At its core, the difference between sintering and heat treatment is one of purpose. Sintering is a fabrication process used to create a solid object from a starting powder. In contrast, heat treatment is a modification process used to alter the properties of an existing solid object.
The simplest way to understand the distinction is to think about creation versus refinement. You use sintering to create the part itself, and you use heat treatment to refine the properties of that part after it has already been made.

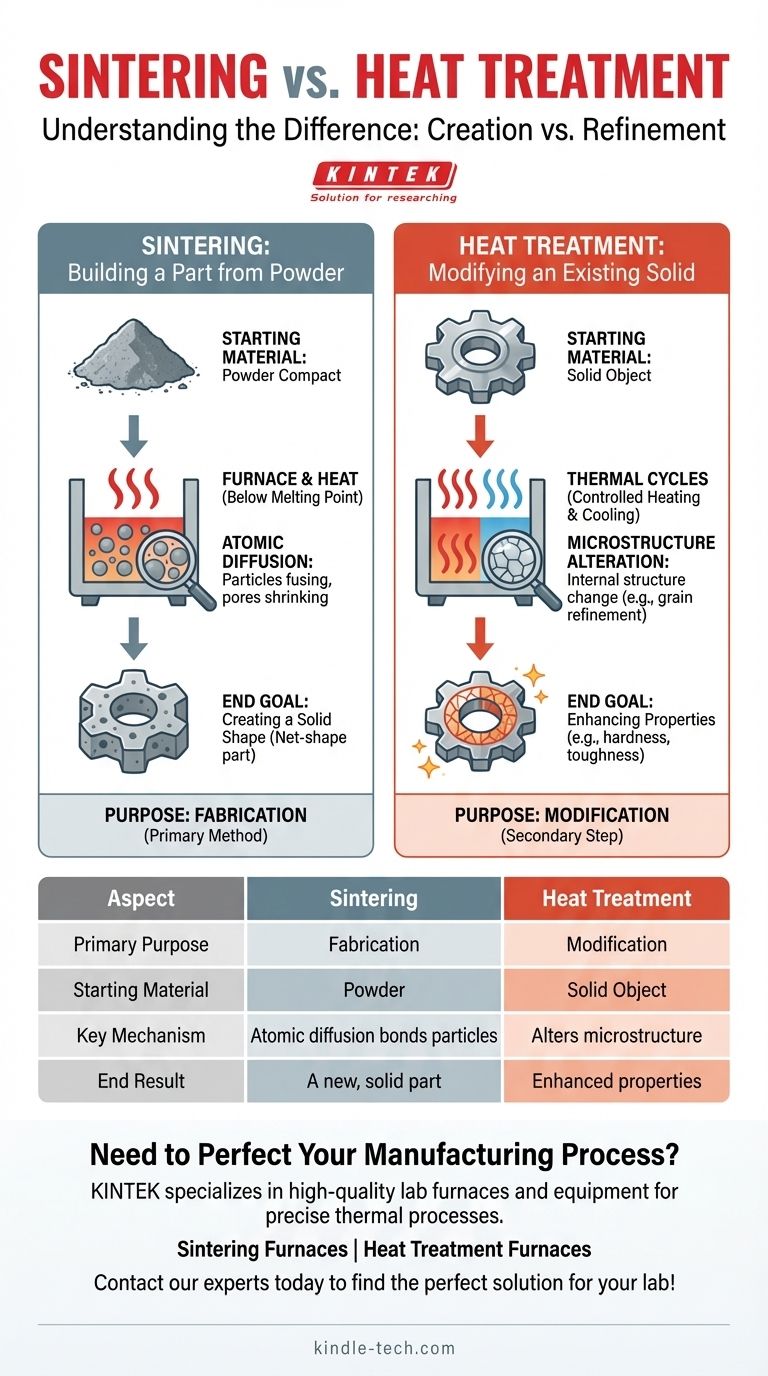
Sintering: Building a Part from Powder
Sintering is a foundational technique in a field known as powder metallurgy. It is a method for manufacturing solid components without ever melting the material.
The Starting Material: A Powder Compact
The process always begins with a fine powder of a metal or ceramic. This powder is first pressed into a desired shape, often called a "green compact," which is fragile and has low density.
The Mechanism: Atomic Diffusion
The green compact is then heated in a furnace to a temperature below its melting point. At this high temperature, the atoms at the contact points of the powder particles begin to diffuse across the boundaries, effectively welding the particles together.
The End Goal: Creating a Solid Shape
As the particles fuse, the pores between them shrink, causing the part to densify and strengthen into a solid, coherent object. The goal is to produce a net-shape or near-net-shape part that requires minimal finishing. This process is essential for materials with extremely high melting points.
Heat Treatment: Modifying an Existing Solid
Heat treatment encompasses a wide range of processes, but they all share the same fundamental goal: to change the characteristics of a part that has already been formed.
The Starting Material: A Solid Object
Unlike sintering, heat treatment requires an existing solid component. This part could have been created by casting, forging, machining, or even by a sintering process itself.
The Mechanism: Microstructure Alteration
The process involves carefully controlled cycles of heating and cooling. These thermal cycles do not fuse particles; instead, they alter the material's internal crystal structure, known as its microstructure. Different structures result in vastly different mechanical properties.
The End Goal: Enhancing Properties
The goal of heat treatment is never to create the part's shape, but to enhance its performance. For example, annealing (slow cooling) can make a metal softer and more workable. Conversely, quenching (rapid cooling) can make steel extremely hard and wear-resistant.
Understanding the Key Differences
The choice between these processes is never an "either/or" for the same task. They serve entirely separate functions in the manufacturing lifecycle.
Purpose: Fabrication vs. Modification
This is the most critical distinction. Sintering is a primary fabrication method. Heat treatment is a secondary modification or finishing step.
Starting State: Powder vs. Solid
Sintering is impossible without a powder starting material. Heat treatment is only performed on an object that is already a solid mass.
Outcome: A New Part vs. New Properties
The successful outcome of sintering is a solid component where there was once only powder. The successful outcome of heat treatment is a component with new physical properties, such as increased hardness, toughness, or ductility.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Often, these two processes are used sequentially to create a single high-performance component.
- If your primary focus is to create a complex part from metal or ceramic powder: You are looking for a sintering process to form the component.
- If your primary focus is to improve the mechanical properties of an existing metal part: You need to apply a specific heat treatment process like annealing or quenching.
- If your primary focus is to produce a high-performance part via powder metallurgy: You will use sintering to form the part, followed by a specific heat treatment cycle to achieve the final desired properties.
Understanding this distinction is the key to controlling a material's journey from raw powder to a finished, high-performance component.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Sintering | Heat Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Fabrication (to create a part) | Modification (to alter properties) |
| Starting Material | Powder | Solid Object |
| Key Mechanism | Atomic diffusion bonds particles | Alters the material's microstructure |
| End Result | A new, solid part from powder | A part with enhanced properties (e.g., hardness) |
Need to Perfect Your Manufacturing Process?
Whether you are creating components from powder via sintering or enhancing the strength and durability of existing parts through heat treatment, having the right laboratory equipment is critical.
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab furnaces and equipment designed for precise thermal processes. We provide the reliable tools you need for:
- Sintering Furnaces: For creating net-shape parts from metal or ceramic powders.
- Heat Treatment Furnaces: For annealing, quenching, and tempering to achieve desired material properties.
Let us help you control the entire journey from raw material to high-performance component. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and find the perfect solution for your lab!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
People Also Ask
- How does a high-temperature vacuum sintering furnace facilitate the post-treatment of Zirconia coatings?
- What is vacuum sintering? Achieve Unmatched Purity and Performance for Advanced Materials
- Why is a high vacuum environment necessary in sintering equipment for TiAl alloys? Ensure High-Purity Metal Bonding
- How does precise temperature control affect FeCoCrNiMnTiC high-entropy alloys? Master Microstructural Evolution
- Why is a high vacuum required for sintering Ti-43Al-4Nb-1Mo-0.1B? Ensure Purity & Fracture Toughness



















