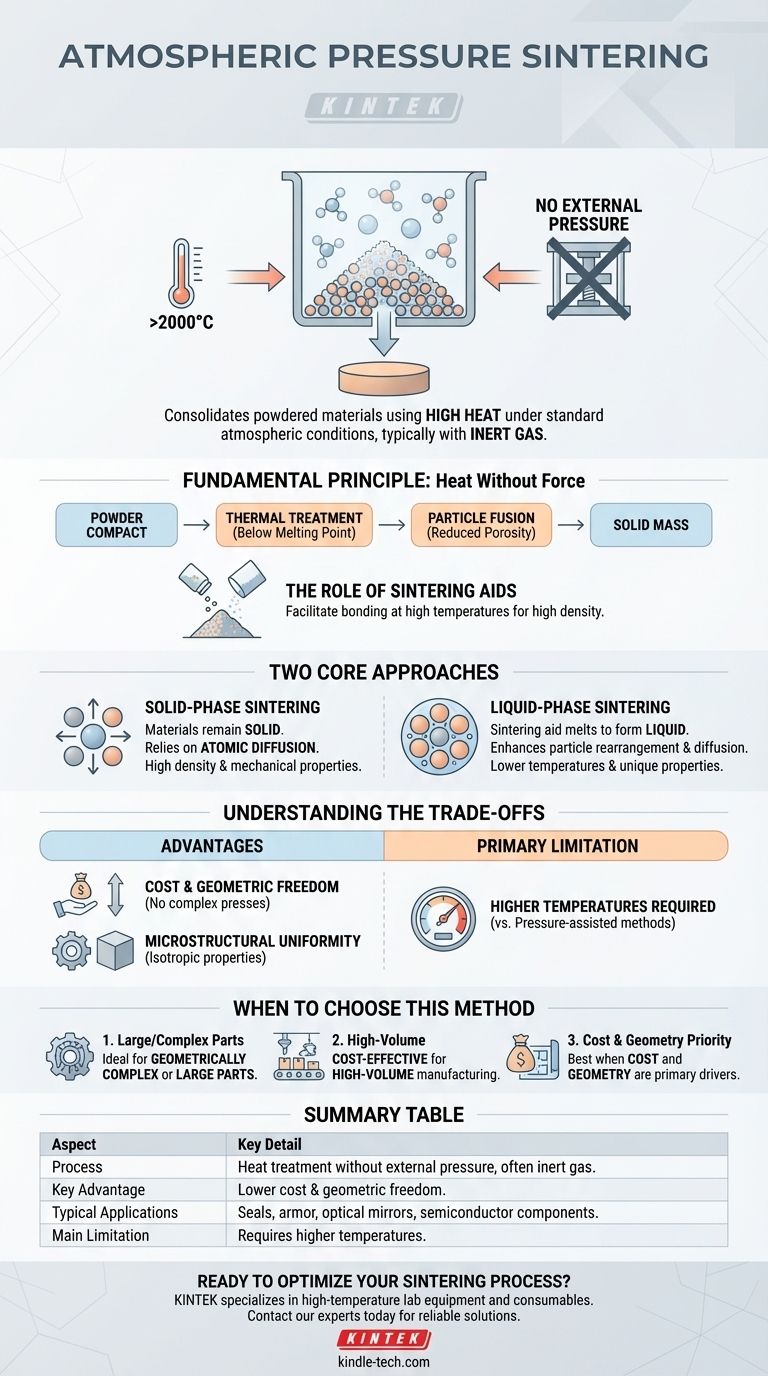
At its core, atmospheric pressure sintering is a manufacturing process that consolidates powdered materials into a solid, dense object using high heat without applying external mechanical pressure. It typically operates under standard atmospheric conditions (around 1.01×10⁵Pa) in a controlled, inert gas environment. This method relies on carefully selected additives and precise temperature control, often over 2000°C for advanced ceramics, to achieve high densification.
The primary advantage of atmospheric pressure sintering is its ability to produce complex or large-scale components at a lower cost than pressure-assisted methods. By eliminating the need for external force, it removes critical constraints on product shape and size, making it a highly versatile solution.

The Fundamental Principle: Heat Without Force
Sintering is a thermal treatment for compacting powdered material into a solid mass. The process occurs at temperatures below the material's melting point, causing the individual particles to fuse together and significantly reduce the porous space between them.
The Role of Sintering Aids
Because atmospheric sintering forgoes external pressure, it often requires the use of sintering aids. These are specific additives mixed with the primary powder that facilitate the bonding process between particles at high temperatures, ensuring the final part achieves high density.
Two Core Approaches
The process is generally divided into two distinct methods, depending on the behavior of these aids.
Solid-Phase Sintering
In this method, all materials remain in a solid state throughout the process. It relies on atomic diffusion at the contact points between particles to densify the material. This approach is known for producing parts with high density and excellent mechanical properties at high temperatures.
Liquid-Phase Sintering
Here, a sintering aid melts to form a liquid phase that surrounds the solid particles. This liquid enhances particle rearrangement and diffusion, effectively "gluing" the structure together. This method often allows for lower sintering temperatures and can result in unique, improved material properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a sintering method requires a clear understanding of its inherent advantages and limitations compared to its alternatives, primarily pressure-assisted sintering.
Advantage: Cost and Geometric Freedom
The most significant benefit is the elimination of expensive and complex mechanical presses. This not only lowers production costs but also removes limitations on the shape and size of the final product, enabling the creation of intricate or large-scale components.
Advantage: Microstructural Uniformity
Without the directional force of a press, atmospheric sintering often results in a more uniform and isotropic microstructure. This uniformity is critical for applications where predictable, consistent material performance is essential.
The Primary Limitation: Temperature
The main trade-off is temperature. To achieve high density without external force, atmospheric sintering requires significantly higher temperatures than pressure-assisted methods. Pressure-assisted techniques can densify materials at temperatures close to half their melting point, offering potential energy savings and preventing unwanted grain growth.
When to Choose Atmospheric Pressure Sintering
This method is ideal for fabricating precision structural components where geometry and cost are primary drivers. Common applications include seals for mechanical pumps, bulletproof armor, optical mirrors, and semiconductor wafer clamps.
- If your primary focus is producing large or geometrically complex parts: Atmospheric pressure sintering is ideal because it is not constrained by the size and shape limitations of a mechanical press.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective, high-volume manufacturing: This method's lower equipment complexity and operational cost make it a superior economic choice for many suitable applications.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum density at the lowest possible temperature: A pressure-assisted sintering method may be more suitable, as external force significantly reduces the required thermal energy.
Understanding these core principles allows you to select the most effective sintering strategy to achieve your specific material and manufacturing goals.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Process | Heat treatment without external pressure, often in inert gas. |
| Key Advantage | Lower cost & geometric freedom for complex/large parts. |
| Typical Applications | Seals, armor, optical mirrors, semiconductor components. |
| Main Limitation | Requires higher temperatures than pressure-assisted methods. |
Ready to optimize your sintering process for complex components?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the high-temperature lab equipment and consumables essential for successful atmospheric pressure sintering. Whether you are developing new materials or scaling up production, our expertise and reliable solutions can help you achieve superior density and performance.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a program-controlled carbonization furnace in the preparation of lignin-based carbon fiber? Explained
- What is the purpose of pre-treating coal samples? Ensure Accurate Pyrolysis with Nitrogen Drying
- What role does an atmosphere sintering furnace play in NMC622 & LLZ co-sintering? Achieve High-Performance Interfaces
- What are the types of furnace atmosphere? Master Your Thermal Process with the Right Environment
- What is the function of the inert atmosphere in sintering nickel-alumina? Achieve High-Purity Composite Bonding
- What is an inert gas and which processes is it used in? A Guide to Protective Atmospheres
- What is carburizing in case hardening? Achieve Superior Wear Resistance and Core Toughness
- What role does the reducing protective gas play in Cu-SiOC hybrid ceramics? Ensure Conductivity via Active Reduction



















