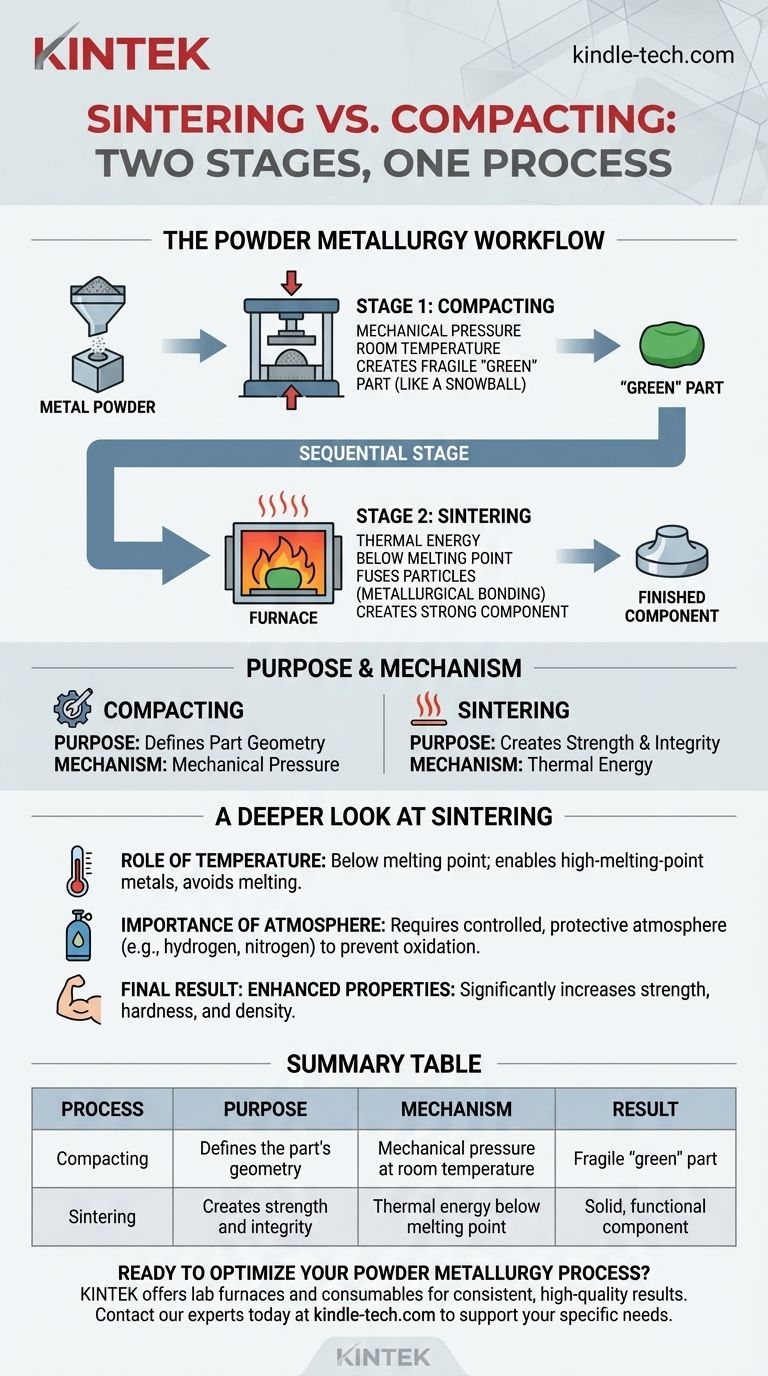
Sintering and compacting are not competing processes; they are two distinct, sequential stages in the powder metallurgy workflow. Compacting is the mechanical step of pressing metal powder into a desired shape at room temperature, while sintering is the subsequent thermal step that heats the part to fuse its particles, giving it strength and integrity.
The fundamental distinction lies in their function and sequence. Compacting cold-presses powder into a fragile 'green' part to define its geometry, while sintering applies heat to bond the particles, transforming that fragile shape into a solid, functional component.

The Powder Metallurgy Workflow: From Powder to Part
To grasp the difference, it's essential to see how they work together. Powder metallurgy is a process that builds parts from the ground up, starting with fine metal powder. Both compacting and sintering are indispensable steps in this journey.
Stage 1: Compacting – Creating the 'Green' Part
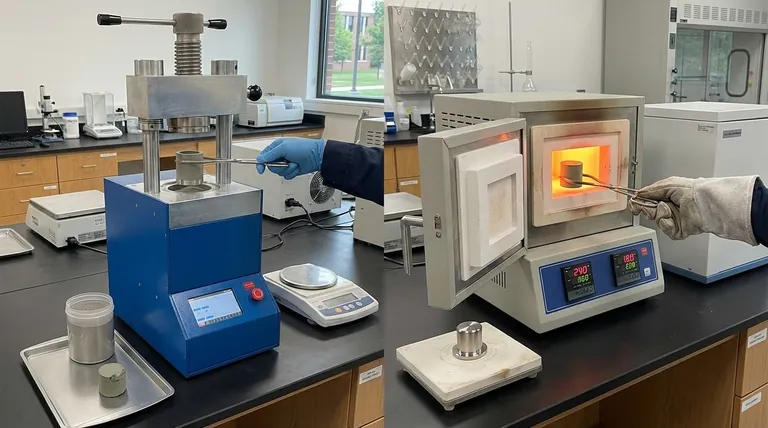
Compacting is the initial shaping process. It involves pouring metal powder into a precision die and applying immense pressure.
This pressure forces the metal particles into intimate contact, creating a shape that is solid enough to be handled. This pre-sintered object is known as a 'green' part.
Think of it like making a snowball. You apply pressure to loose snow (the powder) to create a defined shape (the green part). It holds its form but is still mechanically weak and fragile.
Stage 2: Sintering – Fusing the Particles
Sintering is what gives the green part its final strength and metallurgical properties. The part is placed in a controlled-atmosphere furnace and heated.
The temperature is raised to just below the material's melting point. The particles do not liquefy.
Instead, the intense heat and pressure cause the atoms at the particle boundaries to diffuse and bond together, creating a strong, solid mass. This is what transforms the fragile green part into a finished component.
The Critical Difference: Purpose and Mechanism
Compacting uses mechanical pressure to achieve a specific geometry. Its purpose is purely structural definition.
Sintering uses thermal energy to achieve metallurgical bonding. Its purpose is to create strength, hardness, and final density.
A Deeper Look at the Sintering Process
Sintering is a highly controlled thermal process with critical variables that determine the final outcome. It is far more sophisticated than simply heating a part in an oven.
More Than Just Heat: The Role of Temperature
The key to sintering is that it occurs without melting. This distinction is crucial because it allows for the creation of parts from metals with extremely high melting points, which would be difficult or costly to process via traditional casting.
The Importance of Atmosphere
The environment inside the sintering furnace is critical. As the references note, different materials require different atmospheres to achieve full density and prevent oxidation.
Metals often require reducing gases like hydrogen or inert gases like nitrogen to protect the part during the high-temperature cycle.
The Final Result: Enhanced Properties
The primary goal of sintering is to improve the part's physical characteristics. The process significantly increases strength, hardness, and density, locking the component into its final, durable state.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Context
Recognizing the relationship between these two stages helps clarify the capabilities and limitations of the overall powder metallurgy process.
The Fragility of the 'Green' Part
A key consideration is the mechanical weakness of the part after compacting but before sintering. These green parts must be handled carefully to avoid breakage before they can be strengthened in the furnace.
Sintering Isn't Melting
This process should never be confused with melting or casting. Sintering enables the blending of different metal powders to create unique alloys that would be impossible to form through liquefaction.
Porosity as a Feature or Flaw
Unlike a cast or machined part, a sintered component often retains a small amount of porosity. While this can be a limitation for some structural applications, it can also be a deliberate feature for products like self-lubricating bearings or filters.
How This Applies to Manufacturing Goals
Choosing how to optimize this process depends entirely on your end goal.
- If your primary focus is creating a complex initial shape: Your attention should be on the compacting stage, as the tooling and pressure directly define the part's geometry.
- If your primary focus is achieving specific material properties (like strength or hardness): The sintering stage is paramount, as temperature, time, and atmosphere control the final metallurgical bond.
- If you need to work with high-melting-point materials: This entire two-step process of compacting and sintering is a key advantage over traditional casting or melting.
Understanding this two-stage process is the key to mastering the fundamentals of powder metallurgy.
Summary Table:
| Process | Purpose | Mechanism | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compacting | Defines the part's geometry | Mechanical pressure at room temperature | Fragile 'green' part |
| Sintering | Creates strength and integrity | Thermal energy below melting point | Solid, functional component |
Ready to optimize your powder metallurgy process?
Whether your goal is to create complex shapes through precise compacting or achieve superior material properties with controlled sintering, KINTEK has the expertise and equipment to help. Our lab furnaces and consumables are designed to meet the exacting demands of powder metallurgy, ensuring consistent, high-quality results.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific sintering and compacting needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Automatic Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Electric Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine for Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Manual Cold Isostatic Pressing Machine CIP Pellet Press
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
People Also Ask
- What is cold isostatic pressing of metal powder? Achieve Uniform Density in Complex Metal Parts
- What role does a Cold Isostatic Press (CIP) play in aluminum matrix composites? Achieve 90% Density for Better Hot Pressing
- What is CIP in powder metallurgy? Unlock Uniform Density for Complex Parts
- What temperature is cold isostatic pressing? A Guide to Room-Temperature Powder Compaction
- What advantages does Cold Isostatic Pressing (CIP) offer for nickel-alumina composites? Enhance Density & Strength



















