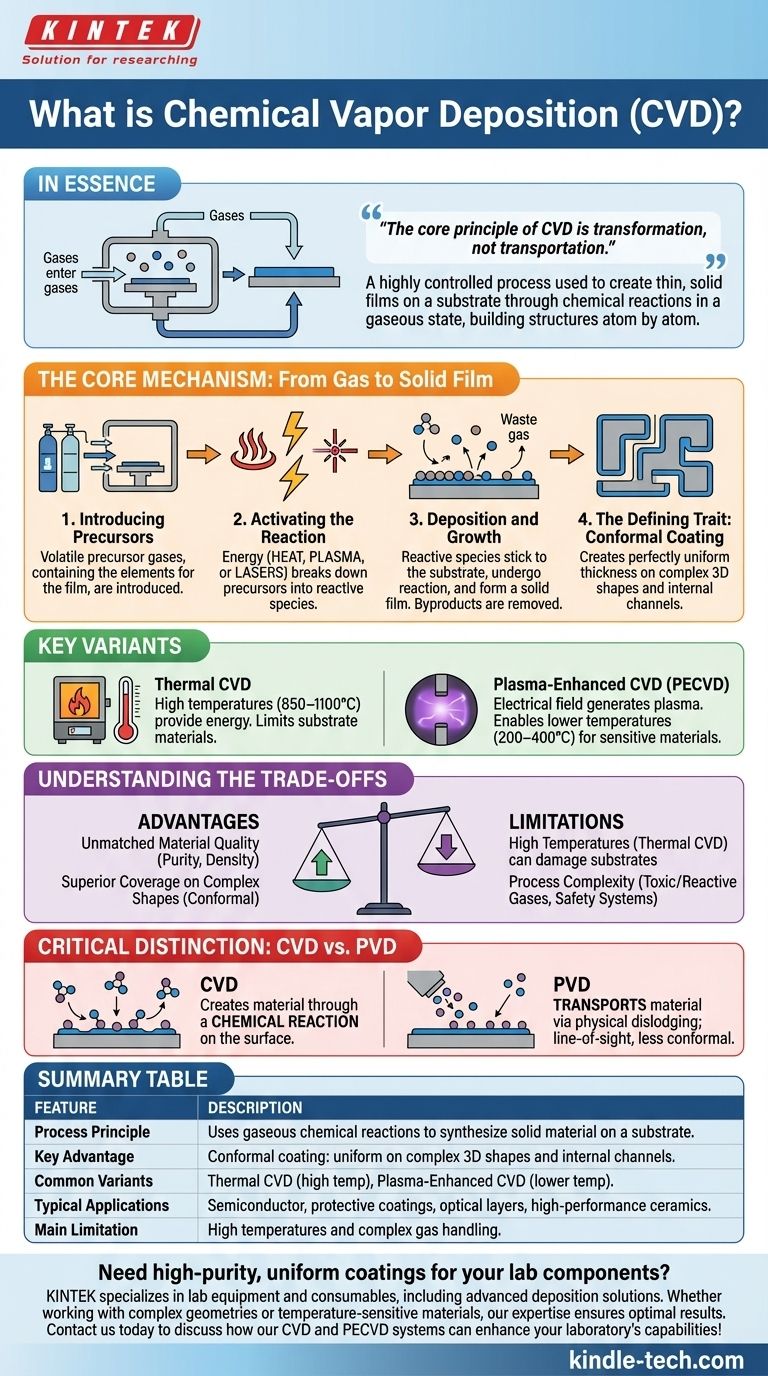
In essence, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a highly controlled manufacturing process used to create thin, solid films on a surface, known as a substrate. It achieves this not by spraying or painting, but by introducing reactive gases into a chamber, which then undergo a chemical reaction directly on the substrate's surface to grow the desired material layer by layer.
The core principle of CVD is transformation, not transportation. It uses chemical reactions in a gaseous state to synthesize a completely new, high-purity solid material directly onto a component, resulting in an exceptionally uniform and dense coating.

The Core Mechanism: From Gas to Solid Film
To understand CVD, it's best to think of it as building a structure atom by atom from airborne chemical building blocks. The process follows a few fundamental steps.
Introducing the Precursors
The process begins by introducing volatile precursor gases into a reaction chamber containing the workpiece. These precursors are chemical compounds that contain the specific elements needed for the final film.
Activating the Reaction
Energy is supplied to the chamber to break down the precursor gases into more reactive molecules or atoms. This energy is most commonly heat, but can also be plasma or lasers, which allows for more control over the process.
Deposition and Growth
These reactive chemical species move through the chamber and adsorb (stick) onto the surface of the substrate. Here, they undergo a chemical reaction that deposits the desired solid material, forming a thin film. Other chemical byproducts from the reaction are volatile and are removed from the chamber as exhaust gas.
The Defining Trait: Conformal Coating
Because the deposition happens from a gas phase that surrounds the object, CVD excels at creating a perfectly uniform coating. The film's thickness is consistent across all surfaces, including complex 3D geometries, internal channels, and sharp corners—a characteristic known as conformal coverage.
Key Variants of the CVD Process
Different methods of supplying energy give rise to several major types of CVD, each suited for different applications.
Thermal CVD
This is the classic form of the process, relying on high temperatures (often 850–1100°C) to provide the energy needed for the chemical reaction. While effective, the intense heat limits the types of substrate materials that can be coated without being damaged.
Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD)
To overcome the temperature limitations of thermal CVD, PECVD uses an electrical field to generate a plasma—a high-energy state of gas. The plasma's energy is highly effective at breaking down precursor gases, allowing deposition to occur at much lower substrate temperatures (typically 200–400°C). This opens the door to coating temperature-sensitive materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Like any advanced process, CVD involves a balance of powerful advantages and specific limitations.
Advantage: Unmatched Material Quality and Versatility
CVD can produce films of exceptional purity and density. By precisely controlling the precursor gases and reaction conditions, engineers can fine-tune the film's chemical composition, crystal structure, and grain size. This allows for the deposition of a vast range of materials, including metals, alloys, and high-performance ceramics.
Advantage: Superior Coverage on Complex Shapes
The conformal nature of CVD is a significant benefit over line-of-sight processes like Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD). Where PVD struggles to coat inside corners or complex shapes, CVD provides a uniform film everywhere the gas can reach.
Limitation: High Temperatures and Process Complexity
The primary drawback of traditional thermal CVD is the high temperature required, which can damage or warp many substrate materials. While PECVD mitigates this, the chemistry involved can be complex. Precursor gases are often toxic, flammable, or corrosive, requiring sophisticated handling and safety systems.
Critical Distinction: CVD vs. PVD
It is crucial not to confuse CVD with physical processes like "spraying" or sputtering, which fall under the category of Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD).
- CVD creates a material through a chemical reaction on the surface.
- PVD transports a material by physically dislodging atoms from a solid source and having them deposit onto the substrate. PVD is typically a line-of-sight process and is less effective at coating complex geometries.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct deposition technology depends entirely on your material constraints and the desired outcome for the finished part.
- If your primary focus is coating a complex 3D shape or achieving the highest possible film purity and density: CVD is likely the superior choice due to its conformal nature and chemical synthesis process.
- If you are coating a temperature-sensitive material like a polymer or a low-melting-point alloy: A low-temperature variant like Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) is essential, or you may need to consider a PVD alternative.
- If your goal is to deposit a simple film on a flat surface quickly and cost-effectively: A physical process like sputtering (PVD) might be a more efficient solution.
Ultimately, choosing the right process means matching the unique capabilities of the technology to the specific engineering requirements of your project.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Process Principle | Uses chemical reactions in a gaseous state to synthesize a solid material directly onto a substrate. |
| Key Advantage | Conformal coating: uniform thickness on complex 3D shapes, internal channels, and sharp corners. |
| Common Variants | Thermal CVD (high temperature), Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD, lower temperature). |
| Typical Applications | Semiconductor manufacturing, protective coatings, optical layers, and high-performance ceramics. |
| Main Limitation | High temperatures (in thermal CVD) and complex handling of reactive precursor gases. |
Need high-purity, uniform coatings for your lab components? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, including advanced deposition solutions tailored to your research or production needs. Whether you're working with complex geometries or temperature-sensitive materials, our expertise ensures optimal results. Contact us today to discuss how our CVD and PECVD systems can enhance your laboratory's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- What are different types of thin films? A Guide to Function, Material, and Deposition Methods
- Why does a PECVD vacuum system require both a rotary vane and turbo pump? Ensure High-Purity Coatings
- What is the process of PECVD in semiconductor? Enabling Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- How do PECVD systems improve DLC coatings on implants? Superior Durability and Biocompatibility Explained
- What is the difference between plasma CVD and thermal CVD? Choose the Right Method for Your Substrate



















