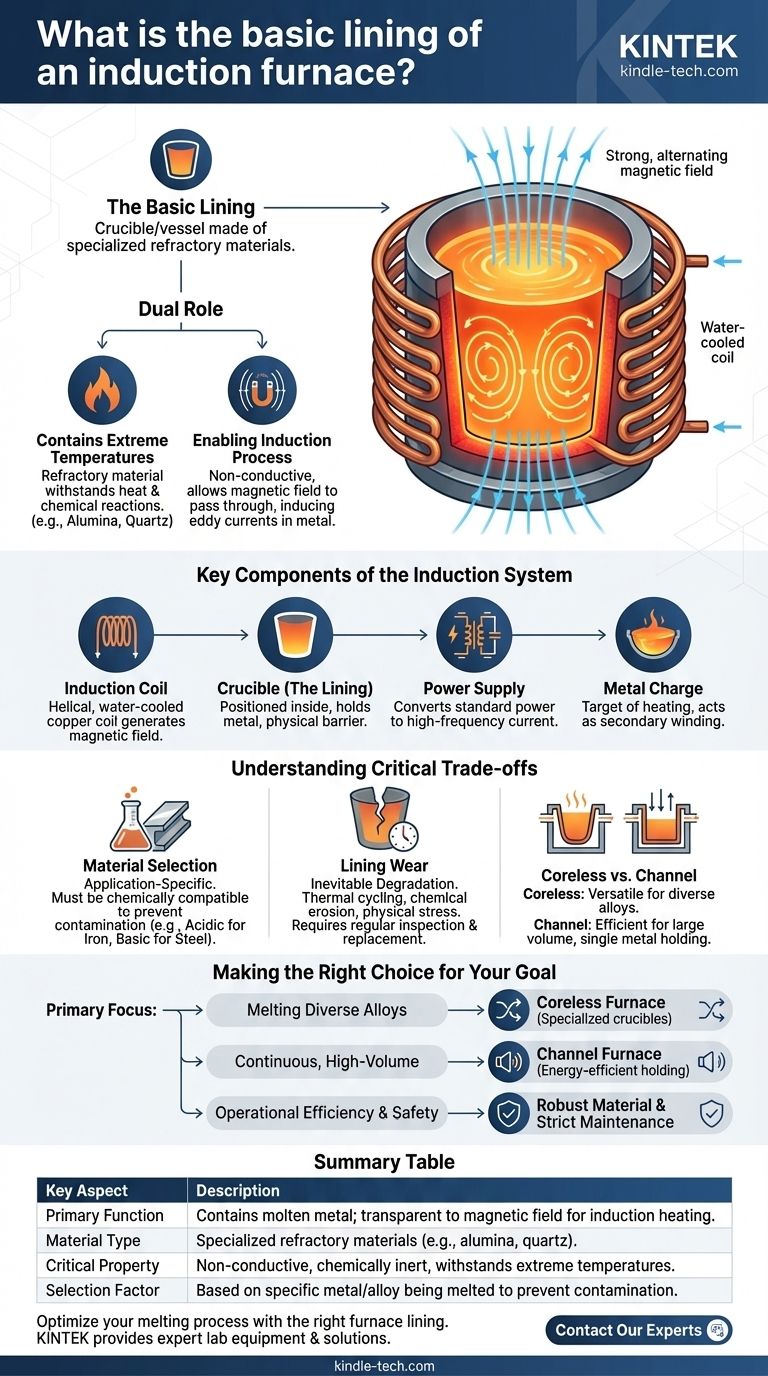
The basic lining of an induction furnace is a crucible or vessel constructed from specialized refractory materials. This lining is designed to contain the molten metal at extreme temperatures while remaining non-conductive, allowing the furnace's magnetic field to pass through it and heat the metal charge directly.
The core principle is that the furnace lining must serve a dual purpose: it must be a robust container capable of withstanding intense heat and chemical reactions, while also being transparent to the magnetic field that is essential for the induction heating process to work.

The Dual Role of the Furnace Lining
The lining isn't just a simple container; it is a highly engineered component that enables the entire induction process. Its properties are fundamental to the furnace's efficiency and safety.
Containing Extreme Temperatures
A refractory material is one that can resist decomposition by heat, pressure, or chemical attack. The lining must maintain its structural integrity without melting or reacting with the specific metal being processed.
Common types of refractory materials include ceramics like alumina and quartz, chosen based on the melting temperature and chemical properties of the metal charge.
Enabling the Induction Process
The furnace works by generating a powerful, alternating magnetic field from a water-cooled copper coil. This field must pass through the lining to induce eddy currents within the metal itself.
These swirling electrical currents are what generate the intense heat that melts the metal. If the lining were electrically conductive, it would heat up instead of the charge, leading to catastrophic failure and extreme inefficiency.
Key Components of the Induction System
Understanding the lining requires seeing how it fits within the larger furnace system. Each component works in concert to achieve controlled, clean melting.
The Induction Coil
This is a helical, water-cooled copper coil that surrounds the crucible. When a high-frequency alternating current is passed through it, the coil generates the powerful magnetic field.
The Crucible (The Lining)
Positioned inside the induction coil, the refractory crucible holds the solid metal to be melted. It acts as the physical barrier between the energized coil and the superheated molten bath.
The Power Supply
An induction furnace requires a specialized power supply that includes a transformer, an inverter, and a capacitor bank. This unit converts standard electrical power into the high-frequency current needed to drive the induction coil.
The Metal Charge
The metal inside the crucible is the target of the heating process. In electrical terms, the induction coil acts as the primary winding of a transformer, and the metal charge itself effectively becomes the secondary winding, allowing energy to be transferred directly into it.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
The choice and maintenance of the furnace lining are among the most critical operational decisions, directly impacting safety, efficiency, and cost.
Material Selection is Application-Specific
The type of refractory material used is not universal. It must be chemically compatible with the alloy being melted to prevent contamination of the metal or premature degradation of the lining. An acidic lining, for example, is used for melting iron, while a basic lining is required for steel.
Lining Wear is Inevitable
Refractory linings degrade over time due to constant thermal cycling, chemical erosion from the molten metal, and physical stress. Regular inspection and scheduled replacement are essential to prevent dangerous furnace run-outs.
Coreless vs. Channel Furnaces
While both use induction, their design affects lining considerations. Coreless furnaces, where a simple crucible sits in a coil, are versatile for various metals. Channel furnaces have a separate induction loop and are more efficient for holding large volumes of a single metal at temperature.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The design and material of an induction furnace system should align directly with its intended industrial application.
- If your primary focus is melting diverse alloys: A coreless induction furnace with a system for using different, specialized refractory crucibles offers the greatest flexibility.
- If your primary focus is continuous, high-volume production of one metal: A channel induction furnace is typically more energy-efficient for holding and processing large, single-alloy melts.
- If your primary focus is operational efficiency and safety: Prioritize a robust lining material specifically matched to your metal and implement a strict maintenance and replacement schedule.
Understanding that the lining is an active component, not just a passive container, is the key to mastering the precision and efficiency of induction furnace technology.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Contains molten metal; transparent to magnetic field for induction heating. |
| Material Type | Specialized refractory materials (e.g., alumina, quartz). |
| Critical Property | Non-conductive, chemically inert, and withstands extreme temperatures. |
| Selection Factor | Based on the specific metal/alloy being melted to prevent contamination. |
Optimize your melting process with the right furnace lining. The correct refractory material is critical for safety, efficiency, and metal purity. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing expert solutions for your laboratory's melting and material processing needs. Contact our experts today to discuss the ideal induction furnace setup for your specific application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is VIM in metallurgy? A Guide to Vacuum Induction Melting for High-Performance Alloys
- What is the difference between induction melting and vacuum induction melting? Choosing the Right Process for Purity
- What is the vacuum induction method? Master High-Purity Metal Melting for Advanced Alloys
- What principle is used to generate heat in a vacuum induction melting furnace? Achieve Clean, Efficient Metal Melting
- What types of metals are typically processed in a vacuum induction melting furnace? High-Purity Alloys for Critical Applications



















