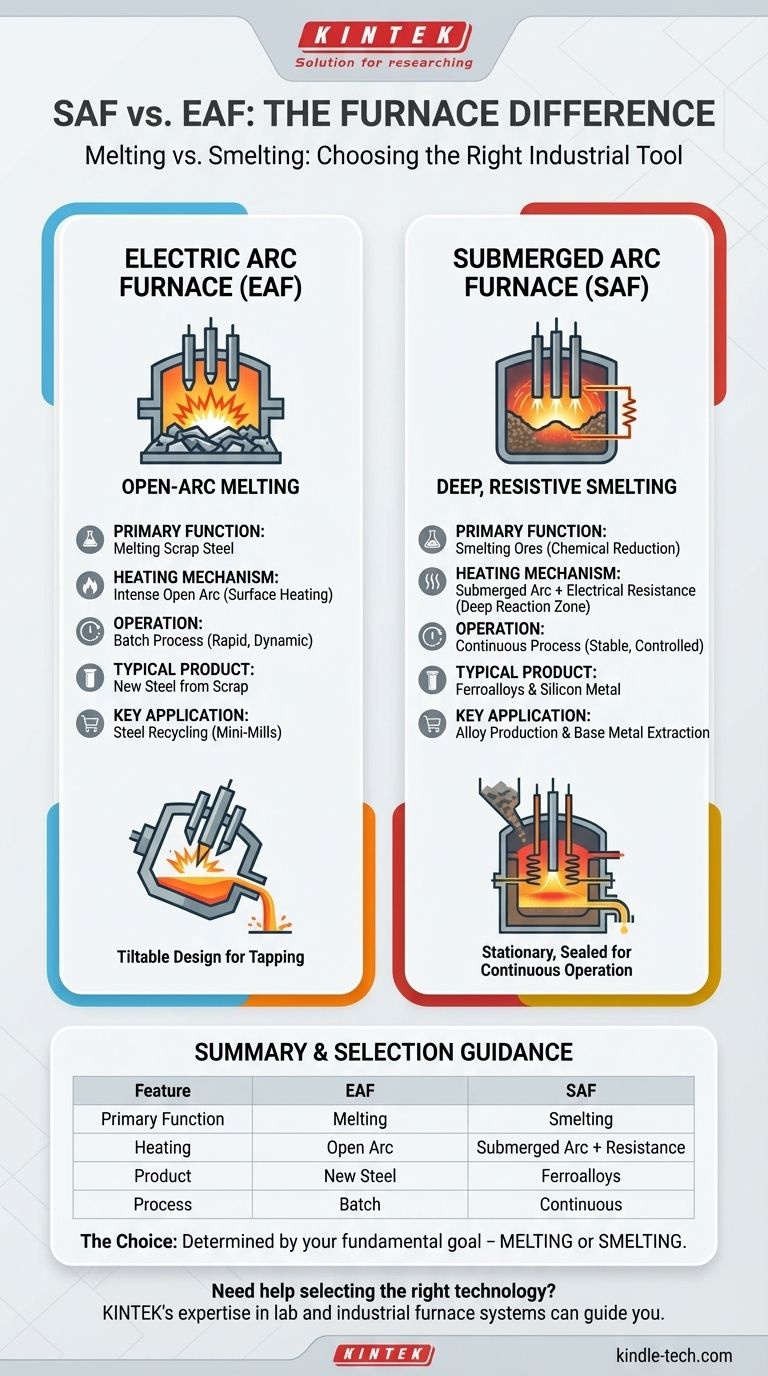
At its core, the primary difference between a Submerged Arc Furnace (SAF) and a conventional Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) is the position of the electrodes and the resulting heating mechanism. An EAF uses an open, high-energy arc above the raw materials primarily for melting, while an SAF buries its electrodes deep within the material, using both the arc and the electrical resistance of the charge itself for smelting and chemical reduction.
The critical takeaway is that these furnaces serve fundamentally different industrial purposes. The EAF is essentially a high-powered furnace for melting scrap steel, whereas the SAF is a chemical reactor designed for smelting ores to produce ferroalloys and other base materials.

The Core Distinction: Heating Mechanism
The most significant difference lies in how each furnace generates and applies heat to the raw material, known as the "charge."
Electric Arc Furnace (EAF): Intense, Open-Arc Melting
In a standard EAF, large graphite electrodes are lowered towards the charge (typically scrap steel). A powerful electric arc is struck between the electrodes and the metallic charge itself.
This open arc is incredibly intense, transferring immense heat directly to the surface of the material. The process is designed for one primary goal: rapid and efficient melting.
Submerged Arc Furnace (SAF): Deep, Resistive Smelting
In an SAF, the electrodes are lowered much deeper, becoming completely buried or "submerged" within the charge of ores, coke, and flux. The furnace is kept continuously full.
Because the electrodes are submerged, heating occurs through two mechanisms. Heat is generated by the arc at the tip of the electrode, but also by the electrical resistance of the charge itself as current flows through it. This is why an SAF is often called an arc resistance furnace.
This dual heating method creates a more stable, controlled reaction zone deep within the furnace, which is essential for chemical processes.
Contrasting Applications and Purpose
The difference in heating mechanism dictates the furnace's ideal application. One is a melter; the other is a chemical reducer.
EAF: The Steel Recycler
The EAF's function is overwhelmingly focused on recycling steel. It is the primary tool used in "mini-mills" that melt scrap steel to produce new steel products.
Its operation is a batch process: charge scrap, melt it down with intense power, tap the molten steel, and repeat.
SAF: The Alloy Producer
The SAF's function is smelting and reduction. It is used to chemically reduce ores to produce bulk ferroalloys (like ferrosilicon and ferromanganese), which are essential ingredients for steelmaking, and other materials like silicon metal or phosphorus.
Its operation is a continuous or semi-continuous process. Raw materials are constantly fed from the top, and the molten product is tapped periodically from the bottom, allowing for long, stable production campaigns.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between these furnaces is never an option for a single process; they are designed for entirely different industrial roles with distinct operational characteristics.
Process Control and Stability
An EAF is a dynamic and almost violent process, characterized by the intense, fluctuating open arc. Its control systems are focused on managing electrode position and power input for the fastest possible melt.
An SAF is a much more stable and slow-reacting process. The large volume of the charge acts as a thermal and electrical buffer. Control is focused on maintaining a balanced chemical reaction and consistent energy input over long periods.
Furnace Design and Construction
The design of each furnace reflects its purpose. EAFs are designed to tilt for tapping molten steel and slag and must withstand the immense thermal shock of rapid, repeated melting cycles.
SAFs are typically stationary, sealed units designed for continuous operation. As noted in technical specifications, they often feature robust refractory linings (carbon or magnesia) and water-cooling systems to ensure the furnace shell can withstand constant, high-temperature chemical reactions for months or years at a time.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The selection is determined entirely by the industrial transformation you need to achieve.
- If your primary focus is melting scrap metal to produce new steel: The Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) is the definitive tool for the job.
- If your primary focus is chemically reducing ores to produce ferroalloys or other base metals: The Submerged Arc Furnace (SAF) is the required technology.
Ultimately, the choice is dictated not by the furnace itself, but by the fundamental process you need to perform: melting or smelting.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) | Submerged Arc Furnace (SAF) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Melting scrap steel | Smelting ores (chemical reduction) |
| Heating Mechanism | Intense, open arc above the charge | Submerged arc + electrical resistance of the charge |
| Typical Product | New steel from scrap | Ferroalloys (e.g., ferrosilicon), silicon metal |
| Operation Type | Batch process | Continuous or semi-continuous process |
| Key Application | Steel recycling | Ferroalloy production, base metal extraction |
Need help selecting the right furnace technology for your specific process? Whether your goal is efficient metal melting or advanced chemical smelting, KINTEK's expertise in lab and industrial furnace systems can guide you to the optimal solution. Contact our experts today to discuss your application requirements and discover how our equipment can enhance your productivity and product quality.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the types of induction melting furnace? Coreless, Channel, and VIM Explained
- What is magnetron sputtering machine? Precision Thin-Film Deposition for Advanced Materials
- What is RF magnetron sputtering? A Guide to Depositing Insulating Thin Films
- What is direct current DC magnetron sputtering? A Guide to High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is the difference between VAR and VIM? Legacy Vimscript Variables vs. Modern Neovim API



















