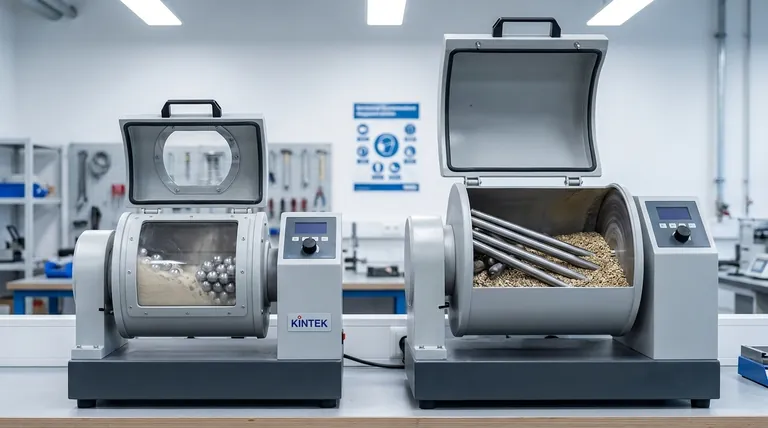
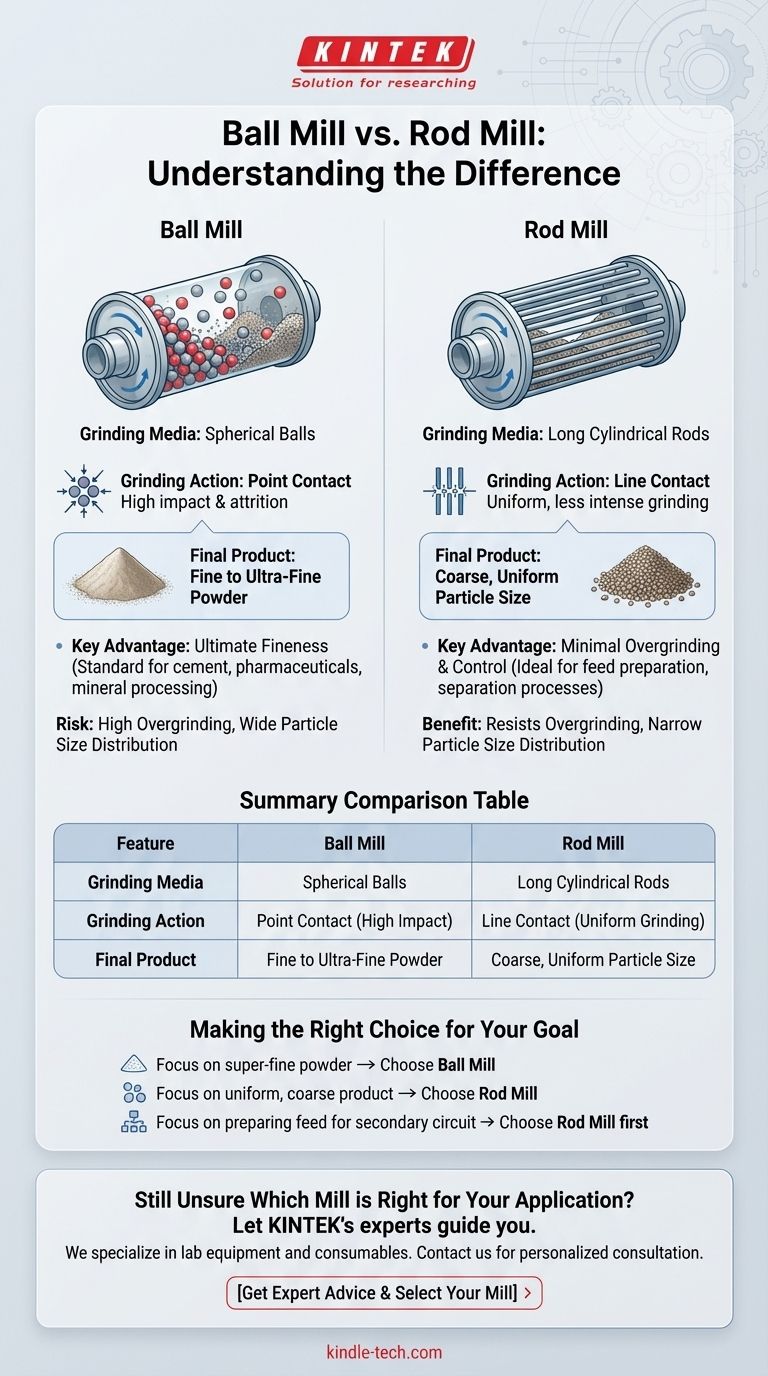
The fundamental difference between a ball mill and a rod mill lies in their grinding media and the type of grinding action they produce. A ball mill uses spherical balls to create a fine powder through point contact, while a rod mill uses steel rods to create a coarser, more uniform product through line contact.
The choice between a ball mill and a rod mill is a choice between product fineness and product uniformity. Ball mills excel at creating ultra-fine powders, whereas rod mills are designed to produce a specific particle size with minimal overgrinding.

The Core Distinction: Grinding Media and Contact Type
The shape of the grinding media—balls versus rods—is not a trivial detail. It completely changes the internal physics of the mill, dictating the final product characteristics and the mill's ideal application.
How a Ball Mill Works: Point Contact
A ball mill is a cylindrical drum partially filled with spherical grinding media, typically steel or ceramic balls. As the drum rotates, the balls are lifted up the side and then cascade or tumble down, crushing and grinding the material trapped between them.
This process is characterized by point contact. The force is concentrated at the tiny points where the balls touch each other and the material, creating an intense impact and attrition action perfect for pulverizing particles into a very fine powder.
How a Rod Mill Works: Line Contact
A rod mill is similar in design but is charged with steel rods that run the full length of the drum. As the mill rotates, the rods are also lifted and tumble, but their interaction is fundamentally different.
This creates line contact. The rods crush material along their entire length, acting as a series of parallel grinding surfaces. This action is less intense than the point impacts in a ball mill but provides a more uniform grinding effect across the material bed.
Comparing Output and Application
The difference in grinding action directly leads to different outcomes in the final product, which in turn defines where each mill is best used.
Final Product Size and Distribution
A ball mill is the superior tool for fine and ultra-fine grinding. It is capable of reducing material to a powder-like consistency, but it often produces a wide distribution of particle sizes, including a significant amount of undesirable dust or "slimes."
A rod mill produces a coarser, more uniform product. Its grinding action is self-classifying—the largest particles are crushed preferentially, while smaller particles are shielded. This results in a product with a very narrow particle size distribution, making it highly predictable.
Risk of Overgrinding
The high-impact nature of a ball mill makes it prone to overgrinding. Material can be pulverized far beyond the target size, wasting energy and creating excessive fine material that can be problematic in subsequent processing steps.
Rod mills are inherently resistant to overgrinding. The line contact and the way the rods sort themselves by size (with the largest rods impacting the coarsest feed) creates a screening effect that minimizes the creation of unwanted fines.
Feed Size and Preparation
Rod mills can typically accept a larger feed size than ball mills. They are often used as the primary stage of grinding to prepare a consistent, finer feed for a secondary grinding circuit, which might then use a ball mill for the final size reduction.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither mill is universally better; they are specialized tools designed for different outcomes. Choosing the wrong one leads to inefficiency and a poor-quality product.
The Ball Mill's Strength: Ultimate Fineness
The primary advantage of a ball mill is its ability to produce an extremely fine product. It is the standard choice in industries like mineral processing, cement production, and pharmaceuticals where the final output must be a fine powder. The trade-off is higher energy consumption and less control over the particle size distribution.
The Rod Mill's Advantage: Control and Efficiency
A rod mill's strength lies in its control. It is exceptionally efficient at grinding to a specific coarse size without producing excessive fines. This makes it the ideal tool for applications where product uniformity is critical, such as preparing feed for flotation or magnetic separation. Its limitation is that it cannot achieve the fineness of a ball mill.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the correct mill, you must first define the characteristics of your desired final product.
- If your primary focus is producing a super-fine powder: A ball mill is the correct tool due to its high-impact, point-contact grinding action.
- If your primary focus is creating a uniform, coarse product with minimal fines: A rod mill is the superior choice because its line-contact grinding prevents overgrinding.
- If your primary focus is preparing a consistent feed for a secondary grinding circuit: A rod mill is often the preferred first stage to efficiently create an ideal feed for a ball mill.
Ultimately, understanding the distinct grinding mechanisms of these mills empowers you to select the right tool to achieve your specific processing objective with maximum efficiency.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Ball Mill | Rod Mill |
|---|---|---|
| Grinding Media | Spherical Balls | Long Cylindrical Rods |
| Grinding Action | Point Contact (High Impact) | Line Contact (Uniform Grinding) |
| Final Product | Fine to Ultra-Fine Powder | Coarse, Uniform Particle Size |
| Key Advantage | Ultimate Fineness | Minimal Overgrinding & Control |
| Ideal For | Mineral Processing, Cement, Pharmaceuticals | Preparing Feed for Separation Processes |
Still Unsure Which Mill is Right for Your Application?
Choosing the correct grinding equipment is critical for your lab's efficiency and the quality of your final product. The wrong choice can lead to wasted energy, poor particle size distribution, and inconsistent results.
Let KINTEK's experts guide you. We specialize in lab equipment and consumables, serving a wide range of laboratory needs. Our team can help you analyze your specific requirements—whether you need the fine powder of a ball mill or the controlled, uniform output of a rod mill—to ensure you get the perfect solution for your process.
Contact us today for a personalized consultation and discover how the right mill can enhance your productivity and results.
Get Expert Advice & Select Your Mill
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- Laboratory Horizontal Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What size is a ball mill? A Guide from Benchtop to Industrial Scale
- What is the product size of a ball mill? Achieve Micron-Level Precision for Your Materials
- What is a ball mill used for in ceramics? Achieve Ultimate Control Over Glaze and Clay Quality
- What are the application of ball mill in food industry? Achieve Ultra-Fine Grinding for Superior Food Quality
- What are the disadvantages of a ball mill? High Energy Use, Noise, and Contamination Risks



















