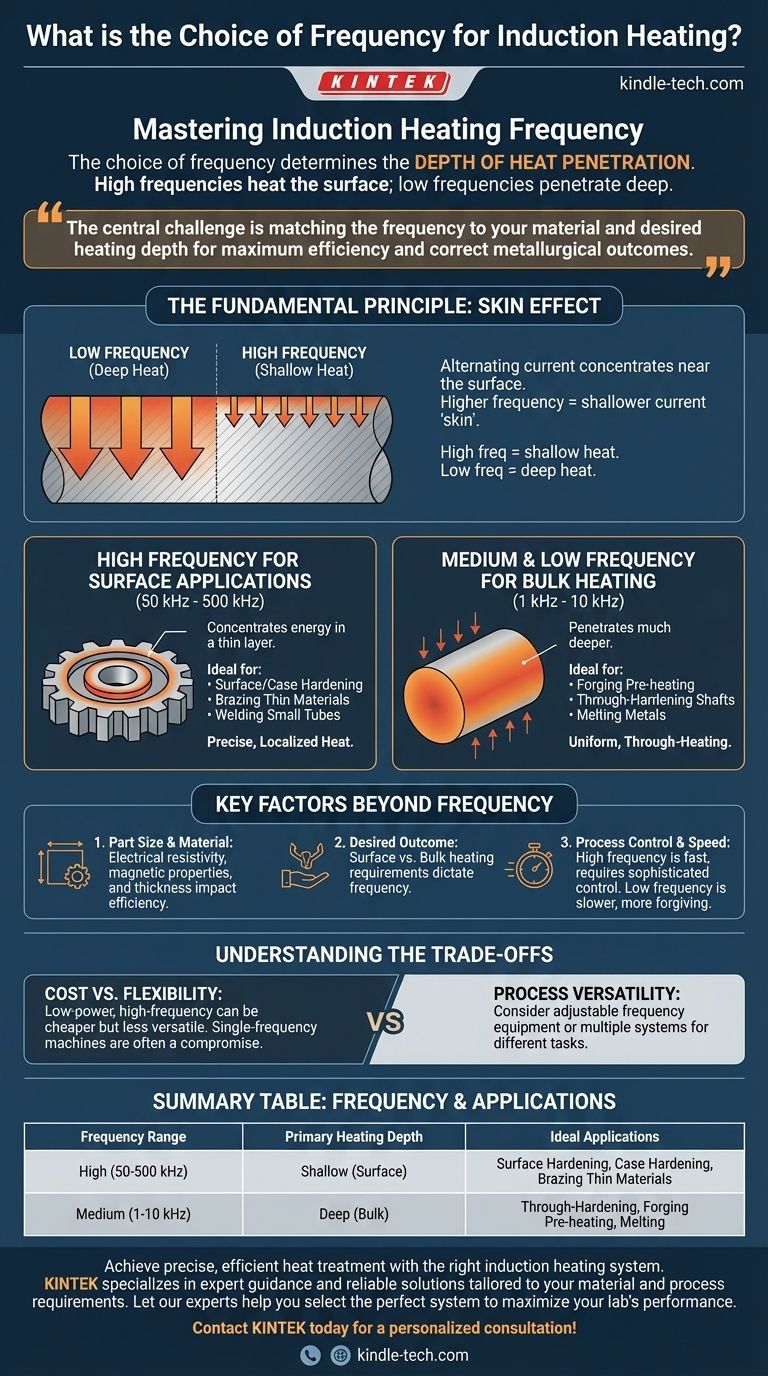
At its core, the choice of frequency for induction heating is determined by the required depth of heat penetration. High frequencies heat the surface of a part, while low frequencies penetrate deeper into the material. This relationship between frequency and heating depth is the single most important factor in selecting the right equipment for your process.
The central challenge is not finding one "best" frequency, but matching the frequency to your material and the desired heating depth. This ensures you heat only the part of the workpiece you intend to, maximizing efficiency and achieving the correct metallurgical outcome.

The Fundamental Principle: Frequency and Heating Depth
The effectiveness of induction heating hinges on a physical phenomenon known as the skin effect. Understanding this principle is the key to making an informed frequency choice.
The Skin Effect Explained
When an alternating current flows through an electrical conductor, it tends to concentrate near the surface. The higher the frequency of the current, the more pronounced this effect is, and the shallower the current "skin" becomes.
Since the current is what generates the heat, this means that high frequencies create shallow heat, and low frequencies create deep heat.
High Frequency for Surface Applications
A high frequency (generally considered to be 50 kHz to 500 kHz) is used when you need to heat the surface of a part quickly without significantly affecting the core. The energy is concentrated in a very thin layer.
This makes it ideal for processes like surface hardening, case hardening, brazing thin materials, and welding small tubes, where you require precise, localized heat.
Medium & Low Frequency for Bulk Heating
A medium frequency (typically 1 kHz to 10 kHz) allows the electrical current to penetrate much deeper into the material. This is used for applications that require uniform, through-heating.
This is the preferred choice for pre-heating large billets for forging, through-hardening of shafts, or melting metals in a crucible, where the entire volume of the material needs to reach a target temperature.
Key Factors Beyond Frequency
While frequency controls the depth, other factors influence the final decision and overall efficiency of the heating process.
Part Size and Material
The properties of the workpiece itself are critical. The material's electrical resistivity and magnetic properties (especially for steel below its Curie temperature) affect how efficiently it couples with the magnetic field.
Furthermore, the heating depth must be appropriate for the part's thickness. Using a low frequency with a deep penetration depth on a very thin part is inefficient, as much of the magnetic field will pass straight through it without generating heat.
The Desired Outcome
The specific manufacturing goal dictates the heating profile. Surface hardening requires a hard outer case with a soft, ductile core, demanding high-frequency surface heat. Forging, conversely, requires the entire workpiece to be malleable, necessitating deep, uniform low-frequency heat.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting an induction system is rarely a simple choice. You must balance performance, cost, and versatility.
Equipment Cost vs. Flexibility
Low-power, high-frequency equipment may be less expensive than high-power, medium-frequency units. However, as noted in some cases, both might achieve a similar heating effect for a specific workpiece. The decision involves analyzing the initial purchase cost against the long-term operational efficiency and throughput.
The "One Size Fits All" Trap
A single-frequency induction machine is optimized for a specific range of applications. If you need to perform both surface hardening on small gears and through-heating on large shafts, a single machine will be a compromise. It may perform one task well and the other inefficiently.
Process Control and Speed
Higher frequencies can heat a surface extremely fast. This is excellent for high-volume production but requires more sophisticated process control to prevent overheating, distortion, or cracking. Lower frequency processes are slower but often more forgiving.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Base your decision on the primary metallurgical goal you need to achieve.
- If your primary focus is surface hardening or case hardening: Choose a high frequency (50-500 kHz) to concentrate heat on the surface without affecting the core.
- If your primary focus is through-heating or pre-heating for forging: Choose a medium or low frequency (1-10 kHz) to ensure the heat penetrates deeply and evenly.
- If your primary focus is brazing or soldering: Use a high frequency for thin parts or small joints, and a medium frequency for heavier sections that require more heat soak.
- If your primary focus is process versatility: Consider equipment with adjustable frequency settings or be prepared to invest in multiple systems optimized for different tasks.
Ultimately, selecting the right frequency transforms induction from a simple heat source into a precise, controllable manufacturing tool.
Summary Table:
| Frequency Range | Primary Heating Depth | Ideal Applications |
|---|---|---|
| High (50-500 kHz) | Shallow (Surface) | Surface Hardening, Case Hardening, Brazing Thin Materials |
| Medium (1-10 kHz) | Deep (Bulk) | Through-Hardening, Forging Pre-heating, Melting |
Achieve precise, efficient heat treatment with the right induction heating system.
Choosing the correct frequency is critical for your application's success, impacting everything from metallurgical outcomes to production efficiency. KINTEK specializes in providing laboratory equipment and consumables, offering expert guidance and reliable induction heating solutions tailored to your specific material and process requirements.
Let our experts help you select the perfect system to maximize your lab's performance. Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is the vacuum system of a Vacuum Hot Pressing furnace critical for ODS ferritic stainless steel performance?
- How does the pressure loading system of a vacuum hot press furnace regulate CoCrCuFeNi alloy microstructure?
- What are the advantages of a vacuum hot pressing furnace? Achieve Superior Lithium Niobate Piezoelectric Density
- How does a vacuum hot press furnace address structural defects in as-cast CoCrPtB alloy ingots? Optimize Your Density
- What is the significance of applying mechanical pressure via a vacuum hot press? Maximize A356-SiCp Composite Density











