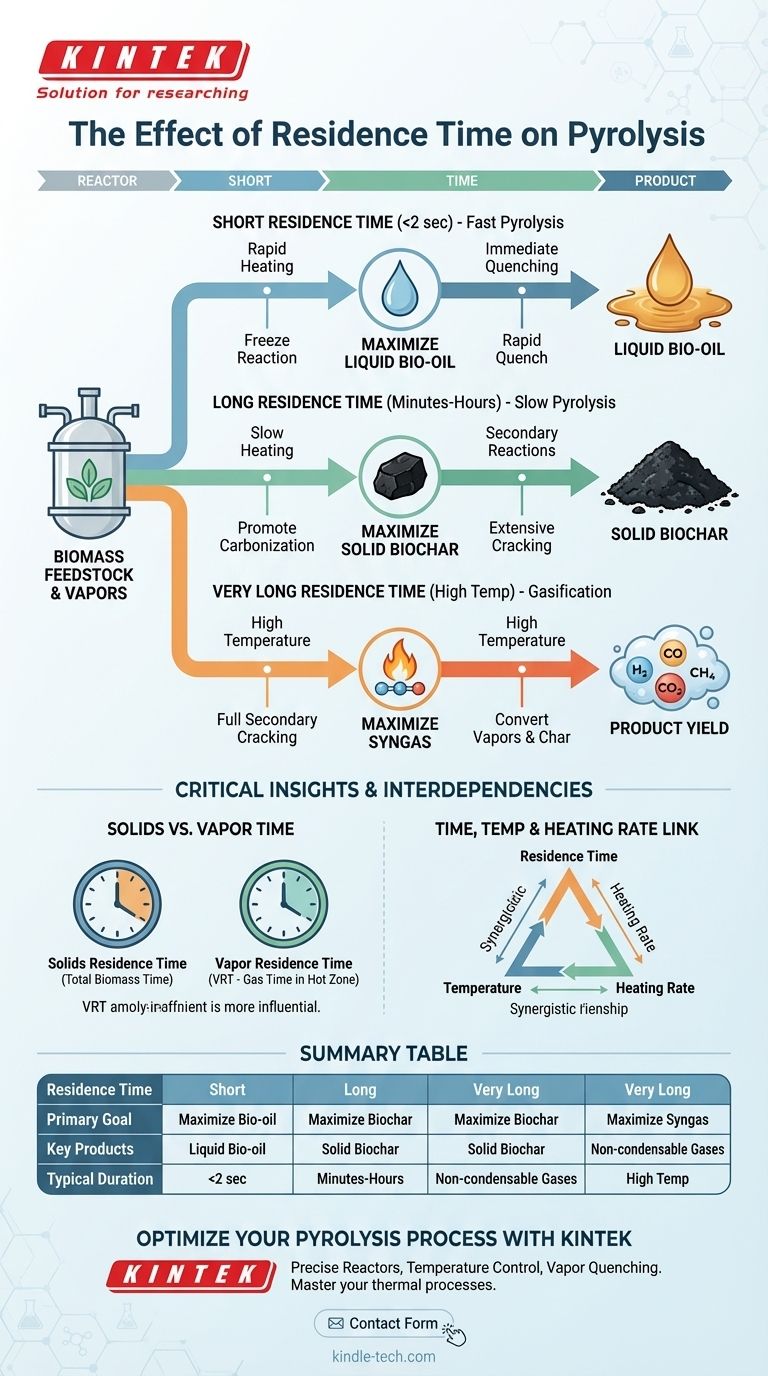
At its core, residence time is the primary lever for controlling pyrolysis product distribution. It dictates how long the raw feedstock and its resulting vapors are exposed to high temperatures within the reactor. In short, shorter residence times favor the production of liquid bio-oil, while longer residence times increase the yield of solid biochar and syngas by allowing secondary reactions to occur.
The critical insight is that residence time determines whether you capture the initial products of decomposition or allow them to transform further. A short time "freezes" the reaction to yield valuable liquid vapors, whereas a long time promotes secondary cracking of those vapors into gas and further carbonization of the solid material.

The Fundamental Role of Time in Pyrolysis
Pyrolysis is a process of thermal decomposition in the absence of oxygen. While temperature sets the stage for the reaction, residence time directs the performance, steering the process toward specific end-products.
Defining Residence Time
Residence time refers to the duration a substance spends within the heated reaction zone. It's crucial to distinguish between two types:
- Solids Residence Time: The total time the solid biomass feedstock remains in the reactor.
- Vapor Residence Time (VRT): The time the gaseous vapors, released from the decomposing solids, remain in the hot zone before being cooled or removed.
This distinction is key, as VRT is often the more influential parameter for determining the final product slate.
Primary vs. Secondary Reactions
The effect of residence time is best understood as a choice between two reaction stages.
- Primary Decomposition: The initial breakdown of biomass into solid char, primary vapors (the precursors to bio-oil), and some non-condensable gases.
- Secondary Reactions: If the primary vapors are held at high temperatures (i.e., long vapor residence time), they will "crack," breaking down into smaller, lighter gas molecules (H₂, CO, CO₂, CH₄) and also deposit more carbon onto the existing solid char.
How Residence Time Dictates Product Yields
By manipulating residence time, you can intentionally favor one set of reaction pathways over another, tailoring the output to your specific goal.
Fast Pyrolysis: Maximizing Bio-oil
This process is defined by extremely short vapor residence times, typically less than 2 seconds.
The objective is to rapidly heat the biomass to generate vapors and then immediately quench (cool) them. This rapid cooling condenses the vapors into liquid bio-oil before they have a chance to undergo secondary cracking.
Slow Pyrolysis: Maximizing Biochar
This process uses very long solids residence times, often ranging from many minutes to several hours.
The slow heating rate and long duration allow for extensive secondary reactions. Vapors have ample time to crack or re-condense onto the solid matrix, maximizing the carbonization of the solid material and resulting in a high yield of stable biochar.
Gasification: A Path to Syngas
While technically a different process, gasification demonstrates the extreme end of the residence time spectrum. By using very long vapor residence times at high temperatures, the goal is to fully promote secondary cracking, converting almost all vapors and char into non-condensable syngas.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Interdependencies
Residence time does not operate in a vacuum. Its effect is deeply interconnected with other critical process parameters.
The Link Between Time and Temperature
Temperature and residence time have a synergistic relationship. A higher temperature accelerates reaction rates, meaning secondary cracking can occur over a much shorter residence time. Conversely, to achieve a high degree of carbonization (biochar) at a lower temperature, a much longer residence time is required.
The Impact of Heating Rate
Heating rate is the speed at which the biomass is brought to the reaction temperature.
- High Heating Rates are paired with short residence times in fast pyrolysis to rapidly generate vapors and minimize char formation.
- Low Heating Rates are paired with long residence times in slow pyrolysis to gradually decompose the material and maximize char.
Reactor Design Implications
The physical design of a pyrolysis reactor is a direct reflection of the intended residence time.
- Fluidized bed and ablative reactors are engineered to move material and vapors through the hot zone very quickly, making them ideal for the short residence times of fast pyrolysis.
- Auger, kiln, and fixed-bed reactors are designed for slow movement and long retention, making them suitable for slow pyrolysis and biochar production.
Optimizing Residence Time for Your Goal
Selecting the correct residence time is a strategic decision based entirely on your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is maximizing liquid bio-oil for biofuel: You must prioritize extremely short vapor residence times (<2 seconds) combined with high heating rates and rapid vapor quenching.
- If your primary focus is producing high-quality, stable biochar for soil amendment or carbon sequestration: You need to implement long solids residence times (minutes to hours) with slow heating rates.
- If your primary focus is generating syngas for energy: You should use longer vapor residence times at higher temperatures to deliberately promote the secondary cracking of tars and vapors into permanent gases.
Ultimately, mastering residence time is mastering control over the final chemical destiny of your feedstock.
Summary Table:
| Residence Time | Primary Goal | Key Products | Typical Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Short (<2 sec) | Maximize Bio-oil | Liquid Bio-oil | Fast Pyrolysis |
| Long (minutes-hours) | Maximize Biochar | Solid Biochar | Slow Pyrolysis |
| Very Long (High Temp) | Maximize Syngas | Non-condensable Gases | Gasification |
Ready to Optimize Your Pyrolysis Process?
Understanding residence time is just the first step. To achieve precise control over your product yields—whether you're targeting bio-oil, biochar, or syngas—you need reliable, high-performance lab equipment.
KINTEK specializes in supplying the precise pyrolysis reactors, temperature control systems, and vapor quenching units that laboratories depend on to master their thermal processes. Our equipment is designed to deliver the exact heating rates and residence times required for your specific research or production goals.
Contact us today using the form below to discuss how KINTEK's solutions can help you optimize your pyrolysis outcomes and drive your research forward.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why are high temperatures required when sintering stainless steels? Unlock Pure, High-Density Results
- How is a high-temperature calcination furnace utilized in BZY20 Sol-gel? Achieve Pure Cubic Perovskite Phases
- What is the range of pyrolysis? Master Temperature Control for Optimal Bio-Product Yields
- What is the difference between pyrolysis combustion and gasification? A Guide to Thermal Conversion Technologies
- How do high-temperature reaction furnaces control in-situ MMCs? Master Material Precision and Structural Integrity



















