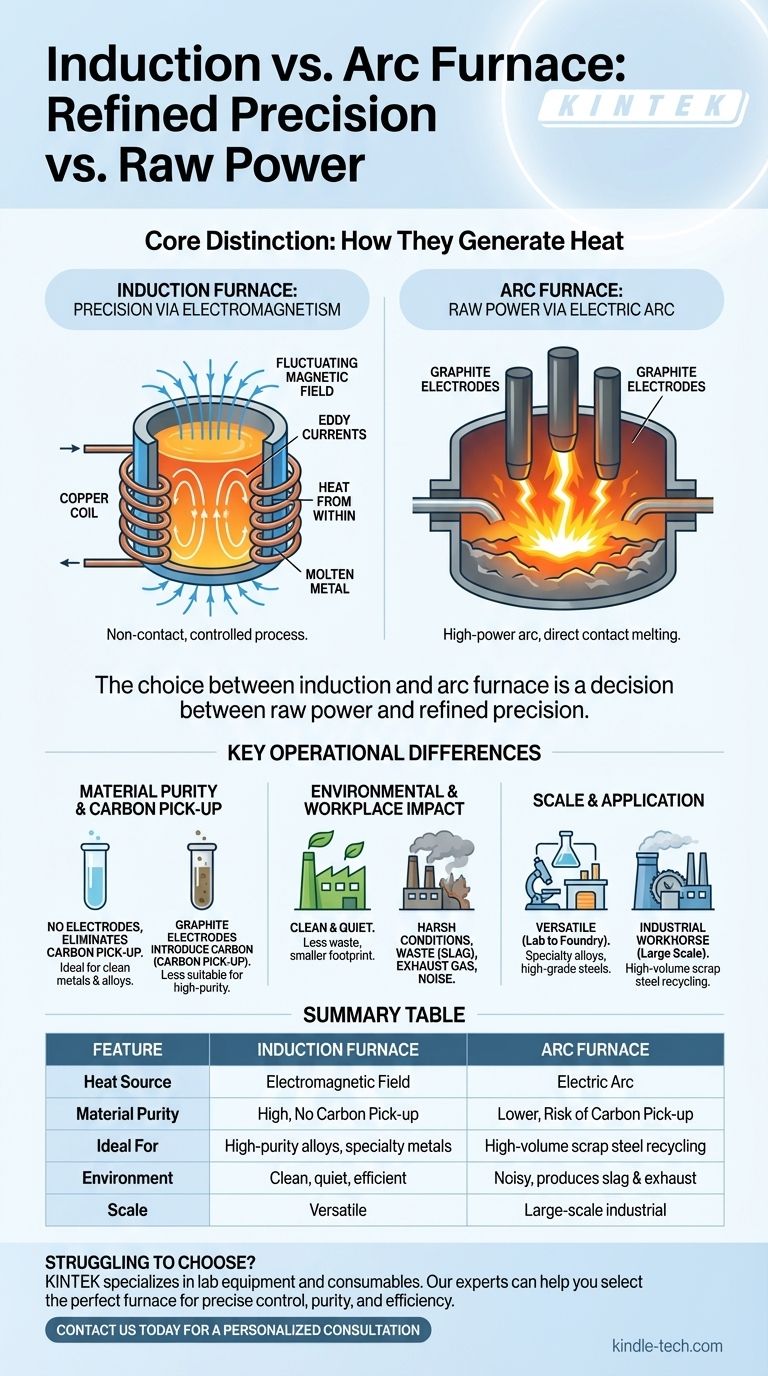
At their core, induction and arc furnaces differ fundamentally in how they generate heat. An electric arc furnace (EAF) uses a high-power electric arc between electrodes to melt metal with raw, intense energy. In contrast, an induction furnace uses a powerful, non-contact magnetic field to heat and melt the metal from within, offering a much cleaner and more controlled process.
The choice between an induction and arc furnace is a decision between raw power and refined precision. Arc furnaces excel at high-volume scrap steel recycling, while induction furnaces provide the clean, controlled melting essential for specialty alloys and high-purity metals.

How They Generate Heat: The Core Distinction
The most significant difference lies in the physical mechanism used to create the immense heat required for melting metals. This single distinction drives all subsequent differences in application, purity, and environmental impact.
The Arc Furnace: Raw Power via Electric Arc
An electric arc furnace operates like a controlled lightning strike. It uses large graphite electrodes which are lowered into a chamber filled with metal scrap.
A massive electric current is passed through these electrodes, creating a powerful electric arc that jumps between the electrodes and the metal charge. This arc generates extremely high temperatures, rapidly melting the metal.
The Induction Furnace: Precision via Electromagnetism
An induction furnace works without any direct contact or arc. It consists of a crucible (a container for the metal) surrounded by a coil of copper wire.
A powerful alternating current is passed through the coil, creating a fluctuating magnetic field. This field induces powerful electrical currents, known as eddy currents, directly within the metal itself, causing it to heat up and melt from the inside out.
Key Operational Differences
The method of heating directly impacts the furnace's performance, the quality of the final product, and its effect on the surrounding environment.
Material Purity and Carbon Pick-up
The graphite electrodes in an arc furnace are a critical point of difference. As they are consumed during operation, they can introduce carbon into the molten metal. This is known as "carbon pick-up" and can be undesirable when producing low-carbon or high-purity specialty steels.
Induction furnaces have no electrodes, completely eliminating the risk of carbon pick-up. This makes them ideal for producing clean metals and alloys where precise chemical composition is critical.
Environmental and Workplace Impact
Arc furnaces are known for their harsh operating conditions. The process produces significant waste residue (slag), exhaust gas, and extreme noise levels.
Induction furnaces are comparatively clean and quiet. They generate far less waste and pollution, creating a much better working environment and a smaller environmental footprint.
Scale and Application
Electric arc furnaces are industrial workhorses, often built on a massive scale. They are the primary technology used in "mini-mills" for recycling huge volumes of steel scrap into new products.
Induction furnaces are generally more versatile in size, ranging from small laboratory units to large foundry furnaces. They are favored for creating specialty alloys, high-grade steels, and melting non-ferrous metals where quality control is paramount.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither furnace is universally "better"; they are specialized tools designed for different tasks. Understanding their inherent trade-offs is key to choosing the right one.
Why Choose an Arc Furnace?
The primary advantage of the EAF is its ability to melt large quantities of low-quality, unprepared scrap steel very quickly. Its raw power can handle impurities and large, dense chunks of material that would be unsuitable for an induction furnace. It is the backbone of modern steel recycling for a reason.
The Case for the Induction Furnace
The induction furnace offers superior energy efficiency (when melting clean, pre-sized scrap), precise temperature control, and a natural stirring action from the magnetic field that improves alloy consistency. Its clean melting process makes it the default choice for foundries producing high-value castings and alloys.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision depends entirely on the material you are processing and your end goal.
- If your primary focus is large-scale steel recycling from scrap: The raw power and high capacity of an electric arc furnace are unmatched.
- If your primary focus is producing high-purity alloys or specialty metals: The clean, controllable heating of an induction furnace is the superior choice.
- If your primary focus is operational efficiency and a better work environment: The induction furnace offers a significantly cleaner, quieter, and often more energy-efficient process for appropriate materials.
Ultimately, understanding the fundamental difference between brute-force arc heating and precise induction heating is the first step to selecting the right tool for your metallurgical goals.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Induction Furnace | Arc Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Source | Electromagnetic field (induction) | Electric arc from graphite electrodes |
| Material Purity | High (no carbon pick-up) | Lower (risk of carbon pick-up) |
| Ideal For | High-purity alloys, specialty metals | High-volume scrap steel recycling |
| Environment | Clean, quiet, efficient | Noisy, produces slag and exhaust |
| Scale | Versatile (lab to foundry) | Large-scale industrial |
Struggling to choose the right furnace for your lab or foundry? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving all your laboratory needs. Our experts can help you select the perfect induction or arc furnace to ensure precise temperature control, material purity, and operational efficiency for your specific metals and alloys. Contact us today for a personalized consultation and unlock the full potential of your melting process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature of a quartz tube furnace? Master the Limits for Safe, High-Temp Operation
- Why does heating increase temperature? Understanding the Molecular Dance of Energy Transfer
- What is a vertical tube furnace? Leverage Gravity for Superior Uniformity and Process Control
- What temperature is tube annealing? A Guide to Material-Specific Ranges for Optimal Results
- How do you clean a tubular furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Maintenance



















