Max Temperature | Very High (>3,000°C) | High |
| Ideal For | Refractory metals, experimental alloys | High-purity melts, large-scale production |
| Contamination Risk | Low (from electrode) | Very Low (contactless) |
| Typical Scale | Lab-scale (grams to kgs) | Lab to industrial-scale (kgs to tons) |
Need to melt challenging materials? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. Our expertise in high-temperature processes like arc melting can help you achieve precise results with refractory metals and novel alloys. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your material science challenges!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- How does vacuum arc remelting work? Achieve Ultra-Clean, High-Performance Metal Alloys
- What is the vacuum arc remelting process? Producing Ultra-Pure, High-Performance Metal Alloys
- What is the remelting process? Achieve Ultimate Purity and Performance for High-Strength Alloys
- What is the VAR melting process? The Ultimate Guide to Vacuum Arc Remelting
- What is a remelting process? A Guide to High-Purity Metal Refinement



















